- Templates
- Block diagram templates
- CPU block diagram
About this template
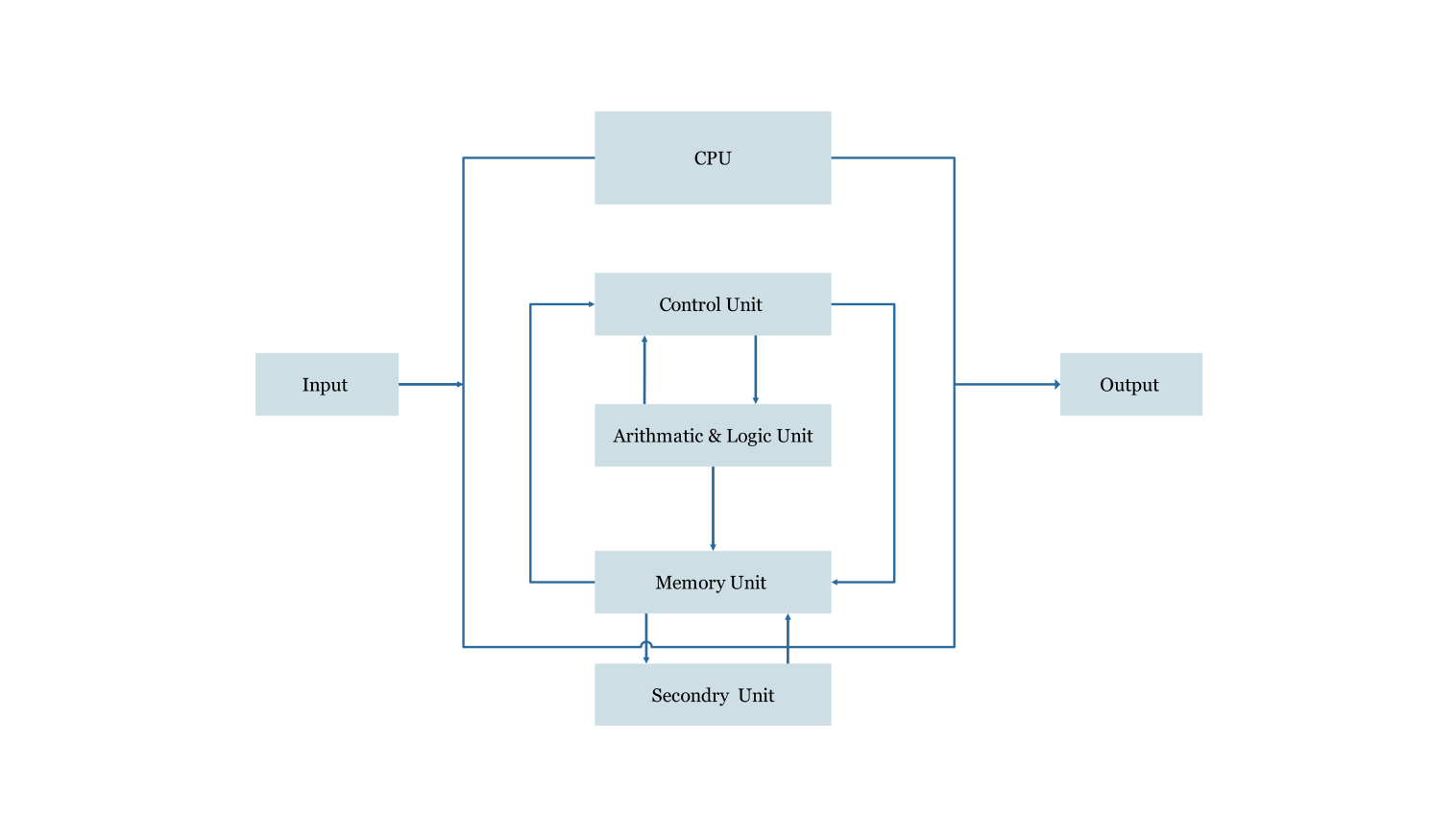
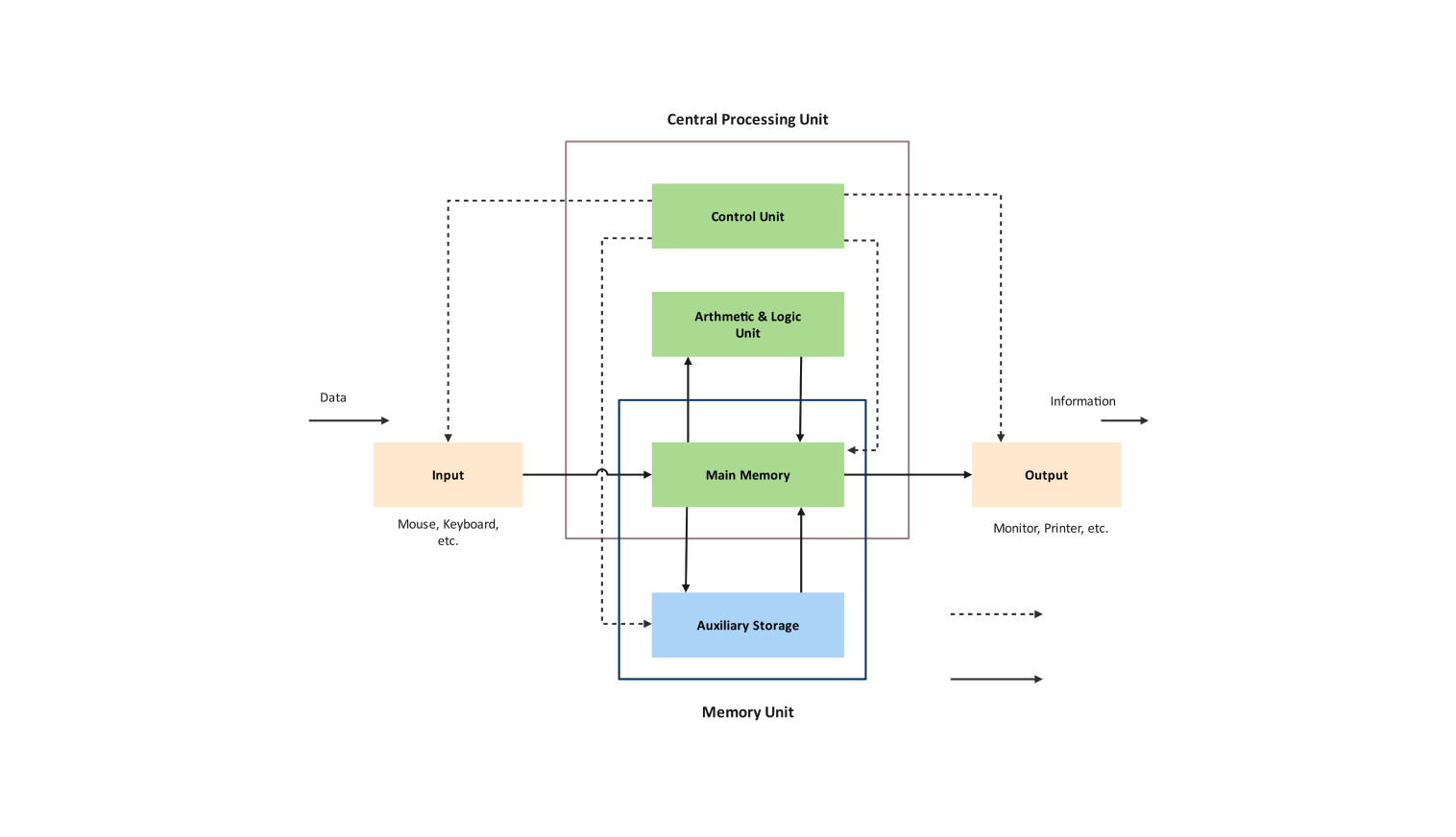
The CPU, the brain of the system, executes complex tasks at lightning speed. But its intricate architecture can be baffling. Here's where the CPU block diagram template comes in! Whether you're a student, educator, or simply curious, this template serves as a powerful learning tool.
This user-friendly template offers a clear visual breakdown of the CPU's core components. See the Control Unit, the conductor of operations, and the Arithmetic Logic Unit, the dedicated math whiz. Witness how data flows seamlessly between them.
How to use this template
Click Use this template.
Log in with a Wondershare ID or your social media credentials. No sign-up required!
For customizing the template, you can change component colors, sizes, or rotations for better clarity, or add labels and text boxes.
Once you're done customizing, click on "File" in the top menu bar. Select "Export" from the drop-down menu that appears. Choose the format that best suits your needs, such as .eddx, .pdf, .png, or .jpg.
Benefits of the template
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the heart of your computer; it directs its activities and executes complex tasks without apparent trouble. This CPU block diagram template aims to be a great resource to aid you in putting pieces of the device together and understanding it.
- Visual learning: Through a representation of the CPU's core building components – Control Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit, registers, and data paths – the complexity of these elements reduces to a transparent process which normally would be cumbersome for one to understand as an individual.
- Enhanced understanding: It allows for customization. The process of tagging as representative of function (ex: "CU", "ALU") as well as adding text boxes with explanatory notes makes the diagram familiar to you and thus you have a perfect understanding of all components' roles.
- Effective communication: These procedures would be quite useful both to managers and other team members in the process of communication. The clear visual representations that are given will allow everyone to have an almost similar understanding of the way these outstanding machines work.
FAQs about this template
-
What are the 3 units of CPU?
- Control Unit: Memory of an instruction and decodes it, then directs other parts of the CPU to the corresponding instruction execution. It can largely be considered as the process driver as it controls all the flows.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit: Here is a processor of the CPU which is responsible for processing all of the math and logical operations. It's for simple arithmetic such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and comparison.
- Registers: Such short-term memories are so fast and small data storage and processes are usually related to CPU. These act as the CPU's virtual memory. Data is being sent and obtained between registers in an endless stream of instructions as the CPU executes the commands.
-
Where is the CPU located in a computer system?
Often times it is the largest chip on the board that's referred to as the motherboard, which is the main circuit board that's found in any computer system. This serves as the central point of the machine, where the motherboard is located housing the CPU and providing connection for other vital elements such as memory, storage drives, and graphics cards.
-
What is a core in a CPU?
Almost all modern processors, which include multiple cores are likened to many processors on a single chip. It consists of individual cores with their separate Control Units, Arithmetic Logic Units, and registers, so they can run programs independently.
The larger the number of cores in a CPU makes the system capable of handling more programs and multitasking efficiently.
-
What is the role of GHz of a processor in a CPU?
GHz is a short form of the clock speed of a CPU measured in gigahertz. That means that this shows how many times the CPU has completed a cycle per second. The higher the clock speed the faster the CPU will process tasks.
Usually, the higher the GHz rating the better CPU performance, and the time taken to execute each instruction will be reduced.
-
Is a passcode the same as a password?
The world knows GSM as Global System for Mobile Communication and CDMA as Code Division Multiple Access. One obvious difference between both terms is the SIM cards. You can find a SIM card slot across GSM phones, while CDMA lacks one in them. Instead, they had a handset-based standard with a phone number linking with the device. With a data rate of 42Mbps, GSM was much more common and widely used as compared to the 3.6Mbps CDMA.
Steps to Check if your Phone is GSM or CDMA
- Lead into its "Settings" on your iPhone and find the "General" options. From the list, select the "About" option to proceed.
- As you get into the respective section, find the MEID, ESN, or IMEI number. Phones with a MEID or ESN number use the CDMA system, while devices with an IMEI utilize GSM. Phones having both numbers are GSM and CDMA simultaneously.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free