- All templates
- Use case diagrams
- Use case diagram atm
About this use case diagram for ATM
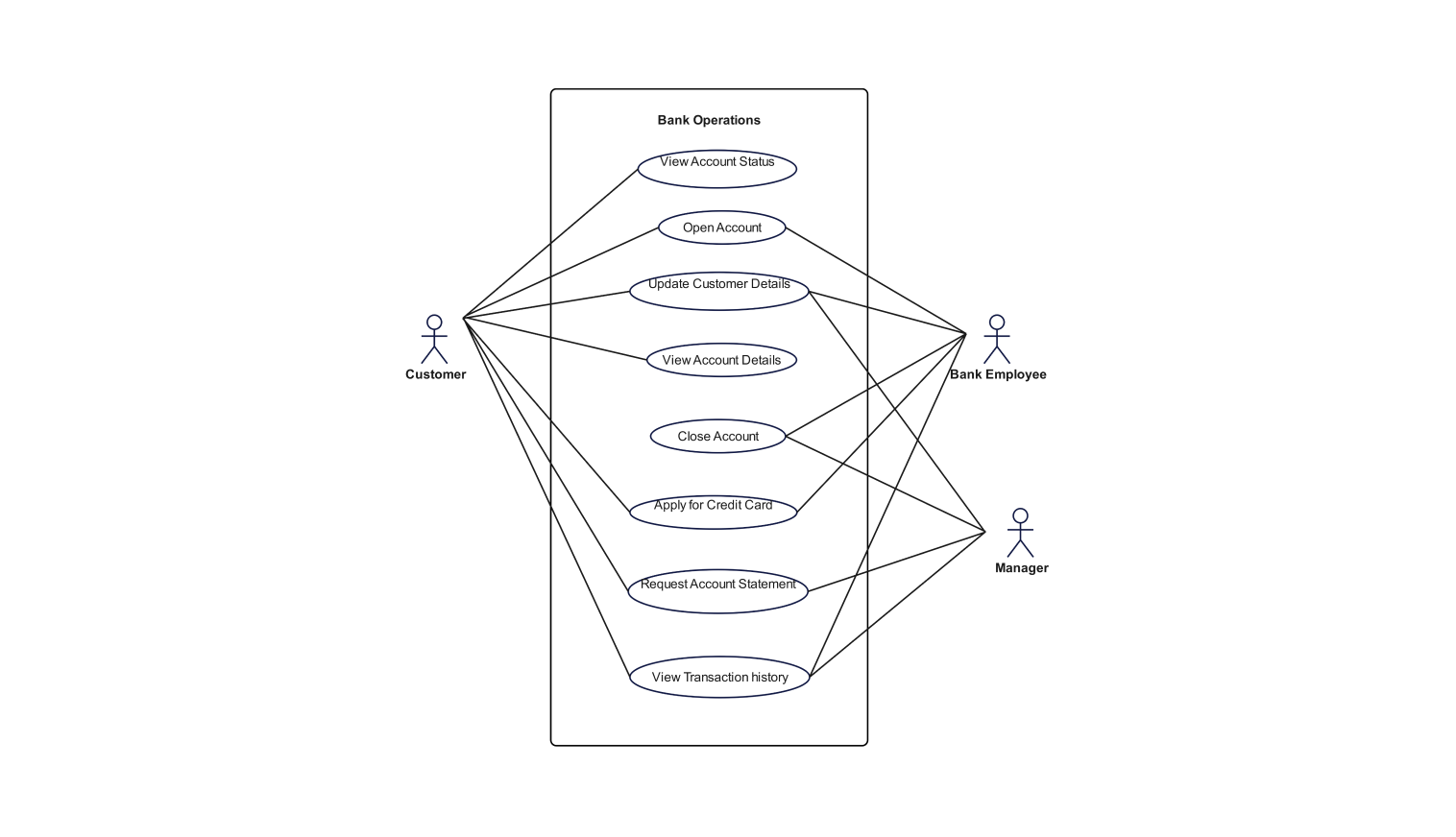
This use-case diagram for an ATM system highlights the key functionalities of ATM systems. It contains multiple actors that work coherently to achieve specific goals. These goals are the functions more commonly known as use cases.
These actors can either interact with the system or other actors in the system to mark the success of these use cases. The actors in this diagram include a customer and a bank server. Notably, customers can perform many actions and a bank server supports these functionalities.
To gain an in-depth knowledge of the system, it is important to study the functionality and purpose of each actor interacting in the system. The customer may deposit cash, check the balance, or transfer funds. Each of these activities is represented as a use case related to the customer actor.
Depositing cash, checking balance, or funds transfer are vital to the customer. Without these features, the system is of no use. Apart from these, there are some other features as well that need to be present in the system for a smooth user experience.
The customers also can withdraw cash, update their PIN, and select the transaction. However, in the later feature, the customer needs to have an authentication mechanism. Withdraw cash is the most crucial feature of an ATM that decides its performance.
The "withdraw cash" use case contains "print receipt" as well as "handle error" and "authenticate user," which indicate any further operations that may be necessary during the withdrawal operation. Print receipt is an optional feature for the user as it may have some charges and is not eco-friendly.
The bank server is considered to be a critical component of the system. This is because all the operations are handled by this server. It enables transactions, user authentication, and safeguarding data security. It also manages errors due to unforeseen circumstances that may arise during transactions.
These features ensure the system's reliability and integrity. In addition to this, it serves as another measure of customer satisfaction by keeping in view the system’s response to the customers' actions.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free