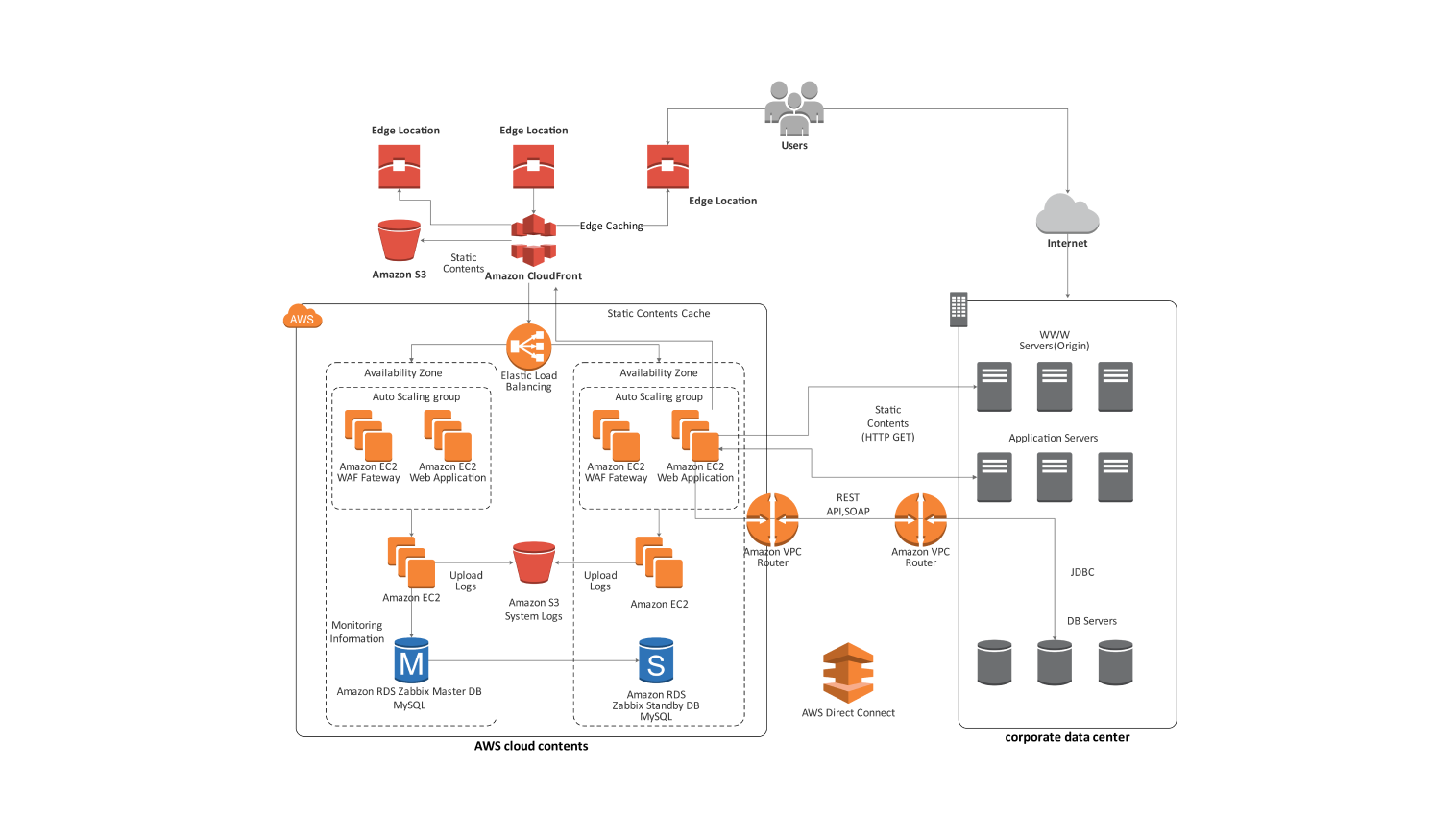
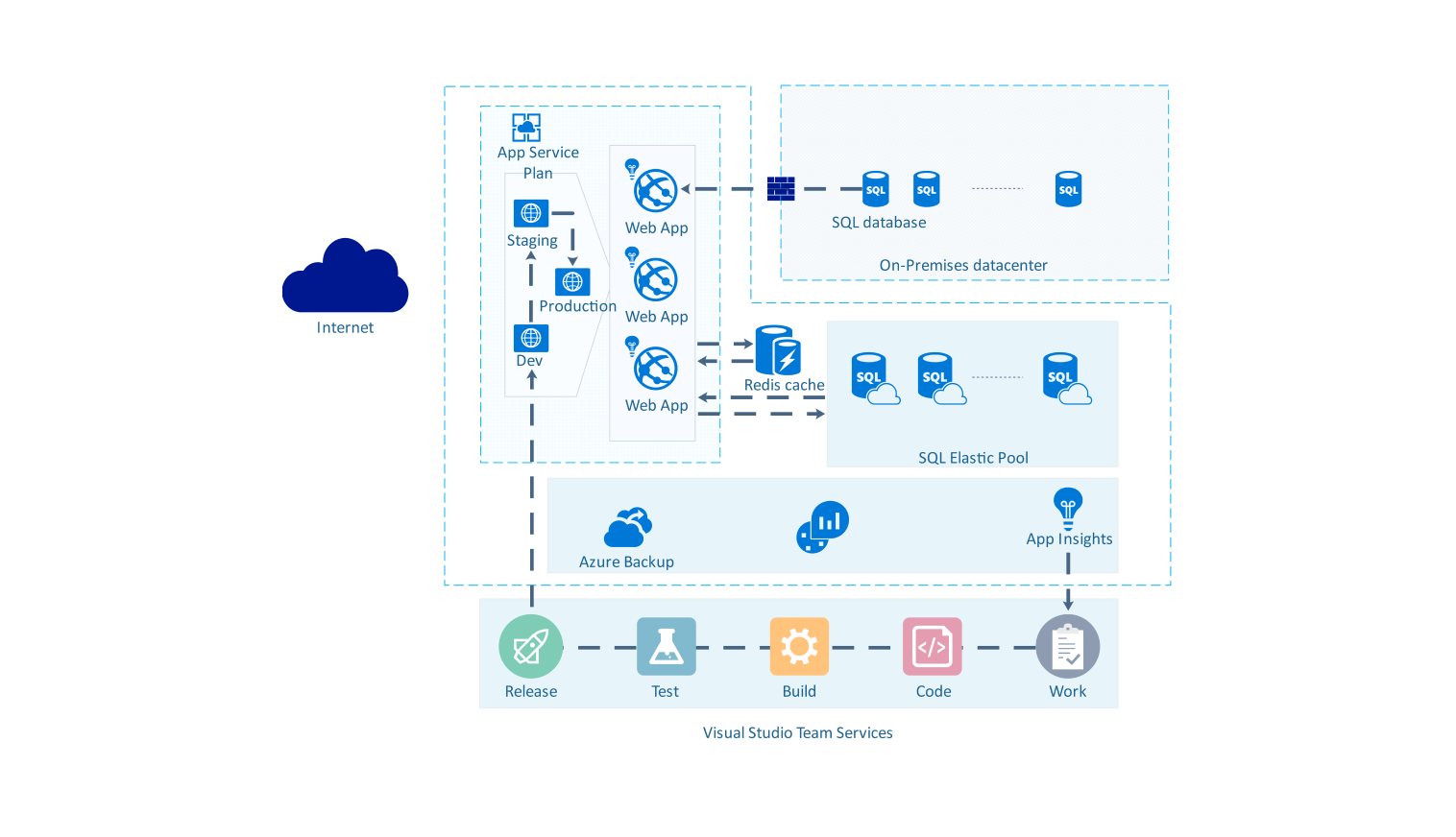
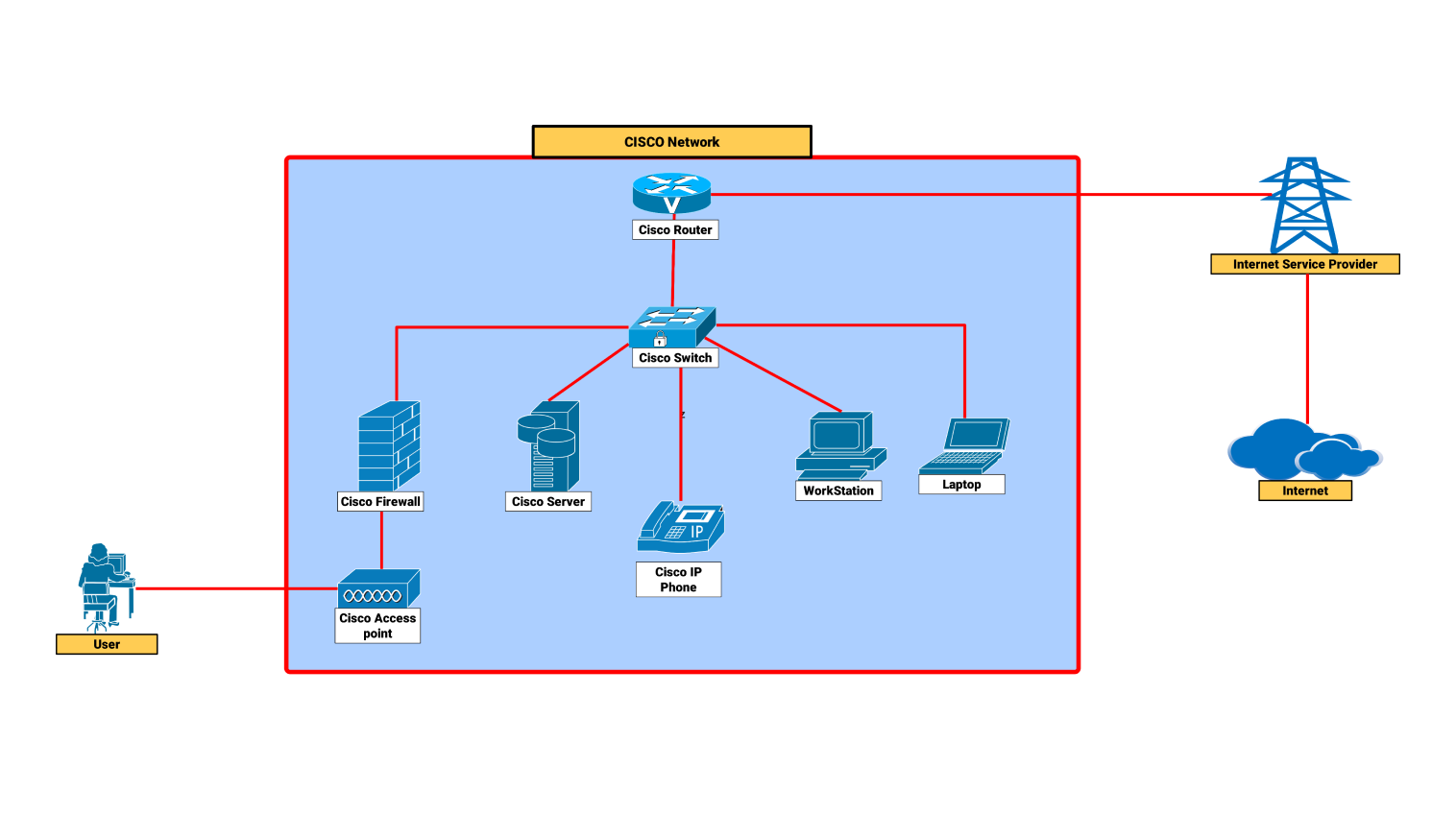
- All templates
- Network diagram templates
- Network diagram p2p
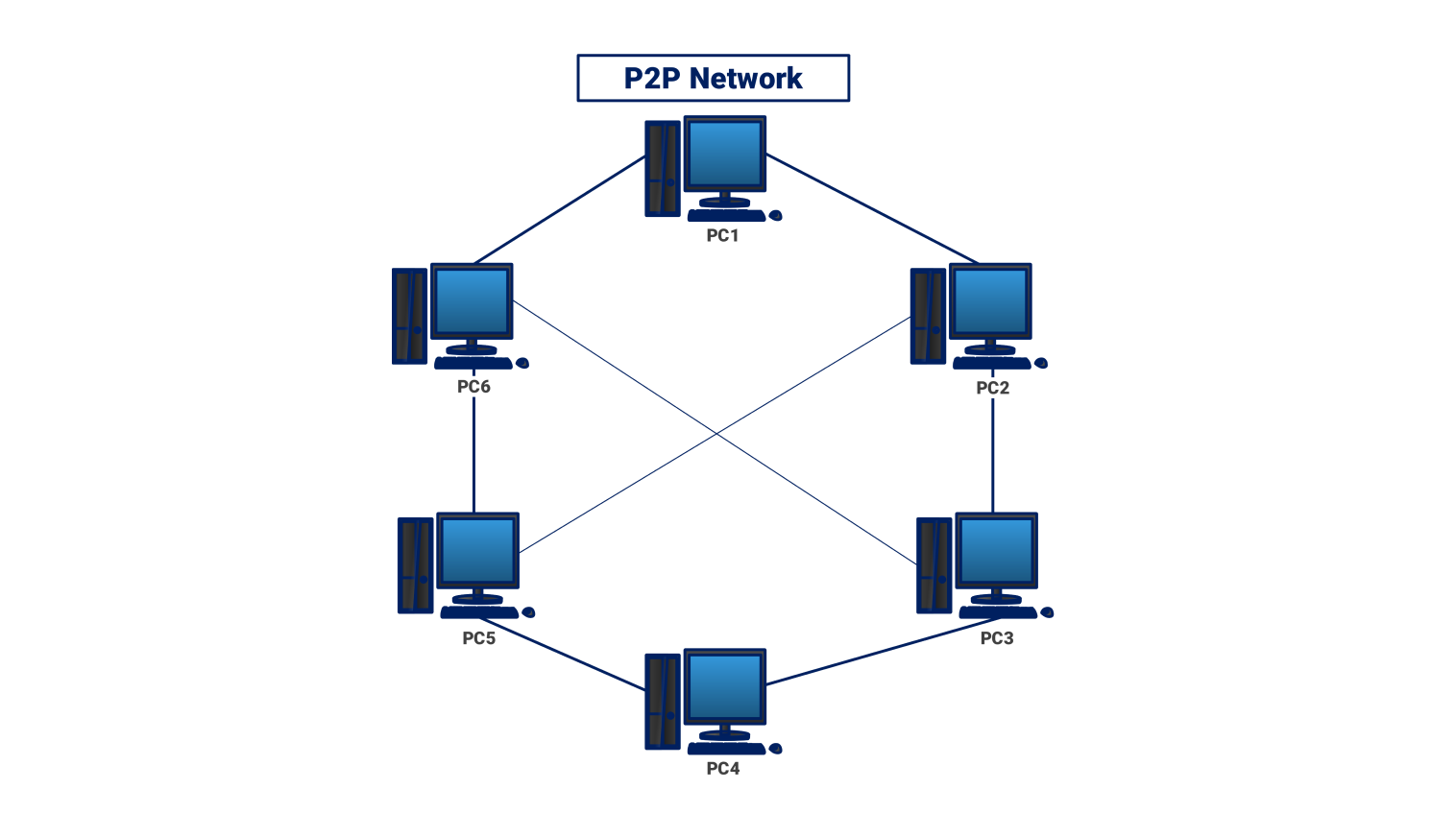
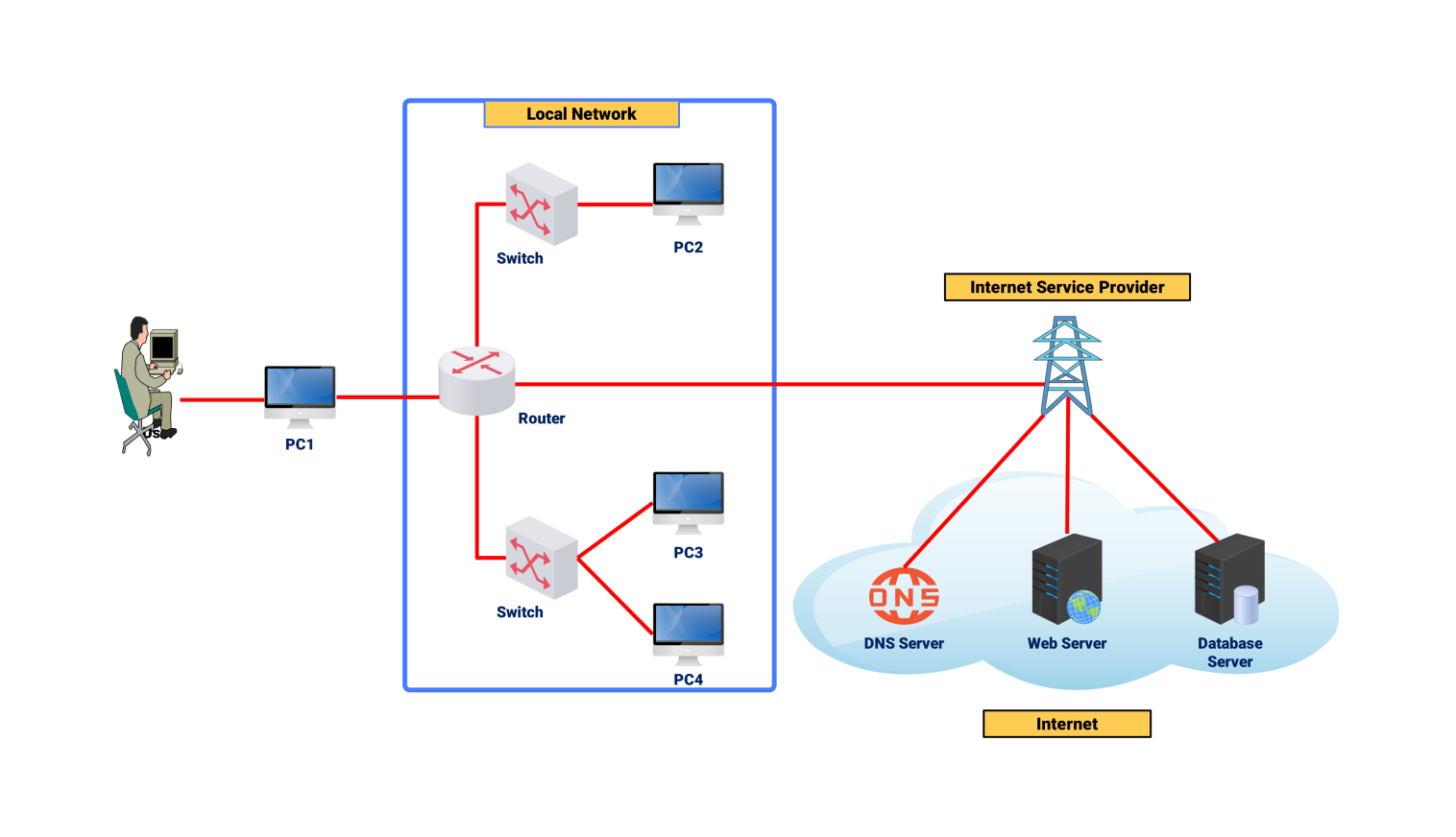
About this network diagram for the P2P
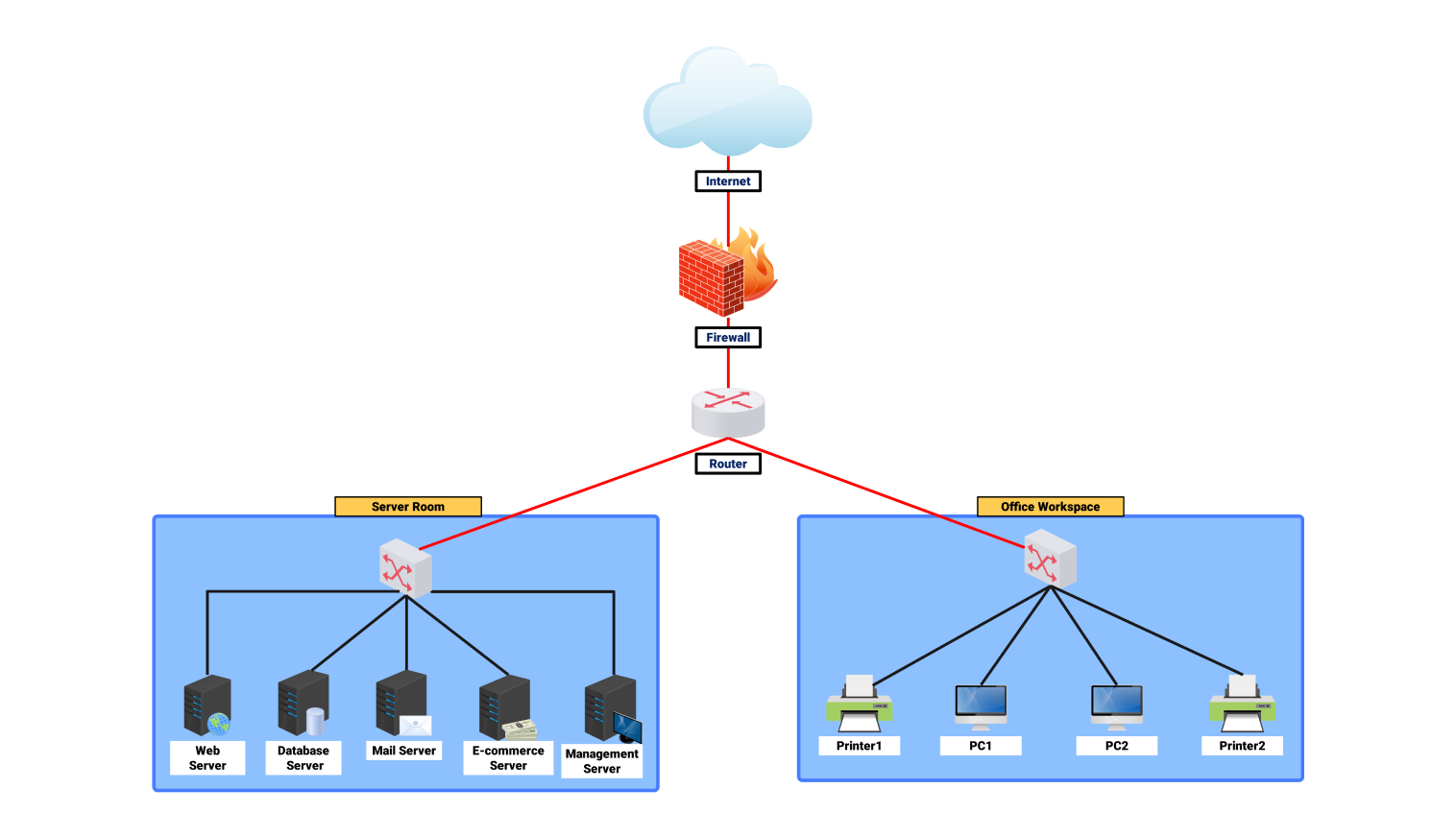
The following peer-to-peer (P2P) network diagram, is a network without a central server. Here, all the devices present in the network called peers play the role of both a client and a server. In such a case, devices communicate directly.
This allows them to share resources, files, and data without a central server. This is typical in applications for sharing content, team spaces, and distributed systems. There, it's better to have less control over the network's structure.
In this network, any peer (PC1 in the picture above, for instance) connects to several other peers. A standard client-server architecture has a server that holds all resources. A P2P network allows all users to become the server too. This approach solves the issues caused by a central server. It also reduces the risk of server failure, making the network more reliable.
Resource sharing is perhaps the most common upside of a P2P network. For any peer with whom one wants to exchange data, that peer can freely upload and download files. For example, a user on PC1 wants to send a file to PC3.
They can connect directly to each other’s PC without going through the central server. This type of communication lets users send and receive information faster. It reduces internet bandwidth waste during peak hours when many users are online.
P2P also allows for distributed computing where work is shared among different peers. This is useful for resource-intensive apps, like scientific research and blockchain tech. In such cases, every peer helps to generate the needed processing power. This allows for labor division and enables the network to perform complex tasks.
The P2P networks have some limits. Security and data integrity are one. Since each peer operates alone, it's tedious to prove data is correct and to prevent intrusion. So, it's vital to have security protocols and data checks. They will prevent the network's promiscuity and ensure trust among its users.
In general, the P2P network diagram shows an effective architecture design. It allows for decentralized resource sharing and communication. Having every device in this architecture act as both a client and a server boosts scalability. It also reduces reliance on a central system and promotes fault tolerance. P2P networks work best where minimal hub control is needed.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free