- Templates
- Circuit diagram templates
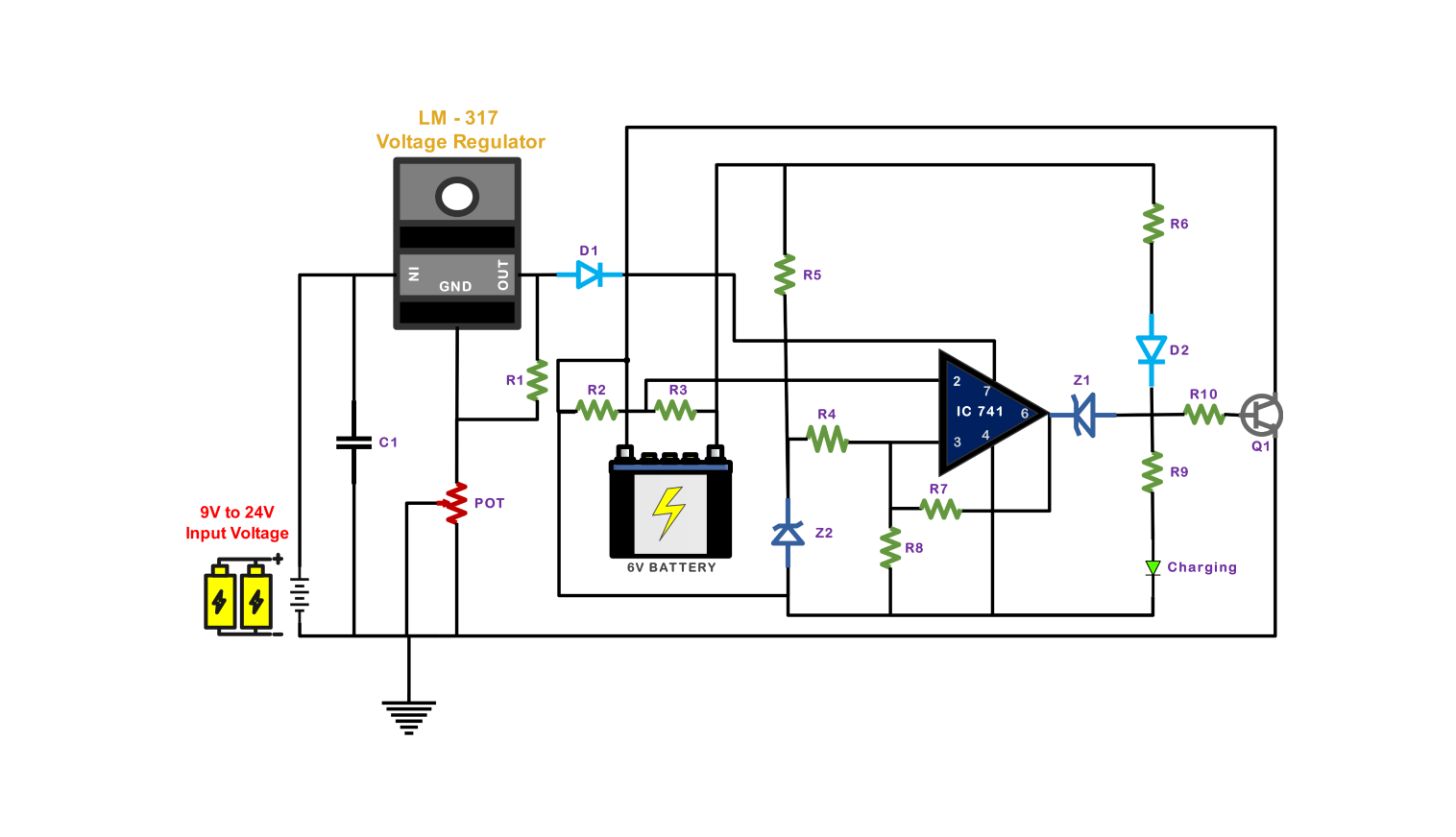
- Battery charger circuit diagram
About this circuit diagram example
The schematic of a battery charger consists of a standard design aimed at converting high-voltage AC electricity from an outlet into a regulated DC which serves for charging the batteries.
Initially, it is the inside transformer that converts high voltage AC electricity to the safer level we can further work with. The procedure initiates with a bridge rectifier which subsequently transforms DC into pulsing AC. After that, the role of a capacitor is to even out fluctuations, respectively this produces a more stable and less pulsating DC voltage.
How to use the circuit diagram template
Click on Edit it online to open a template. Once the template has opened, look for the Libraries panel on the left side. There you can find all the electrical components that you might want to add in. Drag and drop the needed symbols onto your canvas.
Under Electrical Engineering, expand the Basic Electrical category. You can swap components, adjust values, and even add labels to tailor the circuit. You can also change line styles, colors, and text fonts for better clarity.
Click File > Export and choose your preferred format (e.g., image file, PDF, SVG). Finally, click Export to finalize your export process.
Benefits of the template
The circuit diagram of a battery charger helps in electrical design in a few ways:
- This tells us how the different electrical parts are connected and how they function in a general manner. The ability to test circuit design before adding components in the real charger makes electrical designers confident that everything will work smoothly.
- They can also pinpoint areas of anticipated problems as a result of the design stage, such as the case of a resistor that can handle the current it requires. After connecting and then, if they understand the functions of all parts, they get to understand how the whole charger circuit works.
- They can inspect the conversion of AC to DC, and regulation of the voltage, where the current is limited to protect the battery. The insight acquired thus plays an important role in the selection of more advanced circuits.
FAQs about circuit diagrams
-
How do battery charging circuits work?
Battery charging circuits take household electricity and transform it into a safe and controlled current to revitalize your batteries. Here's a breakdown of their inner workings:
-
AC to DC Conversion:
Whether one is dealing with a house (AC) or a battery (DC), there is a need to find some way of converting the current from AC to DC. The charger tackles this disparity in two stages:
- Transformer:
- Bridge Rectifier:
It converts high mains AC voltage (230V) from the wall outlet to a lower voltage level (5V) needed for devices such as smartphones.
This circuit converts the step-down transformed AC into pulsating DC electricity that travels along the planetary circuit.
-
Smoothing the Flow:
The DC output doesn't commence very shortly to be perfect. Thus, to tackle this, the capacitor plays the role of a tank-like device as a storage medium.
-
Precise Voltage Delivery:
All batteries have their especially polished voltage requirements. A voltage regulator circuit can be implemented which bounds the output voltage to the one that corresponds to your battery's needs.
-
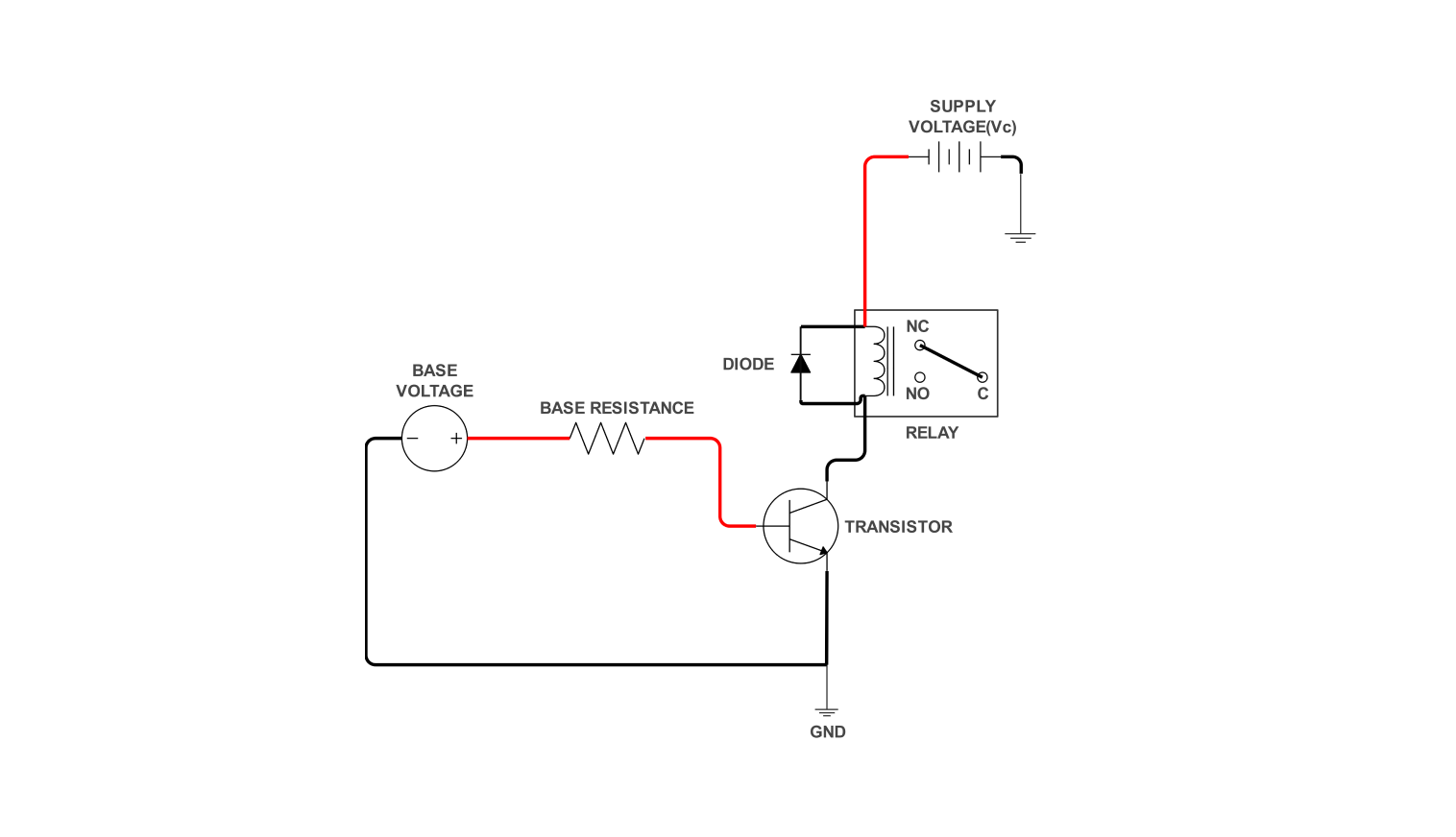
Current on a Leash:
The charger may also contain a circuit for limiting current so that it only supplies the required current to the battery, hence avoiding an overcharging situation.
-
-
Why is the charging circuit needed?
- Safety:
- Efficency:
- Compatibility:
The charging circuit is a safety feature of the charging circuit that guarantees the proper charging current.
Batteries cannot store all needed power. By controlling the voltage and current regulator, the charger makes certain, that the mode of charging is efficient and does not challenge the battery's lifespan and performance.
A soup of battery types (Lithium-ion, NiMh, etc.) calls for different charging methods. The charging circuit supplies the correct voltage and the current waving for every type of device taking part in the charging.
-
How do you know if a circuit is charging or discharging?
- Voltage Measurement:
- Current Flow Direction:
The battery terminal voltage is one of the best samples. At the time of charging, the charger imparts a voltage above the battery’s specified voltage. As discharged, the battery voltage will decline gradually until it reaches the very end of its charge when it starts to deliver power to your device.
When charged, the current stream from the charger is captured and enters into the battery. To recap, during the charging, it is currents that flow into the battery to get it powered, and then during the discharging, it is currents that flow out of the battery to get your device powered up.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free