Risk banking is an essential function within financial institutions, aimed at identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact their stability and viability. By adopting strategies such as identification and assessment of core risk in banking, risk mitigation and control, and stress testing, financial institutions can enhance their resilience, instil confidence among stakeholders, and contribute to the overall stability of the financial system.
In this article
Part 1. Definition and Role of Risk Banking
Risk banking encompasses the management of risks that financial institutions face in their day-to-day operations, for example, reputation risk in banking. Its primary responsibility lies in identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks, which can impact the institution's stability and viability.
Risk banking acts as a protective shield for financial systems against adverse events and helps ensure confidence among stakeholders.
Part 2. Types of Risks Managed in Risk Banking
Risk banking encompasses various types of risks that financial institutions encounter. These core risk in banking should be managed adeptly. Doing this ensures that financial institutions are not affected by these risks.
1. Credit Risk:Potential losses from borrowers' inability to meet financial obligations.
2. Market Risk:Possible losses from volatility in financial markets.
3. Operational Risk:Risks from internal processes, human error, or external events.
4. Reputational Risk: Risks that affect the reputation of financial institutions.
Part 3. Risk Banking Strategies and Techniques
Risk banking institutions adopt various strategies and techniques to mitigate and manage risks effectively, be it for strategic risk in banking or otherwise. These have been proven beneficial in managing risks.
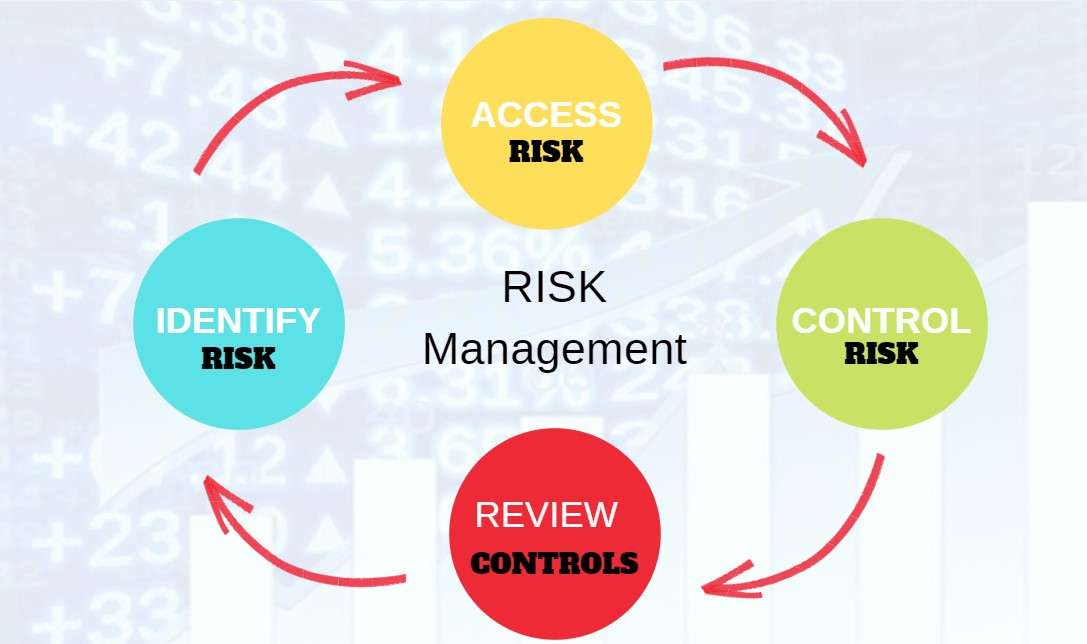
1. Risk Identification and Assessment:Financial institutions use quantitative and qualitative methods to identify and assess potential risks.
2. Risk Mitigation and Control:Institutions develop strategies and control measures to mitigate risks, including diversifying portfolios, setting risk limits, and implementing internal controls.
3. Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis: Institutions conduct stress tests and scenario analysis to evaluate the impact of adverse events on their portfolios.
Part 4. Best Tools to Create Risk Banking Charts
The impact of risk banking on financial institutions cannot be overstated. Effective core risk in banking management practices helps improve financial systems' stability and resilience, safeguarding various stakeholders' interests.
By mitigating risks, financial institutions can instill confidence among investors, enhance market liquidity, and prevent catastrophic events that can undermine the economy's overall health.
Using tools to create risk banking charts offers several benefits. It allows for easy visualization of complex data, enabling stakeholders to quickly understand and assess potential risks. These tools provide real-time updates, ensuring the risk charts are always up-to-date.
1) Wondershare EdrawMax
Wondershare EdrawMax empowers users with its comprehensive set of features and intuitive interface. With an extensive library of templates and symbols, users can effortlessly design visually appealing risk bank charts. EdrawMax's advanced collaboration tools enable teams to collaborate seamlessly, ensuring efficient risk management. You can create a risk banking chart using the tool by following these steps:
Step 1: The first step in creating a risk banking chart is to log into EdrawMax. You can do this by navigating to the EdrawMax website and entering your login information.
Step 2: Once you are logged in, you can open a new document. Just simply select “New” from the file menu.
Step 3: Now go to the templates section, and you will be presented with a variety of templates to choose from. Select a risk banking chart template to get started.
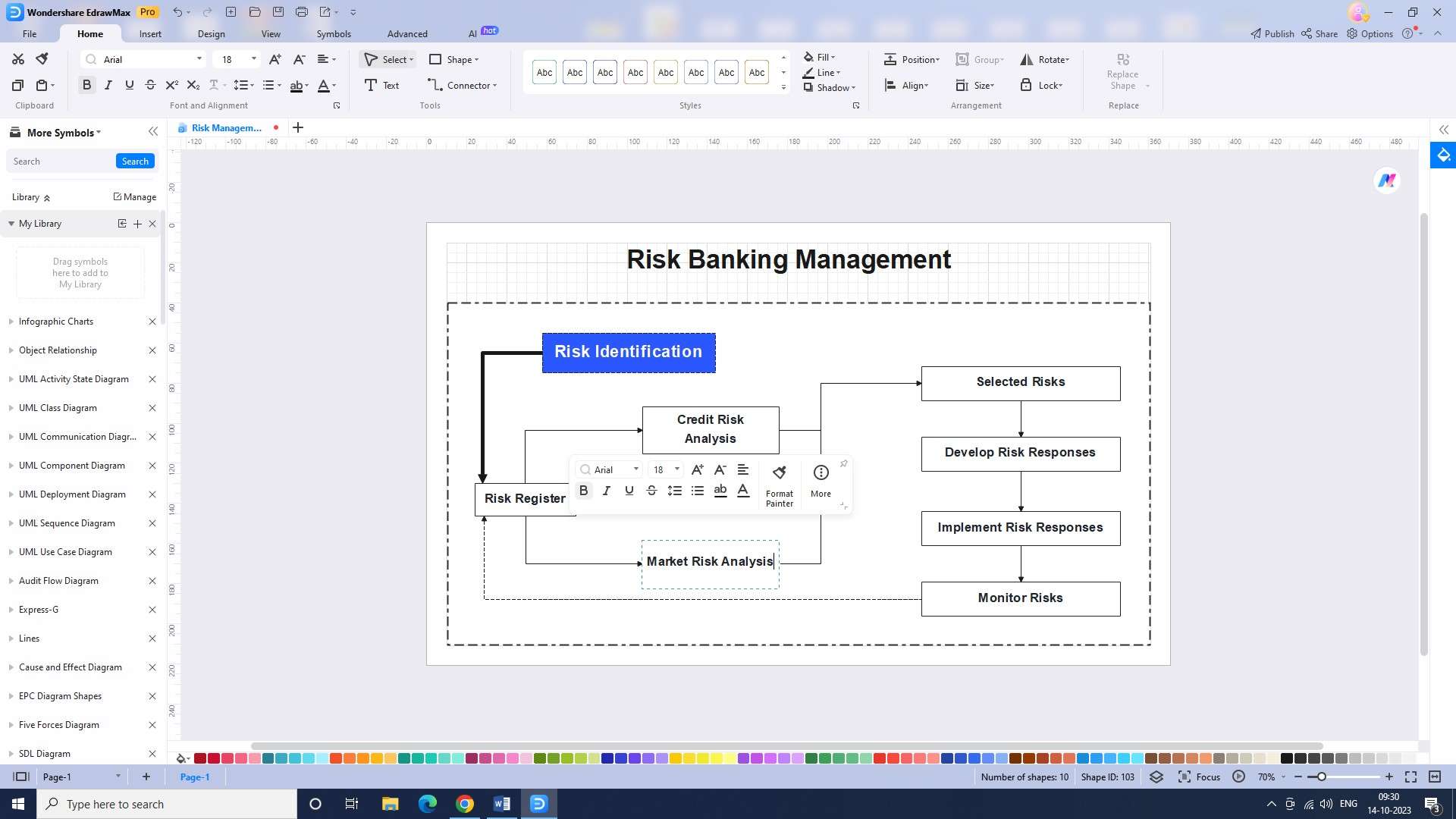
Step 4: Once you have selected the template, you will be able to enter your data into the risk banking chart. This includes any potential risks associated with the project or venture.
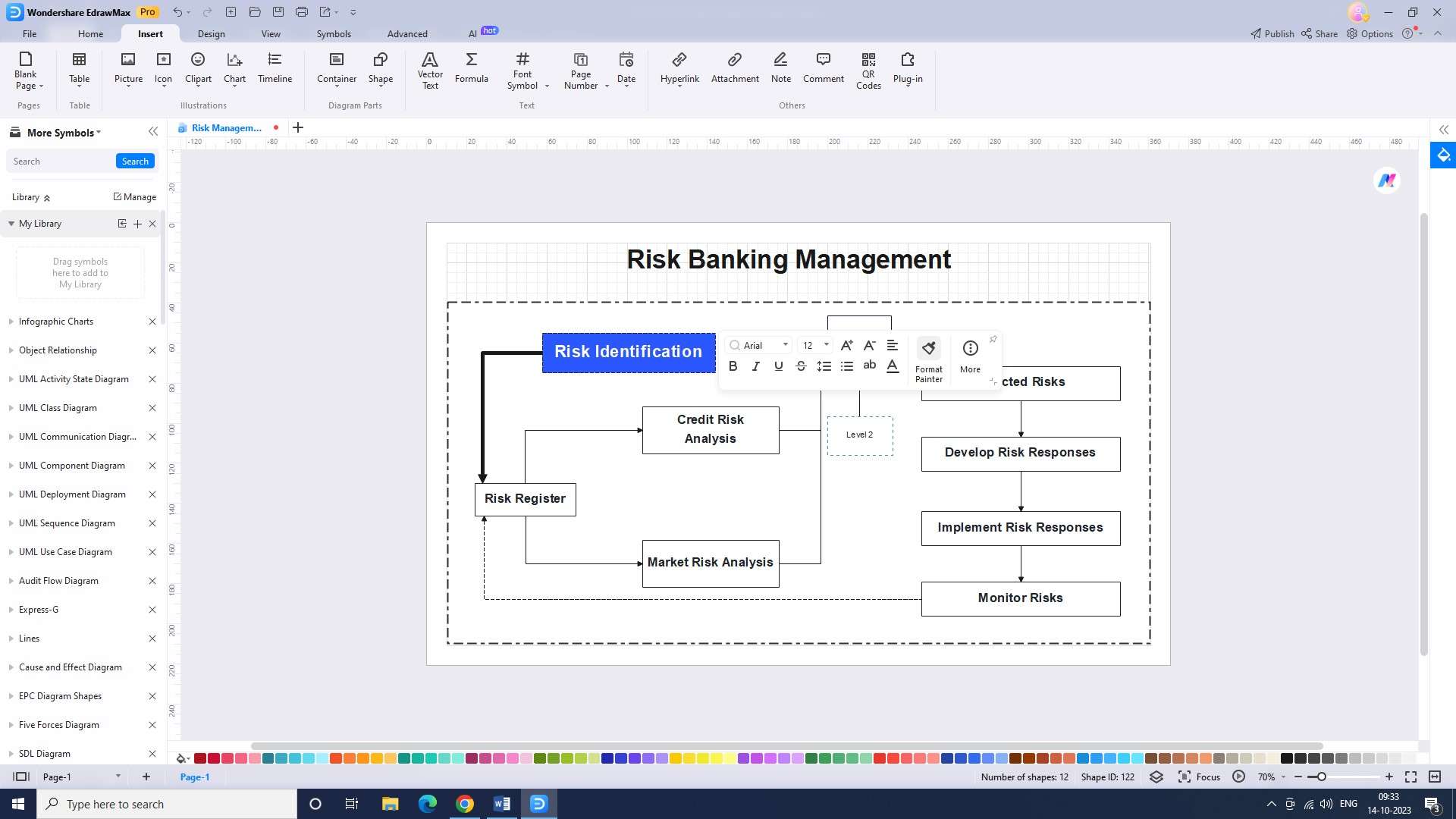
Step 5: The next step is to adjust the categories of core risk in banking. This will help determine which risks should be given more attention.
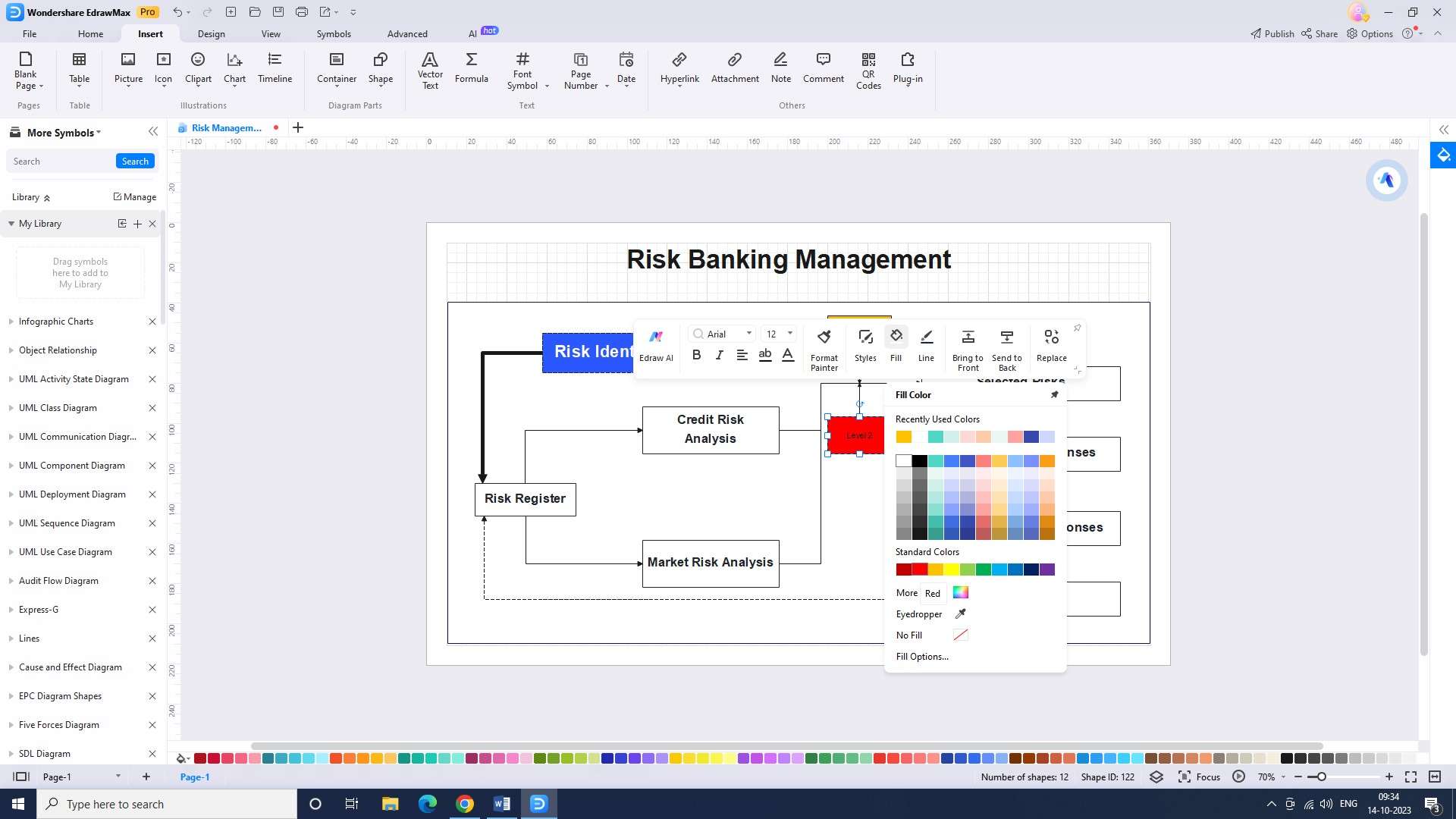
Step 6: Finally, you will be able to adjust the risk level colors. This can be done by selecting the appropriate colors for each risk.
Step 7: Now that your chart has been created, you can save the chart. Go to the file menu and click on “Save” to do this.
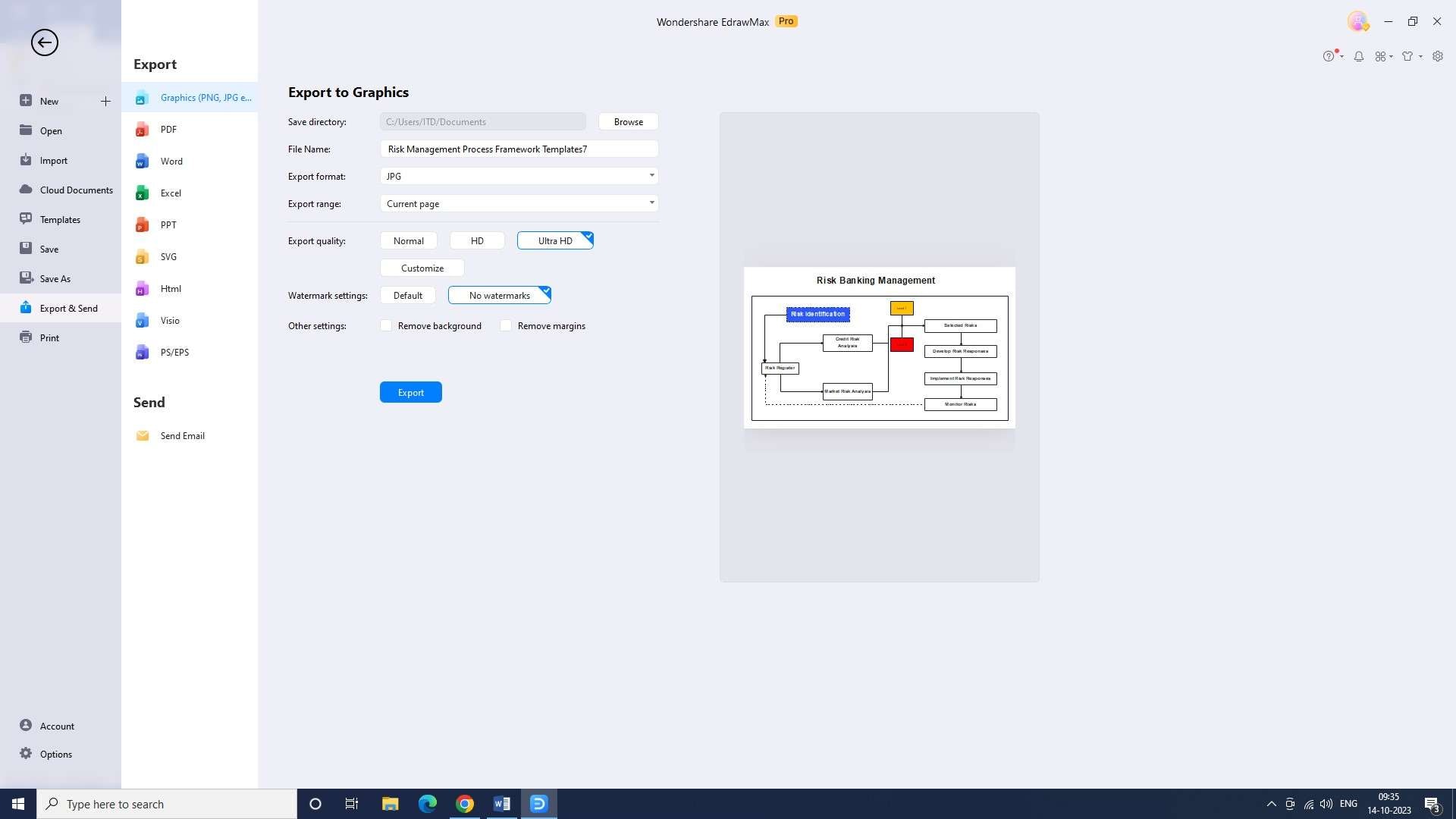
Step 8: Now, you can export the chart. Do this by selecting the “Export” option from the file menu and then selecting the appropriate format for the chart.
2) Pingboard
Pingboard offers a user-friendly platform that streamlines collaboration and enhances communication. With its intuitive drag-and-drop interface, users can easily add and organize risks, controls, and other relevant information.
Features:
- Integration with risk registers
- Trend analysis for identifying emerging risks
- Customizable risk-scoring algorithms
Pros:
- Correlation analysis for identifying dependencies
- Risk mapping for a comprehensive view
- Action tracking for monitoring mitigation
Cons:
- Limited scenario modeling
- Lack of integration with external risk data
3) Creately
Creately provides a robust web-based platform with a plethora of features. With its extensive library of templates and shapes, users can effortlessly design customized risk bank charts that suit their specific needs.
Features:
- Visual risk control representation
- Collaborative risk documentation
- Customizable risk heat maps
Pros:
- Risk simulation and sensitivity analysis
- Automated risk reporting
- Risk alert notifications
Cons:
- Limited risk quantification capabilities
- Limited customization of risk charts
Conclusion
Risk banking plays a crucial role in managing and mitigating the various risks financial institutions face in their daily operations, whether reputation risk in banking or any other type of risk. From credit and market risks to operational and liquidity risks, effective risk banking strategies and techniques help safeguard the stability and viability of these institutions.