In today's fast-changing business world, it's really important to focus on both audits and managing risks. Audits help find weak spots, while risk management plans fix them and make them smaller. This article talks about how these two things work together to make a company stronger and better able to handle challenges.
When these functions work in harmony, businesses can confidently navigate uncertainties, ensuring compliance and securing their long-term success.
In this article
Part 1: What is Audit Risk Management
Audit risk management refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks during an audit. It involves evaluating the likelihood of errors or misstatements in financial statements and determining the impact they could have on a company's overall financial health. By understanding and addressing these risks, auditors can ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting.
Part 2: Understanding Internal Audit Risk Management
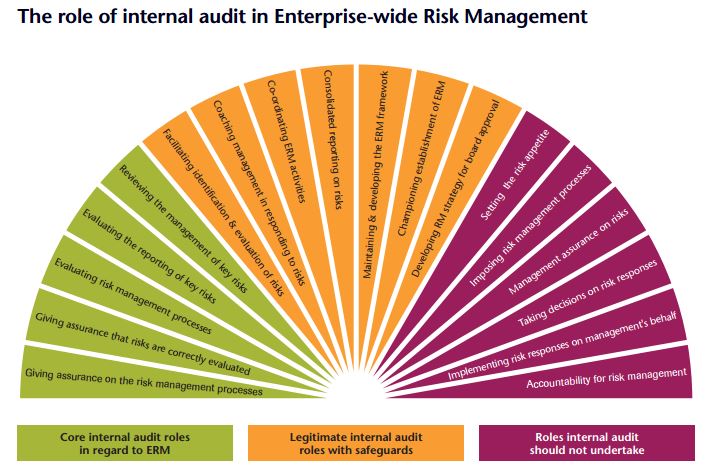
Internal audit risk management is the practice of evaluating and addressing potential risks within a company's operations. It involves identifying areas where errors or mismanagement could occur and taking steps to prevent or mitigate them. This process helps ensure that financial reporting is accurate and reliable.
When companies take steps to handle risks before they become problems, it builds trust and honesty with the people involved in the company. This teamwork between internal audit and risk management is really important for keeping the company's rules and processes strong and reliable.
Part 3: Why is Internal Audit Important for Risk Management
Internal audit plays a pivotal role in effective risk management strategies, providing essential insights and safeguards for organizations. Here's why it's crucial:
- Identifies Weaknesses: Internal audit uncovers operational vulnerabilities and control gaps, providing valuable insights into potential risks.
- Ensures Compliance: It verifies adherence to regulatory standards and industry best practices, reducing the likelihood of non-compliance penalties.
- Enhances Efficiency: By streamlining processes and identifying areas for improvement, internal audit helps optimize resource allocation and reduces wastage.
- Safeguards Assets: It helps protect company assets by identifying and mitigating risks related to fraud, mismanagement, or external threats.
- Builds Stakeholder Trust: Through rigorous oversight, internal audit instills confidence in stakeholders, showcasing a commitment to sound risk management practices.
Part 4: Relationship Between Internal Audit And Risk Management
Internal audit and risk management work hand in hand to keep a company safe and running smoothly. The internal audit team checks all the important areas of the business to find any weak spots or things that aren't following the rules. They then share this information with the risk management team. This team looks at how serious these issues are and figures out how to make them better. Together, they make sure the company is strong and follows all the right steps for success.
Part 5: Types of Audit Risks
Understanding the various types of audit risks is essential for maintaining a robust and effective risk management framework within an organization. Here are brief descriptions of three key categories:"
1. Financial Audit Risk:
Financial audit risk focuses on the accuracy of financial statements, aiming to detect any errors or misstatements that could lead to financial losses or incorrect business decisions. It ensures the reliability of financial information.
2. Operational Audit Risk:
Operational audit risk assesses the efficiency and effectiveness of operational processes. It identifies areas where resources may be wasted or where improvements can be made to enhance productivity and streamline operations.
3. Strategic Audit Risk:
Strategic audit risk evaluates the alignment of an organization's strategies with its overall goals and objectives. It examines whether the chosen strategies are suitable for achieving long-term success and competitive advantage in the market.
Part 6: Create an Internal Audit Diagram using EdrawMax
Creating an internal audit diagram using EdrawMax holds significant importance in visualizing and organizing the audit process. This powerful tool allows for a clear and structured representation of the entire audit cycle, from planning and execution to reporting and follow-up.
The diagram serves as a visual roadmap, enhancing communication, comprehension, and transparency within the audit team and across departments.
Here are the steps to create an internal audit diagram using EdrawMax:
Step1
Launch the EdrawMax software on your computer. Click on "New" or "File" > "New" to start a new document. In the template gallery, type "Internal Audit" in the search bar to find relevant templates.
Step2
Drag and drop shapes or symbols from the library onto the canvas to represent different elements of the audit process. These may include boxes for processes, decision points, data inputs, etc.
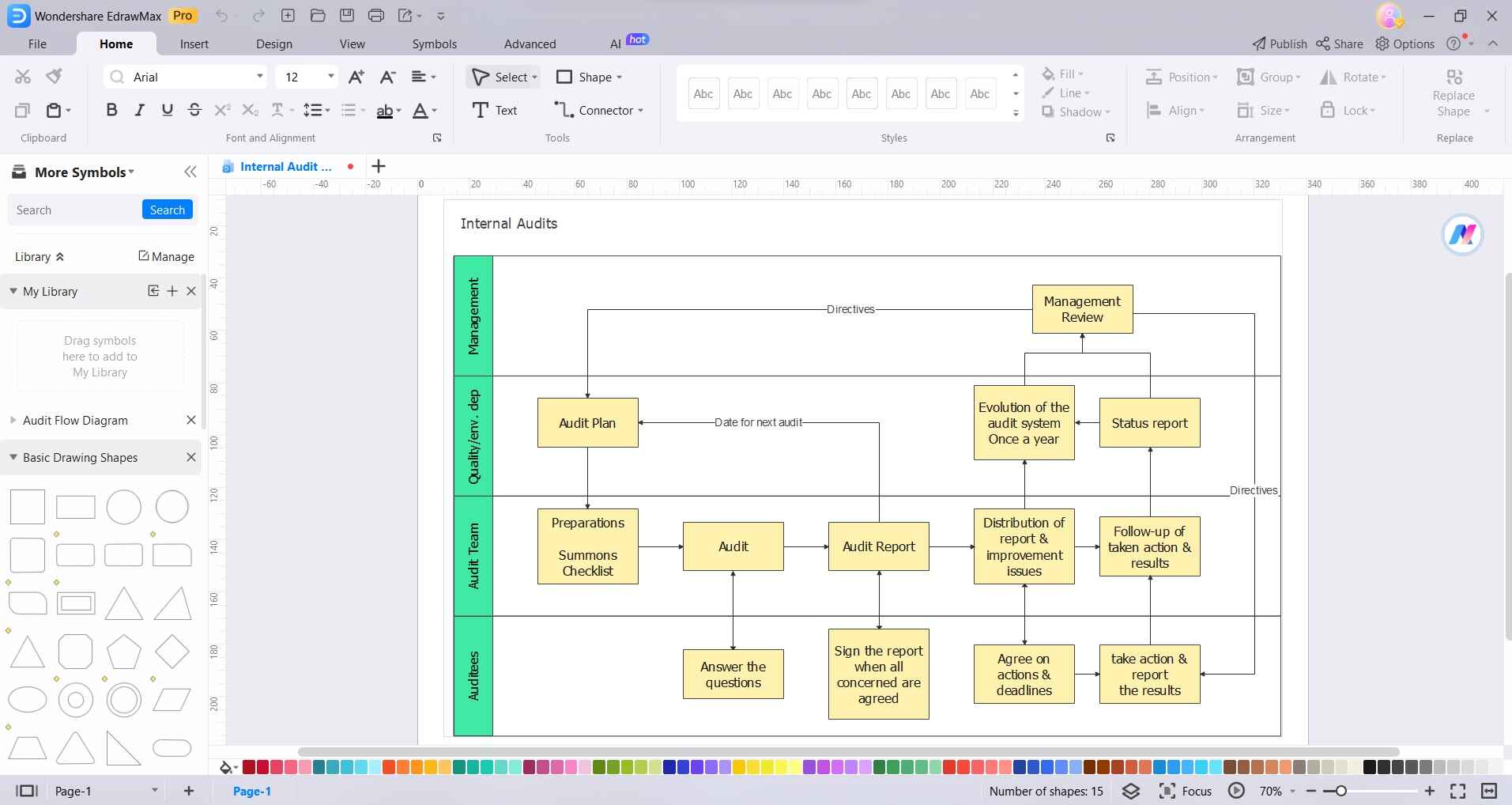
Step3
Step 3: Use lines or arrows to connect the shapes, indicating the flow of the audit process. You can find these tools in the drawing toolbar.
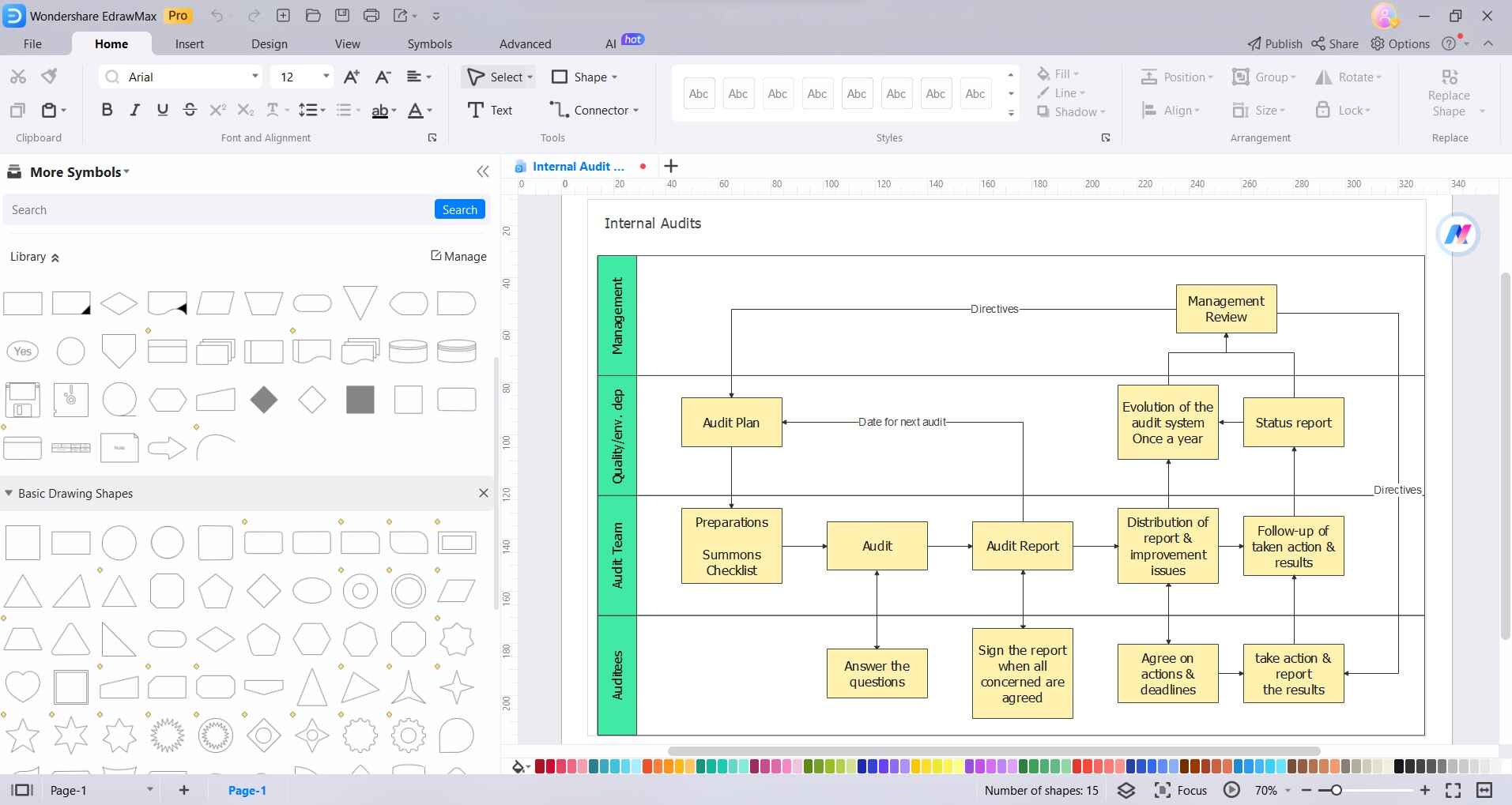
Step4
Insert data or information relevant to each step of the audit process. This could be in the form of text, tables, or charts. Select an entity and click on “Styles” to review formatting options.
Step5
Once you're satisfied with your internal audit diagram, save your work. You can also export it in various formats, such as PNG, JPG, PDF, etc., for easy sharing and presentation.
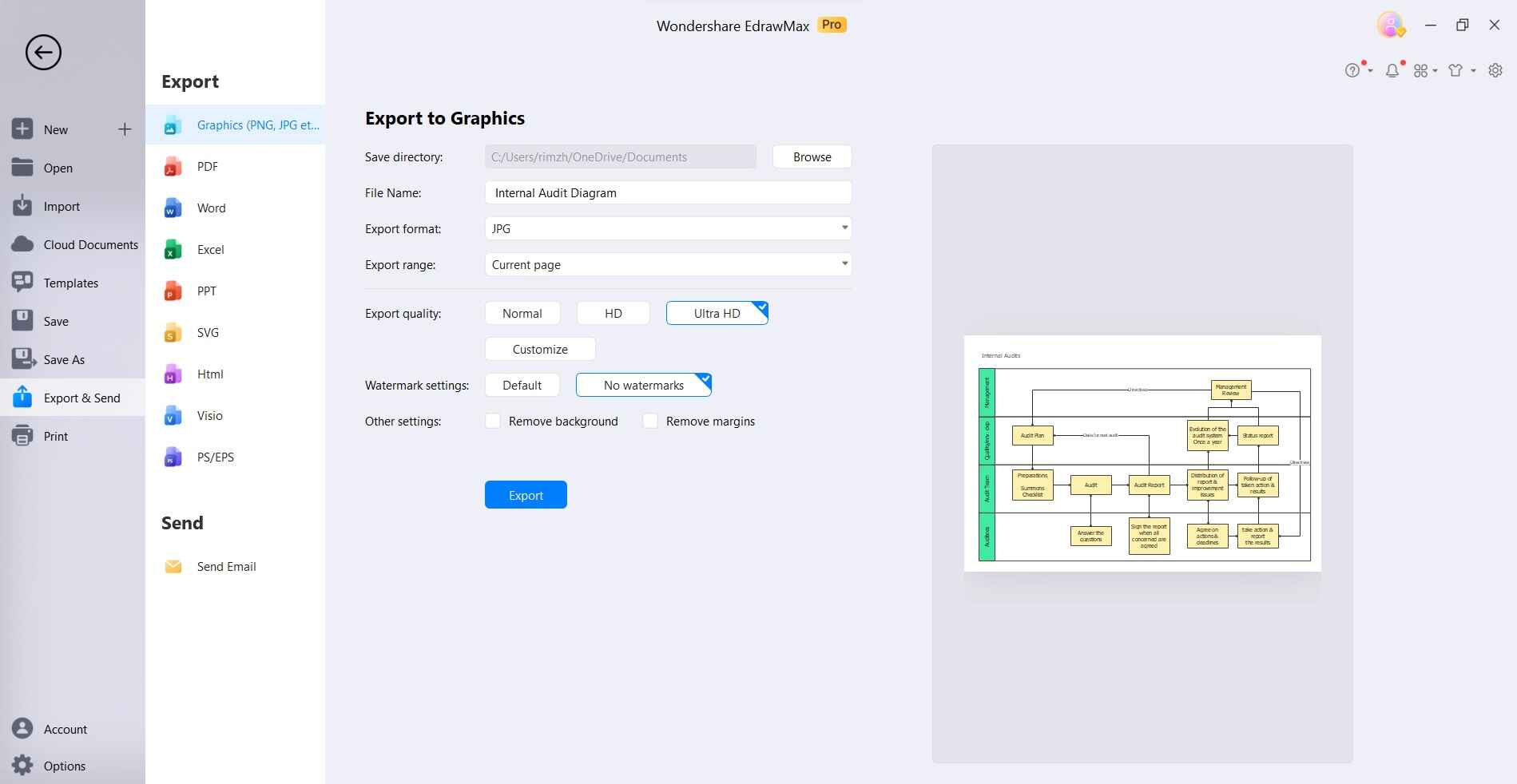
With EdrawMax's intuitive interface and extensive library of shapes and templates, creating an effective internal audit diagram becomes a straightforward process.
Conclusion
In simple terms, when internal audit and risk management work together, they make a company strong and secure. Internal audit finds weaknesses, and risk management figures out how to fix them. In addition, using user-friendly tools like EdrawMax simplifies the process of creating visual aids, enhancing communication and understanding in the audit process.
[没有发现file]



