Effective risk management is integral to the success of any business. Employing a systematic method to recognize, evaluate, and address risks empowers organizations to make informed choices and establish necessary safeguards to mitigate potential losses. The ISO 31000 standard outlines principles and guidelines for effective risk management that businesses of all types and sizes can use.
In this article, we will explore what ISO 31000 entails, its key components, differences between the 2009 and 2019 versions, and steps for utilizing it to improve risk management.
In this article
Part 1: What is ISO 31000?

ISO 31000 is an international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization that provides principles and guidelines for risk management. First published in 2009, it was updated in 2018 with a revised version called ISO 31000:2018.
The standard outlines a generic approach that can be applied to different types of risks across any industry or sector. The objective is to create a common risk management language and approach that enables consistent implementation across an organization. Adopting ISO 31000 helps embed risk-based thinking into an organization’s objectives and processes.
Part 2: Overview of ISO 31000 2009 Framework
The original ISO 31000 2009 standard provides a three-part framework for risk management:
- Principles - Outlines the key principles an organization should follow when managing risks. This includes things like having an open, inclusive culture around risk, integrating risk management into processes, and customizing the approach to be suitable for the organization.
- Framework - Provides the process steps involved in implementing risk management, from establishing the scope and context to monitoring and review.
- Process - Details the risk management process, including risk identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment.
The standard emphasizes the need for risk management to be integrated into overall governance, strategy, planning, management, and reporting processes. Leadership and commitment from managers are critical for effective implementation across an organization.
- Read also: ISO 31000 Risk Management Process Simplified
Part 3: Role of Risk Assessment ISO 31000 in Business
Risk assessment is a central component of ISO 31000. It involves identifying what might happen or existing risks, analyzing the potential causes and consequences, and evaluating the level of risk. Risk assessment provides crucial decision-making inputs for determining where resources should be allocated to treat risks.
Key roles of risk assessment per ISO 31000 include:
- Enabling evidence-based decisions through a clear understanding of risks
- Allowing comparison of different types of risks and prioritization of resources
- Demonstrating due diligence and meeting compliance obligations
- Providing insights on whether risk controls are effective as conditions change
- Identifying emerging risks proactively to minimize surprises
Overall, risk assessment gives organizations the information needed to determine appropriate responses and allocate resources in a way that reduces losses and protects value.
Part 4: Major Difference Between ISO 31000 2009 and ISO 31000 2019
While ISO 31000:2009 provided a useful framework for risk management, ISO identified some opportunities to clarify and enhance the principles and guidelines. As a result, an updated ISO 31000:2018 was published.
Here are some of the major differences between the 2009 and 2018 versions:
- Increased emphasis on the integration of risk management into the overall governance and culture of an organization.
- Made risk management principles more prominent instead of just being in an appendix.
- Streamlined the risk management process steps from 5 to 4 by merging identification and analysis.
- Added more guidance around assessing risk interactions and aggregation.
- Expanded components of risk communication and consultation.
- Introduced the concept of a risk management system to continually improve risk management maturity.
Overall, the 2018 update provides more guidance and clarity without fundamentally changing the ISO 31000 approach. It aims to make adoption easier for diverse organizations.
Part 5: Benefits of Implementing ISO 31000 Framework
Adopting the ISO 31000 standard can provide organizations with the following key benefits:
- Improved risk identification and assessment for better-informed decisions
- Increased capability to mitigate risks and minimize potential losses
- Enhanced risk monitoring and review processes
- Stronger corporate governance and compliance through structured risk management
- Better allocation of resources to address critical risks
- A proactive culture of risk-based thinking and opportunity identification
Part 6: Creating a Risk Management Diagram Using EdrawMax
A valuable step in implementing ISO 31000 is to visualize the risk management framework in an easy-to-understand diagram. Edrawmax is user-friendly diagramming software that makes it simple to create ISO 31000 overview diagrams.
Here are the steps for using EdrawMax effectively for creating a risk management diagram:
Step 1:
Open EdrawMax on your computer. Switch to the “Template” category. Search for “Risk Management” and select a suitable template.
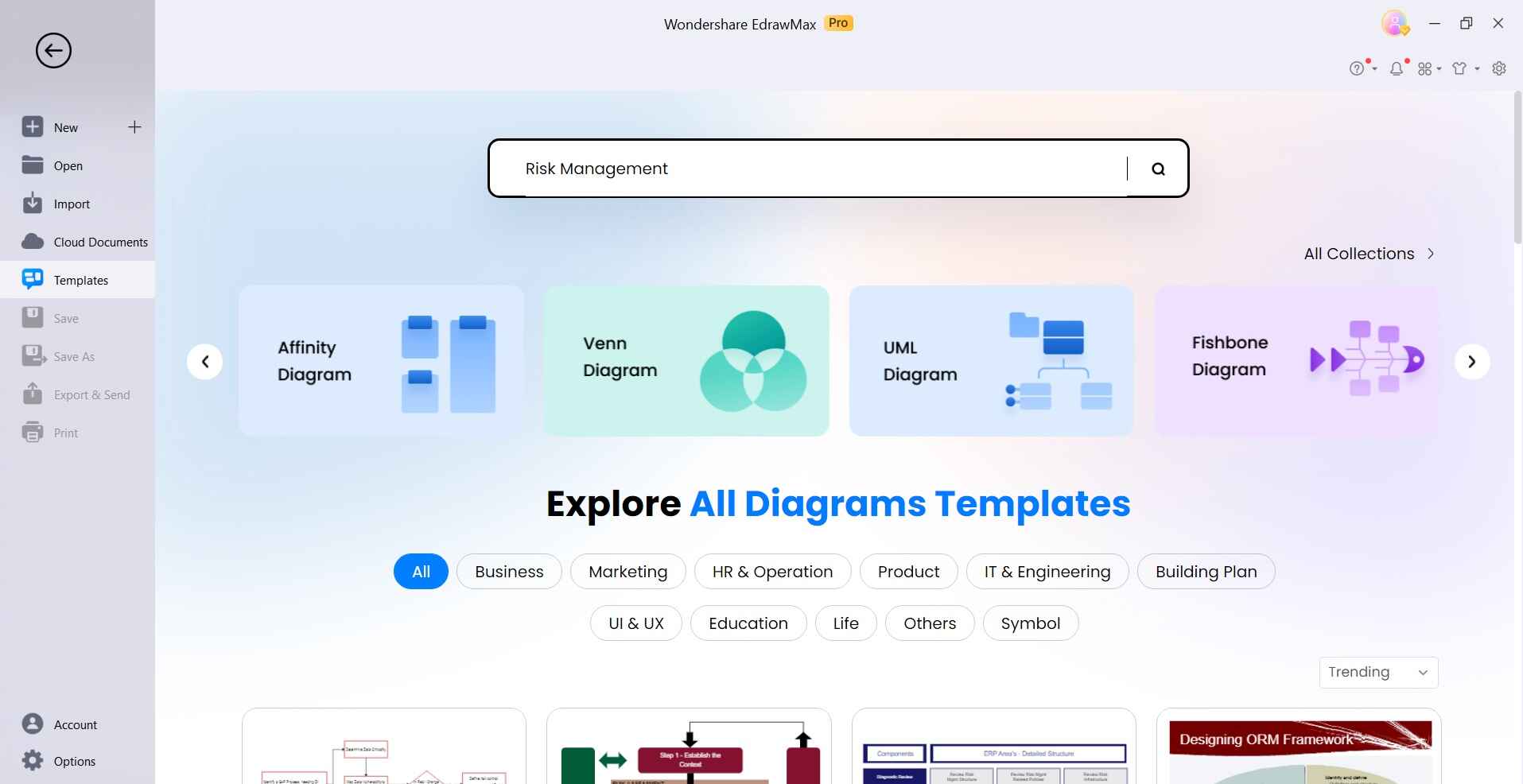
Step 2:
Drag and drop elements like principles, framework, and process onto the canvas.
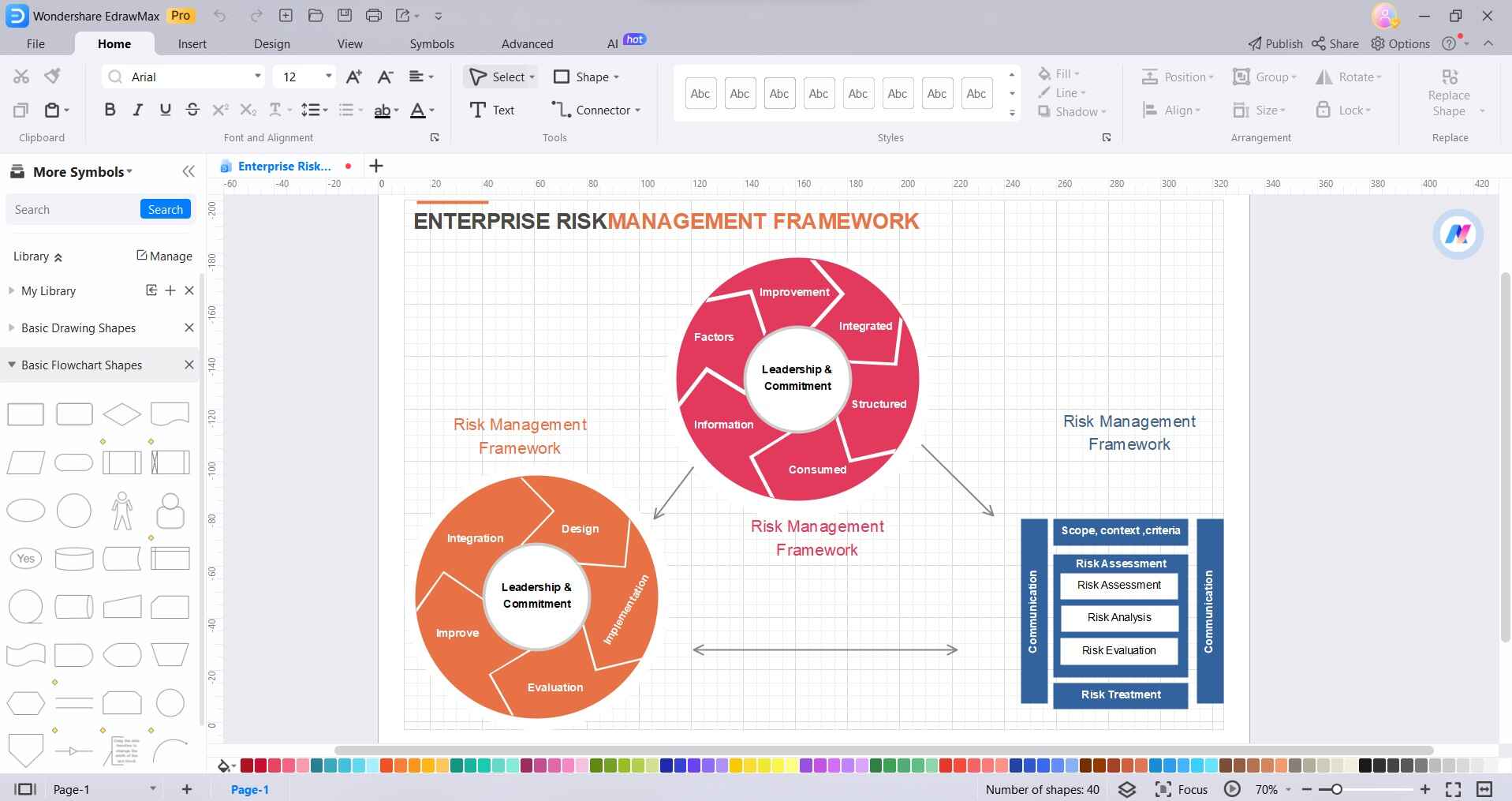
Step 3:
Add symbols and connectors from the left sidebar for clarity. Use auto-align and formatting tools to organize the diagram.
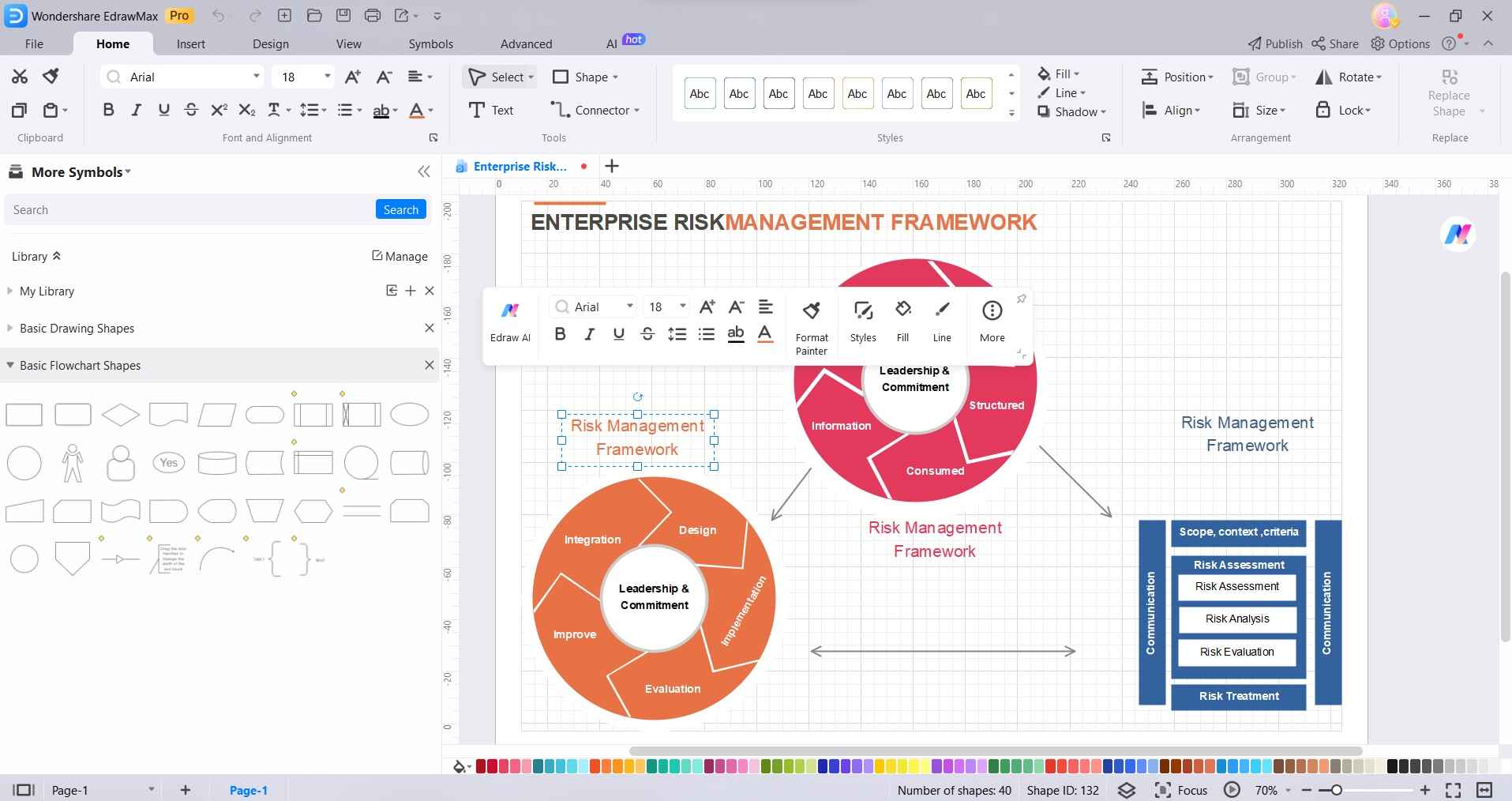
Step 4:
Customize colors, fonts, and shapes to tailor the visuals.
Step 5:
Export the finished diagram in various formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG.
Creating an ISO 31000 overview diagram enables organizations to communicate important information about their risk framework and processes to stakeholders.
Conclusion
Implementing the ISO 31000 risk management framework enables organizations to effectively identify, analyze, evaluate, and respond to risks. The standard provides guidelines to integrate risk-based thinking into governance and decision-making. Organizations can realize significant benefits by leveraging ISO 31000 principles and processes to build ISO risk management capability.