As cyber threats become more frequent and devastating, organizations need robust risk management programs to protect critical systems and data. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a flexible and proven Risk Assessment Framework that strengthens cybersecurity through systematic identification, analysis, and mitigation of risks.
This article will explore what risk management entails, provide an overview of the NIST framework, and deliver best practices for implementation. Weíll also showcase how EdrawMax's diagramming capabilities can visualize risk processes and relationships.
Part 1: What is Risk Management?
Risk management refers to the coordinated process of identifying, assessing, and responding to risks that could negatively impact an organization's operations or assets. Effective risk management is proactive rather than reactive ñ it seeks to minimize harm before adverse events occur.
Key goals include determining acceptable risk levels, implementing appropriate safeguards, and providing the foundation for informed decision-making about security priorities. Though complex, mature risk management programs reduce costs, protect reputation, and foster resilience.
Part 2: Overview of NIST Risk Management
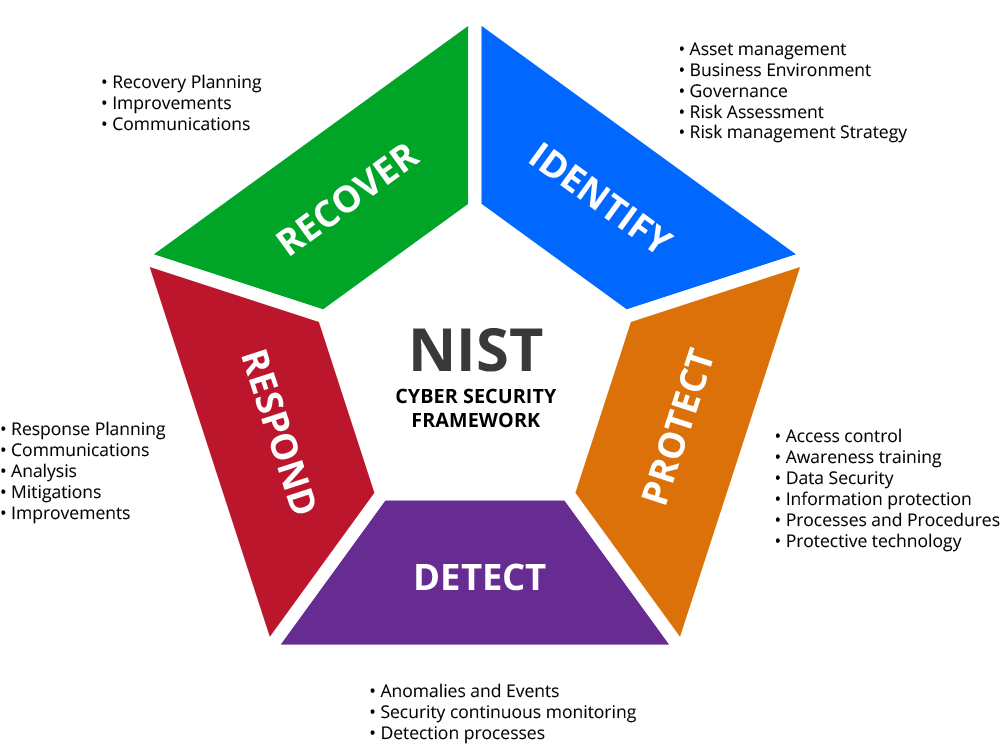
NIST provides guidelines for applying risk management practices to information systems and organizations. Widely adopted by both government and private sector entities, the NIST approach outlines an organized framework for cybersecurity risk:
- Risk Framing: Establishing scope, parameters, and criteria for assessments
- Risk Assessment: Identifying threats, analyzing impacts, and determining levels of risk
- Risk Response: Selecting and implementing approaches to mitigate risk
- Risk Monitoring: Continually tracking risk over time and improving methods
This lifecycle-based model emphasizes starting with robust framing to enable effective assessments tailored to organizational needs. Communication and coordination are also stressed across roles and levels.
Part 3: Types of NIST Risks
The NIST framework addresses three primary types of risk that information systems face:
- Security risks: Threats that could negatively impact confidentiality, integrity, or availability of systems and data. Examples include hackers, malware, and unauthorized access.
- Privacy risks: Vulnerabilities that could imperil privacy protections and disclose personal/sensitive data improperly. Insider threats and unauthorized surveillance play roles.
- Supply chain risks: Exposures within product and service supply chains that malicious actors could exploit to compromise systems.
Understanding these risk categories allows organizations to tailor assessments to their specific threat environments and priorities.
Part 4: Key Components in the NIST Risk Assessment Framework
While flexible, NIST outlines several repeatable phases to achieve effective assessments:
- Prepare: Define purpose, scope, and methodology parameters to align with organizational drivers.
- Conduct: Identify threat sources, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts, and determine risk levels per defined criteria.
- Communicate and Share: Report findings to stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Maintain: Monitor ongoing risks continually. Keep assessments current and identify emerging risks.
Robust implementation requires identifying systems and assets, profiling threats based on control assessments, determining risk impacts, and prioritizing responses. Ongoing assessments and open sharing of risk information are also emphasized.
Part 5: Best Practices for Implementing NIST Risk Management
Organizations can optimize outcomes and build mature risk programs by adhering to standards and proven methods. Recommended best practices include:
- Secure leadership commitment and resource support
- Integrate risk processes into system lifecycles from design through disposal
- Maintain a detailed and accurate inventory of systems and assets
- Utilize all available data to identify threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts
- Focus resources on prioritized risks with the greatest potential impact
- Foster open communication between technical, leadership, and operations staff
- Provide regular training to maintain workforce expertise
- Document risk management activities thoroughly for auditing
- Continually monitor the threat landscape and control effectiveness
- Automate processes to improve efficiency, consistency, analysis, and reporting
Part 6: Creating a Risk Management Diagram with EdrawMax
Risk management diagrams can help teams understand and communicate complex concepts and workflows. EdrawMax provides an intuitive canvas and extensive shape libraries to quickly create NIST risk framework diagrams.
Users can select from templates for risk matrices, data flow diagrams, and other NIST graphics. Drag-and-drop shapes, auto-align and connectors, and styling tools help tailor professional visuals. Finished diagrams can be exported in various formats to share via documents and presentations. Interactive HTML even allows teams to collaborate on diagrams online.
EdrawMax empowers both technical and non-technical staff to better grasp risk processes through appealing, customizable diagrams.
Here are the steps to create a risk management diagram using EdrawMax:
Step 1:
Open EdrawMax and select the "Risk Management" category under diagrams. Browse the templates to find one relevant to your needs, like a risk matrix template.
Step 2:
Customize the template by dragging appropriate shapes from the shape libraries on the left sidebar. Add or remove shapes to match your specific requirements.
Step 3:
Enter text into shapes to label elements or add descriptions. Resize, align and arrange shapes cleanly on the canvas.
Step 4:
Change shape colors, line styles, and fonts using the formatting panels. Apply custom colors to delineate levels of risk, impacts, etc.
Step 5:
Click "Save As" to save the diagram.
Following these steps allows you to leverage the pre-made templates in EdrawMax to efficiently build custom, publication-ready risk management diagrams that resonate with stakeholders.
Conclusion
Implementing NIST's flexible but rigorous Risk Assessment Framework allows organizations to get ahead of threats before they become crises. Prioritizing resources based on data-driven risk analysis provides strategic advantages. Diagramming software like EdrawMax also bolsters understanding across an enterprise. With vigilance and commitment to maturing risk management, organizations can transform vulnerability into resilience.




