Critical infrastructure systems such as energy, water, transportation, and communications provide the essential services that underpin our society. Securing these vital assets from modern cyber threats requires a holistic approach rooted in established risk management principles. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides pivotal cybersecurity frameworks that help owners and operators of critical infrastructure manage risks and strengthen resilience.
This article will explore the key elements of the NIST 800-37 and NIST 800-161 frameworks and how infrastructure owners can leverage them to enhance security.
Part 1: What is NIST 800-37?
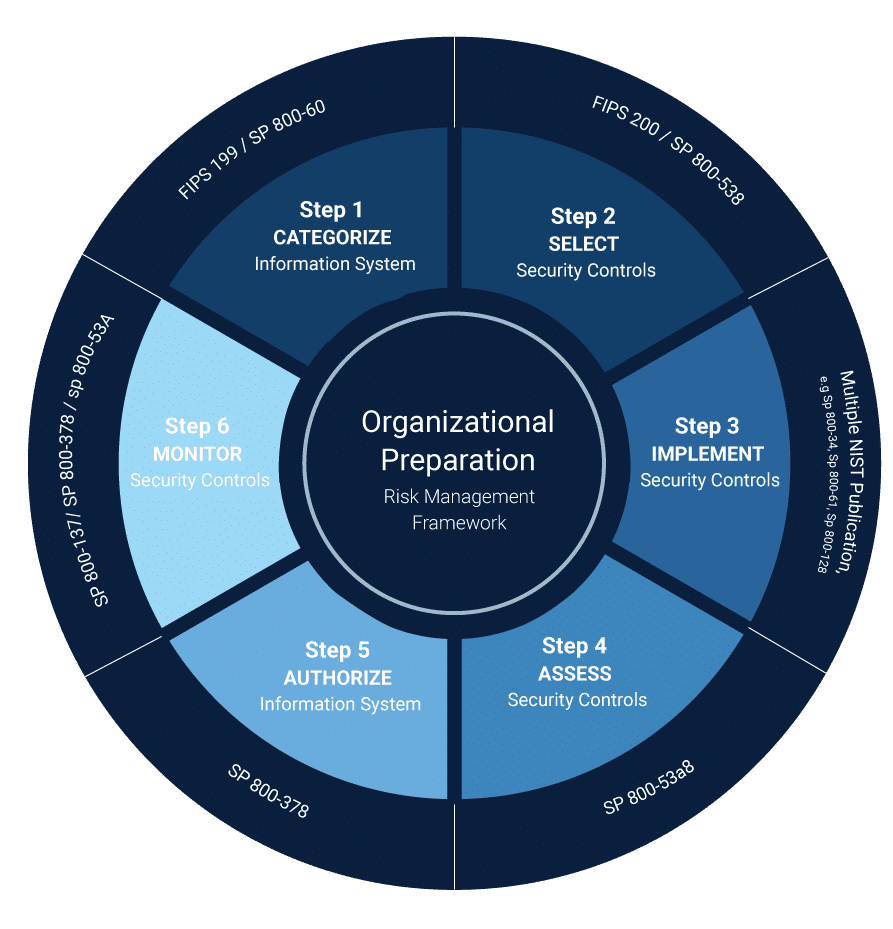
NIST Special Publication 800-37 provides guidance on the Risk Management Framework (RMF) for information systems and organizations. First published in 2010 and updated in 2018, this seminal document outlines a flexible, lifecycle-based process for integrating information security and risk management.
Part 2: Key Components of NIST SP 800-37 Framework
NIST 800-37 provides a flexible baseline organizations can tailor to their unique needs. However, several key principles form the core of a successful RMF implementation:
- Life cycle view: The RMF is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process to manage risks continually.
- Technology-neutral: The RMF can apply to all types of technologies and systems.
- Risk-based: Effective risk assessments, both at the organization and system level, are essential to identifying appropriate controls.
- Controls-based: Minimum security requirements are defined through reusable and customizable control catalogs outlined in NIST standards.
- Tiered assessments: Assessment depth and rigor scale according to system criticality.
- Continuous monitoring: Controls are periodically reassessed to account for changes.
- Streamlined process: The RMF consolidates steps from other NIST standards into a unified framework.
These foundational principles make NIST 800-37 adaptable across diverse critical infrastructure sectors and technologies while promoting security and resilience.
Part 3: Best Practices for Implementing NIST 800-37 Framework
Successfully implementing the NIST RMF requires commitment from both leadership and staff. Here are the best practices for infrastructure operators:
- Integrate security early: Consider security implications through all phases of the system life cycle, from design to disposal.
- Know your assets: Maintain detailed inventories of systems, components, and data to define security categories and controls.
- Prioritize controls: Focus resources on controls that offer the greatest security value for critical assets.
- Promote awareness: Provide RMF training and access control policies to personnel.
- Document rigorously: Keep records of all activities to facilitate quality control and oversight.
- Automate processes: Leverage automation tools to streamline workflow, improve consistency, and save time over manual methods.
- Report concisely: Produce concise reports on security status for leadership and oversight bodies.
- Foster communication: Encourage open communication between security and system staff to understand operational needs.
Following these best practices helps bake security into normal system operations while optimizing scarce resources. Staff across infrastructure organizations must work together to implement RMF principles focused on their highest priority systems and data.
Part 4: Brief Overview of NIST Cybersecurity Frameworks
While NIST 800-37 provides a broad risk management framework, NIST offers additional guidelines to help secure critical infrastructure:
NIST 800-39
Published in 2011, this manual outlines the risk management process used across NIST publications. It guides risk framing, assessments, responses, and monitoring. NIST 800-39 complements 800-37 by detailing how to evaluate and monitor information security risks systematically.
NIST 800-161
This recent supply chain risk management standard guides on identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities within product and service supply chains. Supply chain security is a major exposure for infrastructure operators, making NIST 800-161 an invaluable companion to the RMF.
Part 5: Creating a Risk Management Diagram Using EdrawMax
Visual diagrams can help infrastructure security teams understand and communicate risk management processes outlined in NIST standards. EdrawMax is user-friendly diagramming software with extensive template libraries ideal for this task.
With EdrawMax, users can select from premade NIST 800-37 diagram templates and customize them by adding shapes and aligning elements. Smart drawing aids like alignment guides, auto-spacing, and snap-to-object help create professional diagrams quickly.
With powerful customization options boiled down to simple drag-and-drop, EdrawMax makes communicating intricate NIST guidelines a breeze.
Here are the steps for creating a risk management diagram using EdrawMax:
Step 1:
Open EdrawMax and select the "Risk Management" category under diagrams. This will open a list of risk management diagram templates. Browse through the templates and select one that best matches the type of risk management diagram you want to create.
Step 2:
Customize the template by dragging and dropping shapes from the shape libraries on the left. Add or remove shapes to tailor it to your specific needs.
Step 3:
Enter text into shapes to label elements or show descriptions. Resize, align and arrange shapes and connectors on the canvas.
Step 4:
Change shape colors, line styles, and fonts using the formatting panels on the right. Apply custom coloring to emphasize levels of risk.
Step 5:
When finished customizing, click "Save" or "Save As" to store the diagram for future editing.
By leveraging the risk management templates in EdrawMax, you can efficiently create customized, professional-quality diagrams.
Conclusion
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, critical infrastructure sectors can leverage proven NIST frameworks to manage risks and harden defenses. NIST 800-37 provides a flexible blueprint to continually assess threats, implement controls, and make systems more resilient.




