- All templates
- Network diagrams
- Network diagram stp
About this network diagram for STP
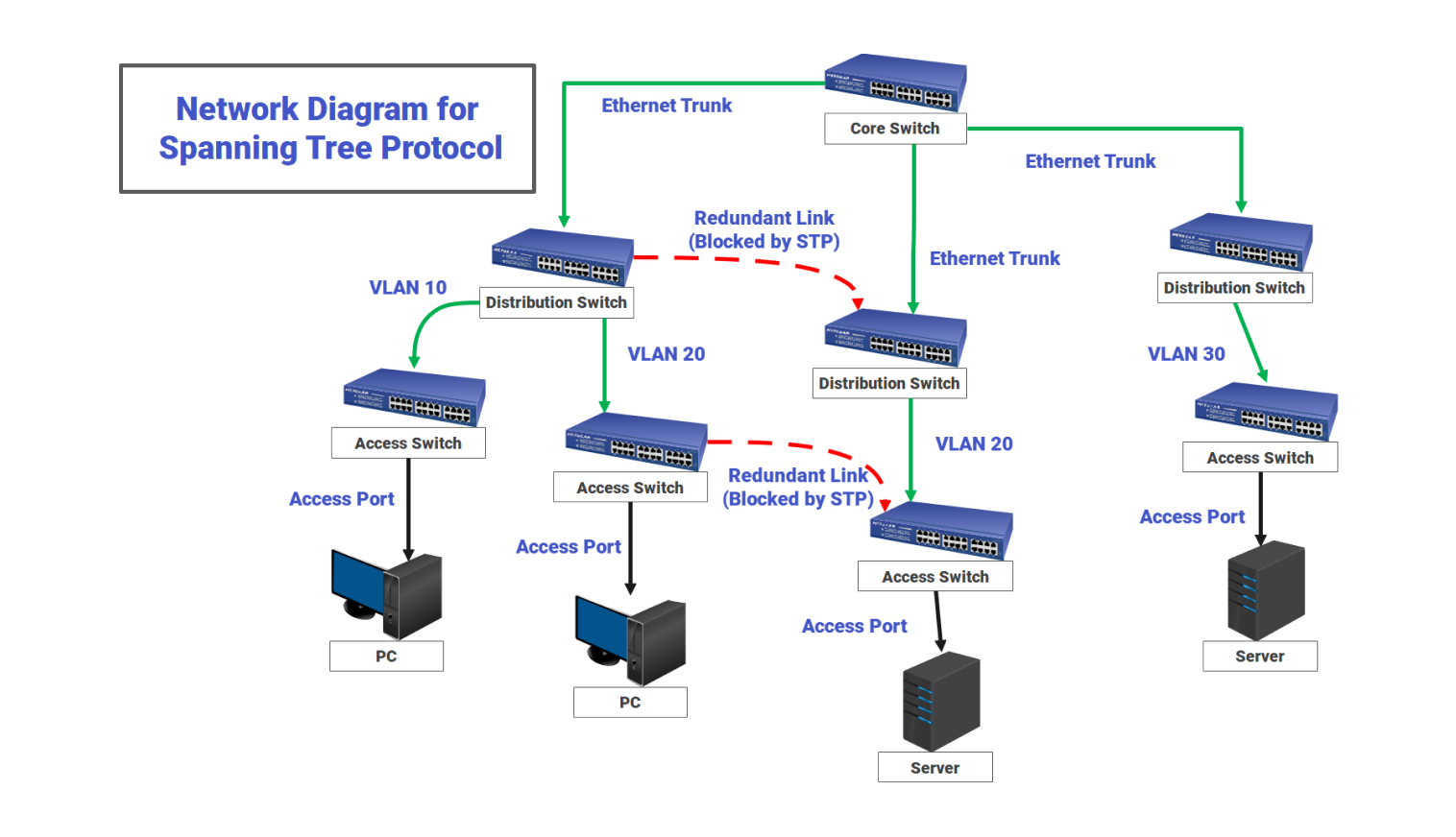
In this network, several switches link together. They form main and backup paths for data. Ethernet networks can't detect loops. So, the spanning tree protocol runs on all switches. This prevents endless data circulation. The process begins when each switch sends bridge protocol data units. This lets them announce their presence and compare roles.
All switches review these messages and agree on one root switch. This root switch serves as the main point for deciding which connections stay active. Each switch calculates the shortest path to the root. It checks link speeds and sees if paths are available. Ports with the lowest cost become forwarding ports. Other ports that offer alternate paths enter a blocking state.
Traffic from access ports goes to the distribution layer. Then, it moves to the core through the forwarding port. If a switch detects a failure in one of its main links, it quickly checks the other network paths. STP automatically turns a blocked redundant link into a forwarding state. This keeps the connection active. This switch-over happens without user input, so the network runs smoothly.
VLAN assignments keep devices apart. Each VLAN uses the spanning tree structure for its segment. Access switches send traffic from devices to distribution switches. Blocked links stay ready but unused until a failure happens.
The system sends protocol messages regularly. This checks if all connections are stable. If messages stop arriving, STP recalculates the network topology. This cycle ensures there is always one active path between switches. It prevents loops while keeping backup routes ready.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free