- All templates
- Network diagrams
- Network diagram voip
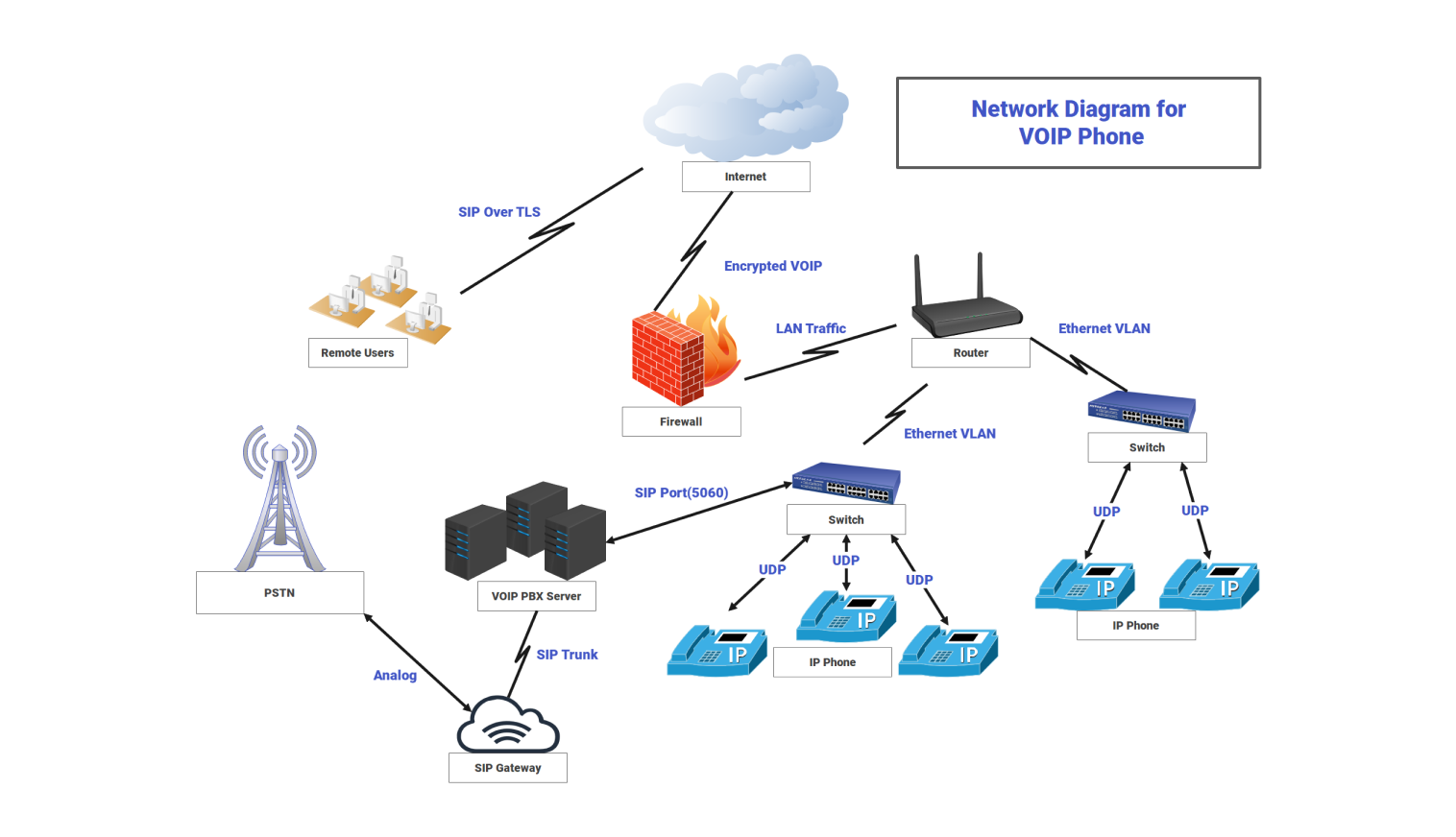
About this network diagram for VOIP
The VOIP phone network sends voice calls over IP instead of traditional analog lines. It starts when a user calls from an IP phone on the local network. Each IP phone sends signaling traffic via the SIP protocol, usually using UDP, to the nearest switch.
The switch then forwards this traffic through the Ethernet VLAN set up for voice. From the switch, the SIP signaling reaches the VOIP PBX server. The PBX handles call setup, routing, and registration. It checks user credentials, finds the call destination, and sets up the voice path.
If the call is internal, the PBX connects both phones to exchange media streams within the same VLAN. This setup allows the conversation to flow with minimal delay. For calls outside the internal network, the PBX works with the SIP gateway or SIP trunk. The SIP gateway changes digital SIP traffic into analog signals for PSTN routes. SIP trunks connect digitally to outside service providers. The firewalls manage all outbound and inbound traffic.
Remote users connect using SIP over TLS or encrypted VOIP channels. Their requests travel through the internet and reach the firewall. The firewall then forwards them securely to the PBX server.
The router forwards packets between the VLANs and the Internet. It prioritizes voice traffic when QOS rules are set. Switches keep voice devices separate from regular LAN traffic. This helps maintain audio quality. The system manages registration, session handling, voice encoding, and audio packet transport. It ensures smooth voice flow between endpoints, whether local, remote, or external.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free