- All templates
- Network diagrams
- Network diagram web application
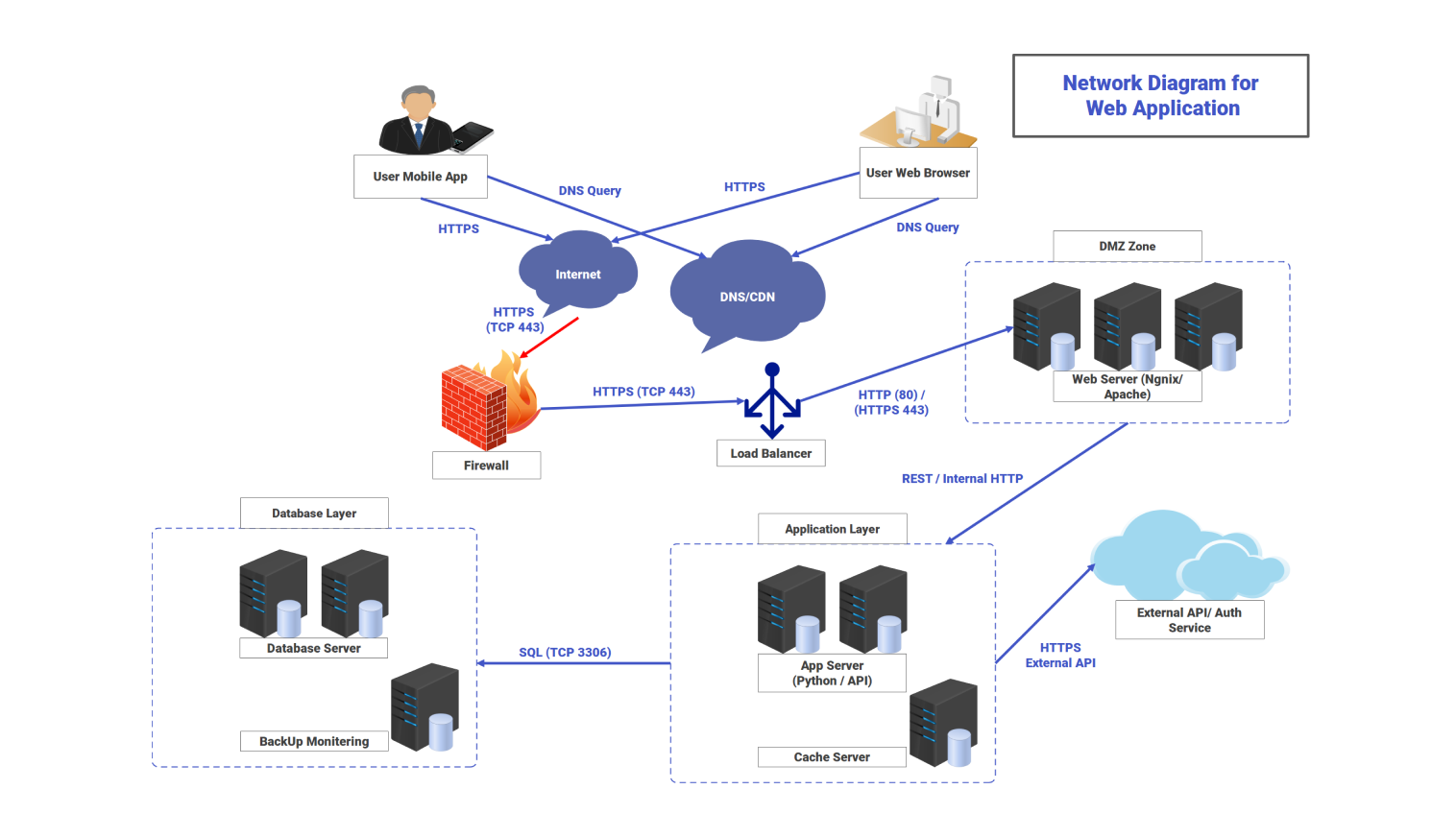
About this network diagram for a web application
The web application network manages user requests from mobile apps and browsers. It routes these requests through several layers for processing. First, a user starts with a DNS query to turn the application’s domain name into an IP address.
This request goes to the internet, reaching a DNS or CDN service, which returns the IP address. The client uses this resolved address to send an HTTPS request. It goes over TCP port 443 to the system’s public endpoint.
The request goes through the firewall. It checks the connection and forwards only valid HTTPS traffic to the load balancer. The load balancer spreads incoming requests evenly to web servers in the DMZ. These servers manage static content. They manage session headers. They also send requests specific to the application layer using REST or HTTP.
In the application layer, app servers hold the business logic. They manage requests. They handle authentication. They apply rules. They connect to the database when needed. If a request needs caching, the app server connects to the cache server. It either stores or retrieves frequently accessed data. The app server sends secure HTTPS requests to the external API. This happens for actions that need verification.
The app server connects to the database layer through an internal network when it needs to store or retrieve data. The database server handles SQL queries over TCP port 3306. The load balancer routes traffic while the firewall filters outside inputs. Each layer talks through secure internal channels. When the operation is done, the app server sends the response to the web server. The web server then passes it back through the load balancer, the firewall, and the internet to the user.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free