- All templates
- Network diagrams
- Network diagram websocket
About this network diagram for WebSocket
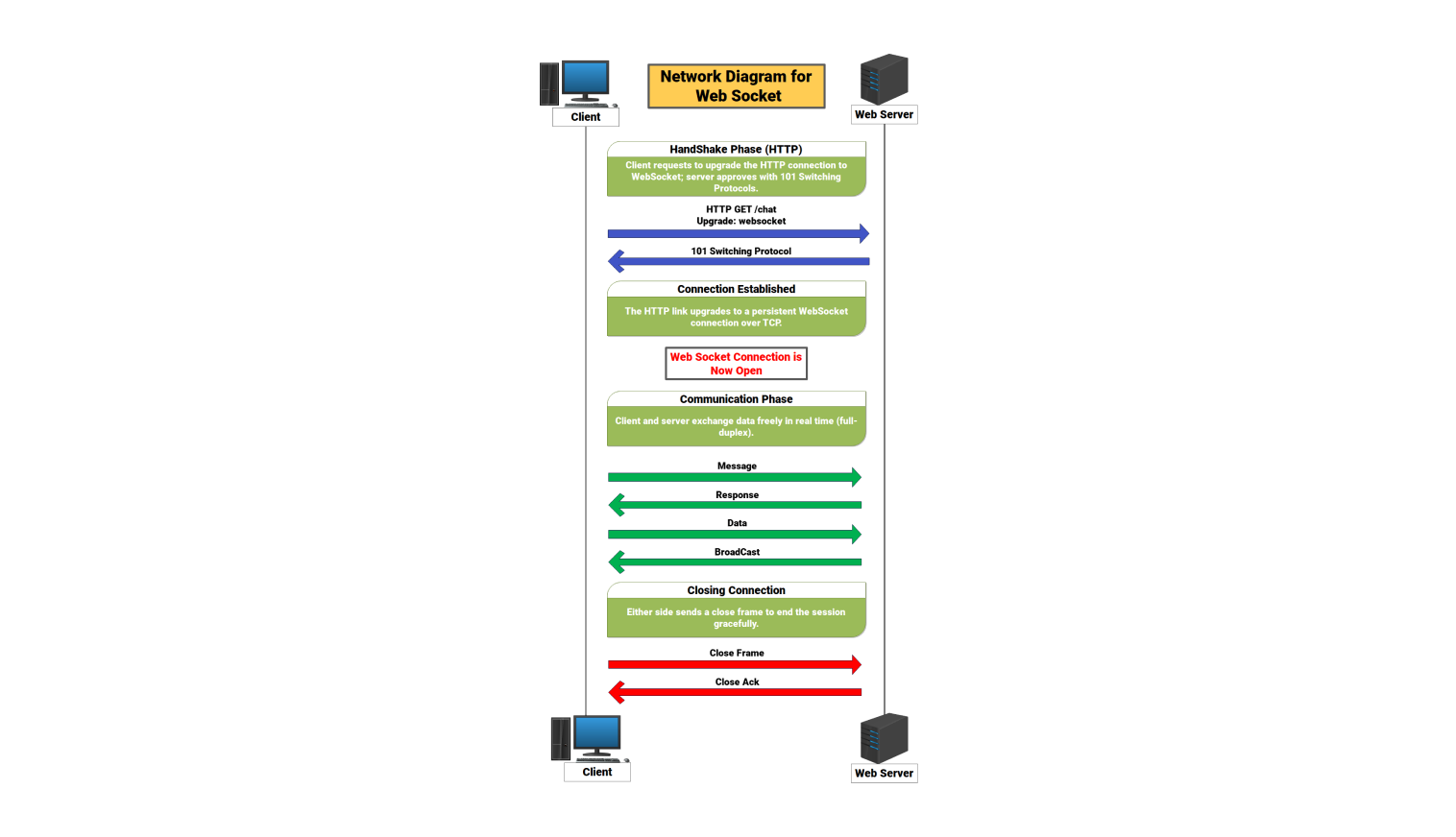
The WebSocket network allows real-time chats between a client and a web server. It starts when the client makes a regular HTTP connection. The client requests to upgrade to WebSocket. This request has headers that ask to switch from standard HTTP to a WebSocket connection that remains open. The server checks the upgrade request. If it's valid, the server replies with a 101 switching protocols message.
After the handshake, the connection changes from HTTP to a WebSocket channel using TCP. This new connection stays open, so there’s no need for repeated HTTP requests. Once live, the server and client can exchange data in full-duplex mode. This means both sides can send and receive information at the same time.
The communication phase allows for a steady flow. It supports real-time messaging, live updates, notifications, and data streams. During the active connection, both sides send frames with structured data. The connection remains open after each message. It stays active until one side decides to end it.
This steady state reduces overhead and boosts efficiency for apps needing constant data exchange. Messages flow without interruption. The server can push updates to the client anytime. When communication is done, either the client or server starts the closing sequence. One side sends a close frame to signal the session's end.
The other side replies with its own close frame, and the connection closes smoothly. The WebSocket network handles the full cycle: from the initial HTTP upgrade to ongoing messaging, and finally to a controlled termination. It offers a stable, low-latency channel for apps needing quick data transfer.
Related templates
Get started with EdrawMax today
Create 210 types of diagrams online for free.
Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free Draw a diagram free