Energy is the foundation of life—but where does it come from, and how do cells actually use it?
The answer lies in two essential biological processes: photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Although they work in opposite directions, they are deeply interconnected and together sustain life on Earth.
Understanding cellular respiration vs photosynthesis can be confusing at first. Both involve energy, glucose, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. This is why a clear metabolism diagram is one of the best tools for learning how these processes relate to each other.
In this guide, we’ll:
- Compare photosynthesis and cellular respiration step by step
- Explain how energy flows through living systems
- Show how to create a clean comparison diagram using EdrawMax
In this article
What Are the Main Differences?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration represent two sides of the same biological coin. They are opposite in function but complementary in nature.
Key Functional Difference
| Process | Main Function |
| Photosynthesis | Stores energy in glucose |
| Cellular Respiration | Releases energy as ATP |
Photosynthesis captures solar energy and converts it into chemical energy.
Cellular respiration breaks down that chemical energy to power cellular activities.
Energy Flow Comparison
- Photosynthesis
- Type: Anabolic and endergonic
- Energy source: Sunlight
- Purpose: Build glucose from CO₂ and H₂O
Light energy is first converted into ATP and NADPH, which then drive glucose synthesis in the Calvin cycle.
- Cellular Respiration
- Type: Catabolic and exergonic
- Energy output: ATP
- Purpose: Release stored energy
Glucose is broken down gradually, allowing energy to be efficiently captured in ATP molecules.
Reactants and Products
One of the most fascinating aspects of cellular respiration vs photosynthesis is that they are chemical reverses of each other.
- Photosynthesis
- Reactants: Carbon dioxide + Water + Light
- Products: Glucose + Oxygen
- Cellular Respiration
- Reactants: Glucose + Oxygen
- Products: Carbon dioxide + Water + ATP
This direct exchange keeps matter cycling and maintains atmospheric balance.
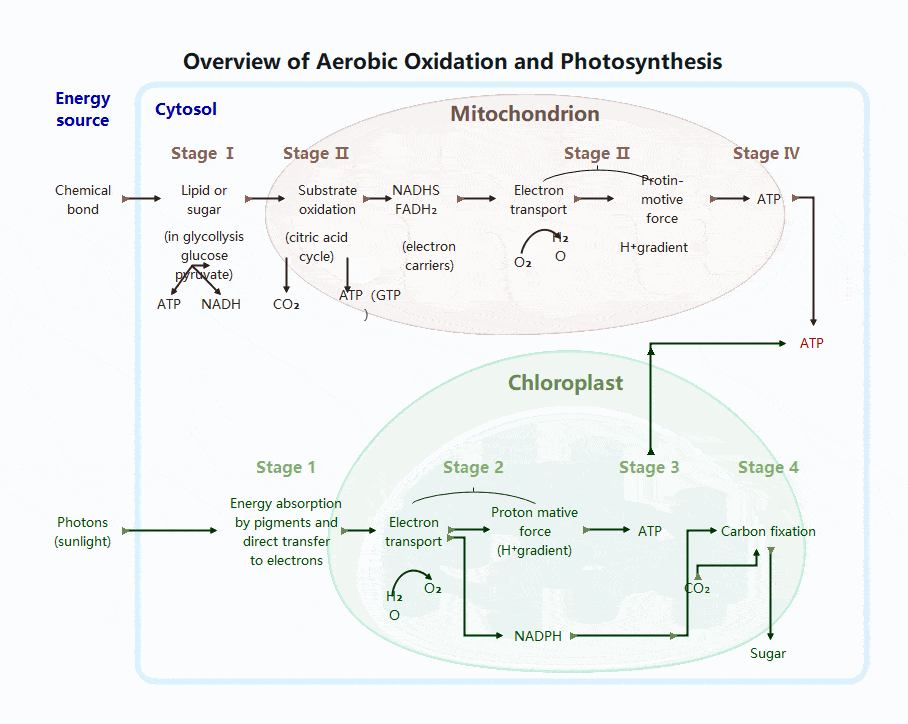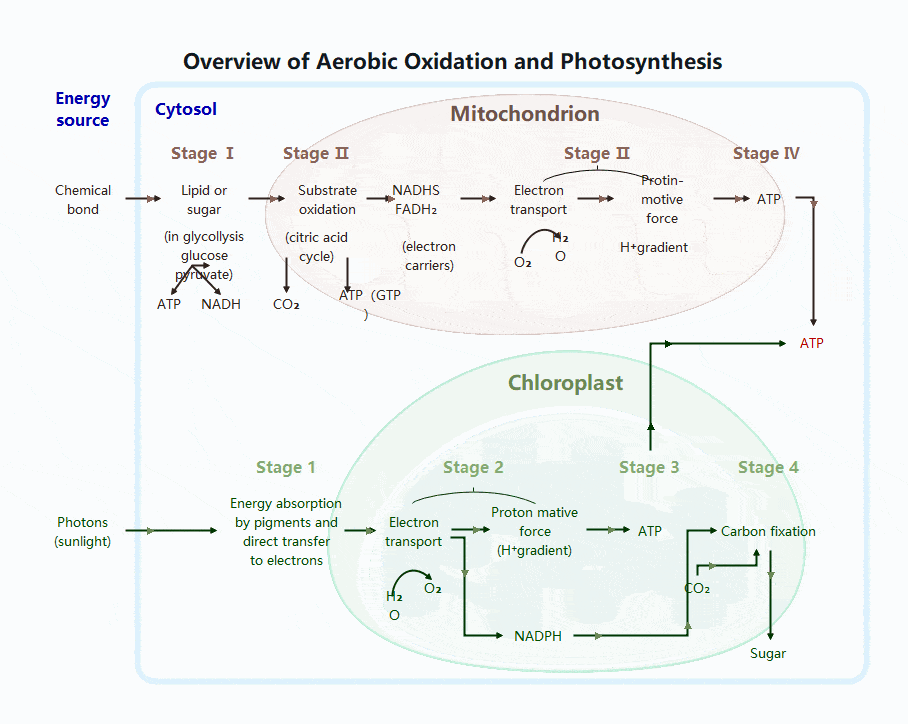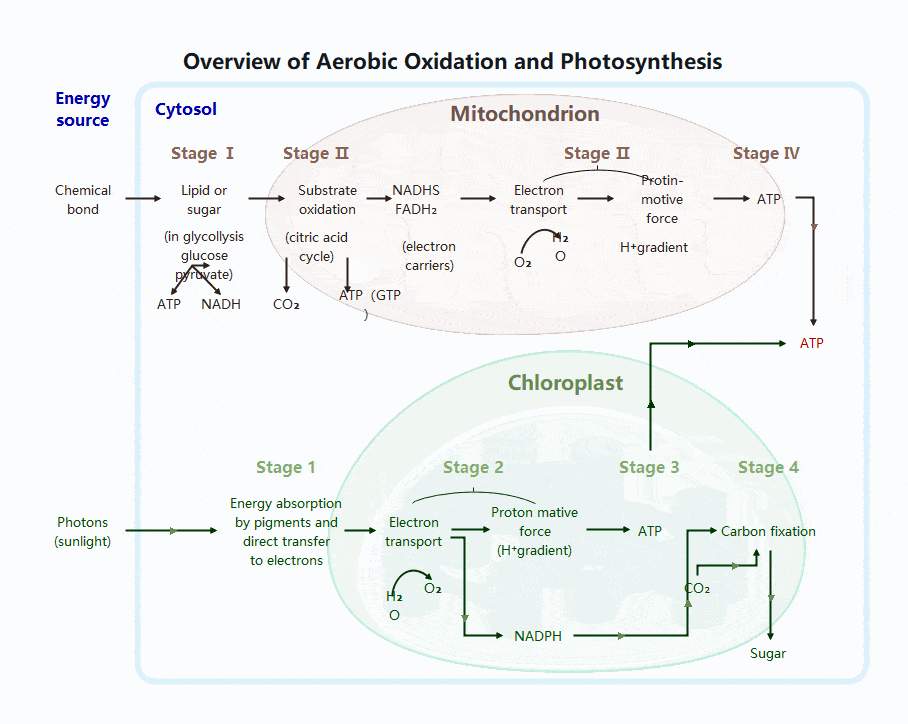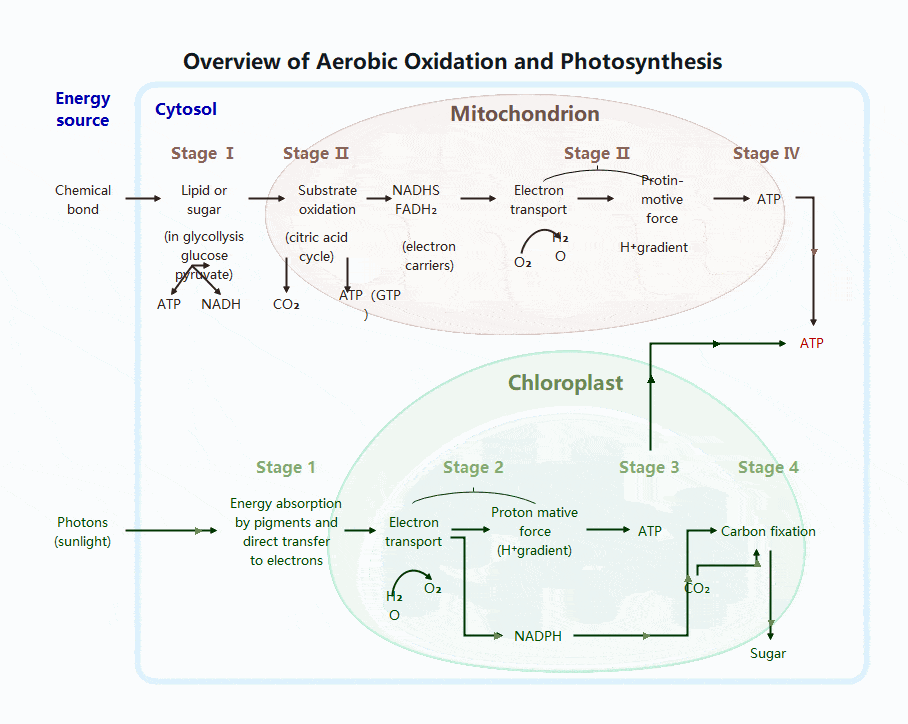
Photosynthesis Process
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts and is carried out by plants, algae, and some bacteria. It is essential because it produces both food and oxygen.
Two Main Stages of Photosynthesis
- 1. Light Reactions
- Location: Thylakoid membranes
- Requires sunlight
- Key events:
- Chlorophyll absorbs light
- Water is split (photolysis)
- Oxygen is released
- ATP and NADPH are produced
- 2. Calvin Cycle
- Location: Chloroplast stroma
- Does not require light directly
- Uses ATP and NADPH to:
- Fix carbon dioxide
- Produce glucose
- Regenerate cycle molecules
Together, these stages store energy in chemical bonds.
How to Create a Cellular Respiration vs Photosynthesis Diagram with EdrawMax
Creating a biology diagram becomes simple and effective with EdrawMax, a user-friendly diagramming tool. By following a structured approach, you can design clear, accurate, and visually appealing diagrams suitable for study, teaching, or presentations.
Step1 Open EdrawMax and Get Started
- Launch EdrawMax on your device and sign in or continue as a guest to access the workspace.
- From the home screen, select “New” and choose a blank canvas or a biology-related template.
- Adjust the page size and orientation to ensure enough space for all biological components.
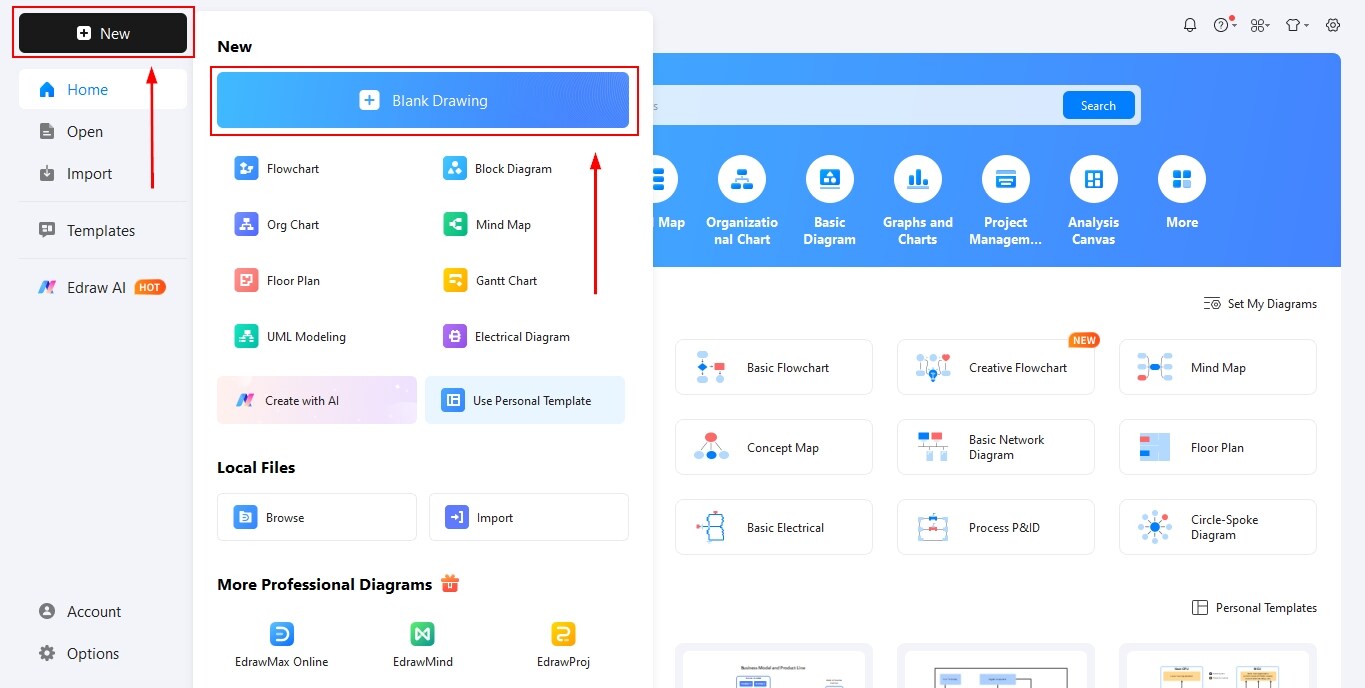
Step2 Add Required Shapes
- Open the symbol library and search for biology-specific shapes such as cells, organelles, tissues, or molecular structures.
- Drag and drop the required shapes onto the canvas based on the type of diagram you are creating.
- Resize and duplicate shapes as needed to maintain consistency and proper proportions.
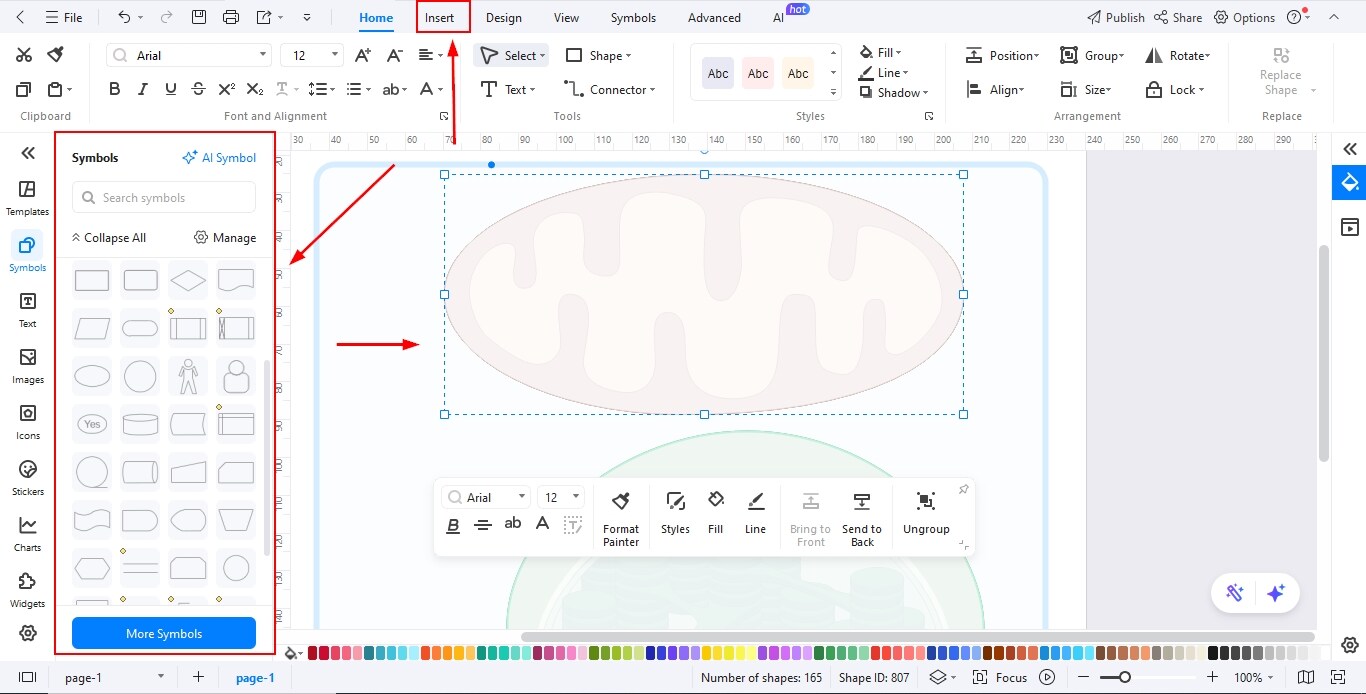
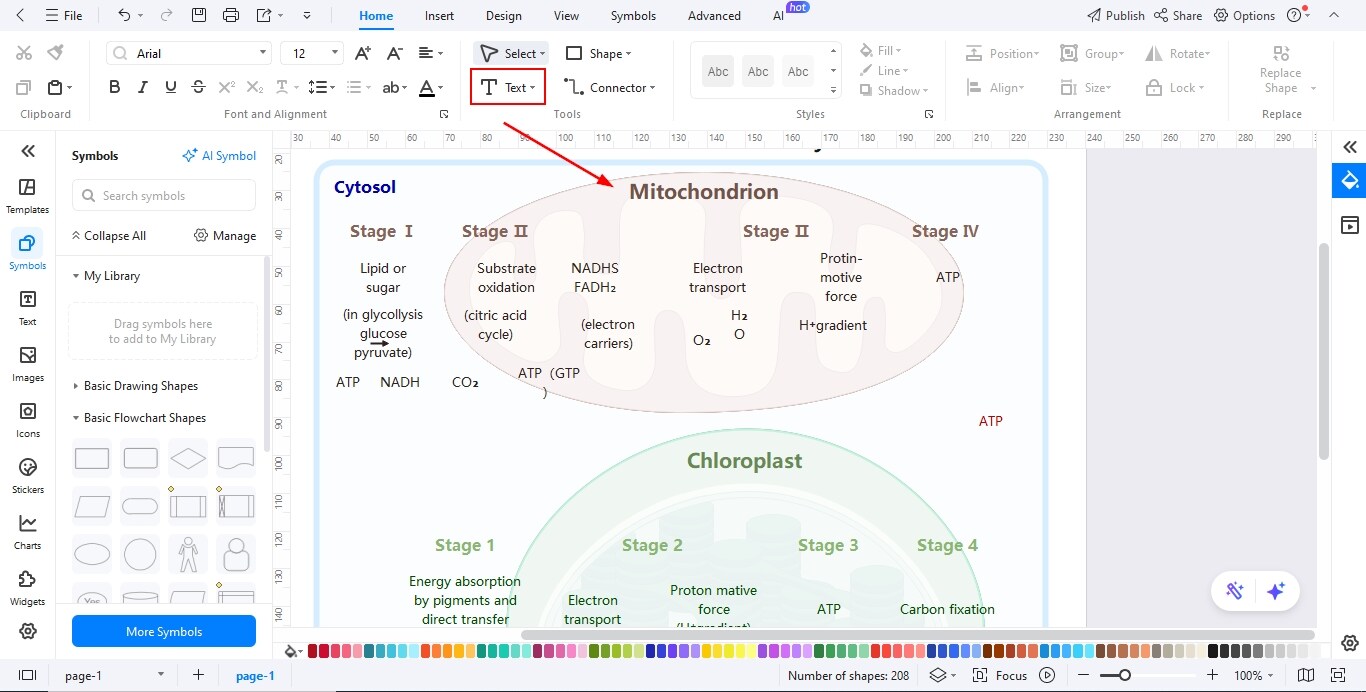
Step3 Add Text in the Diagram
- Use the text tool to label each biological part clearly and accurately.
- Choose readable fonts and maintain uniform text size to improve clarity.
- Add brief descriptions or notes to explain the function or role of each component.
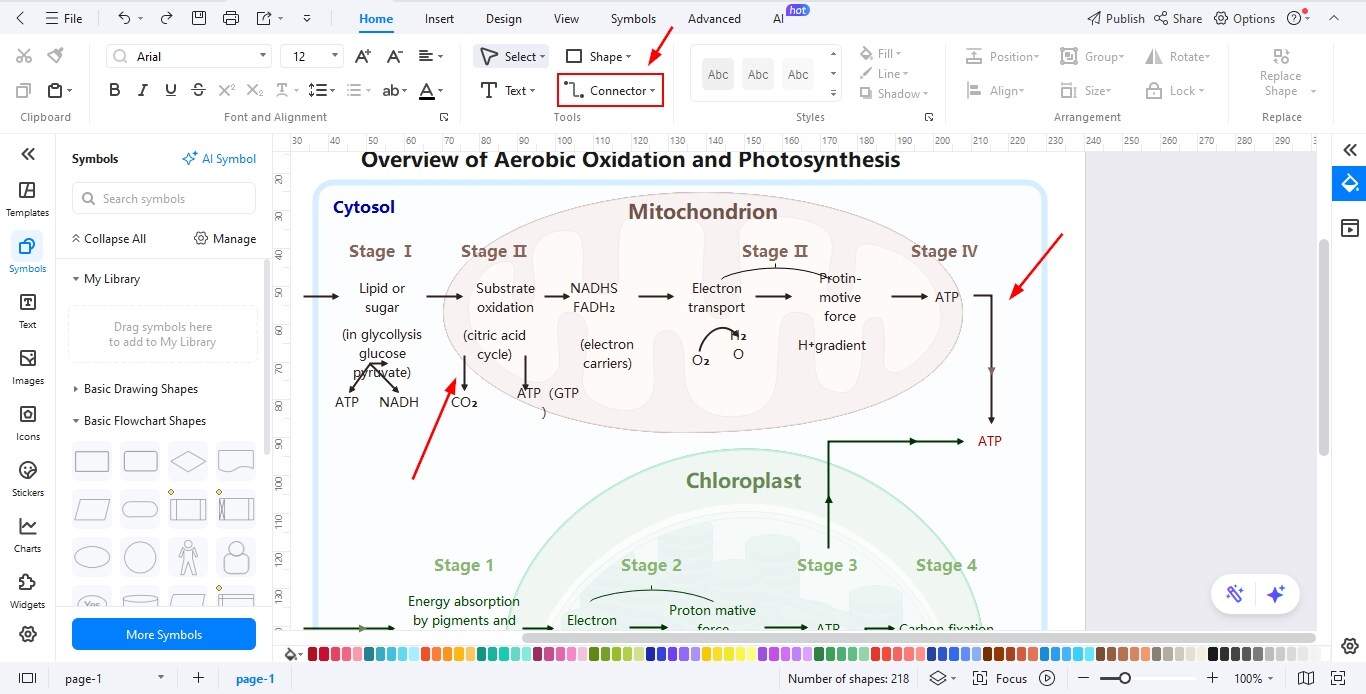
Step4 Use the Connector Tool to Add Relationships
- Select the connector tool to link related parts of the diagram logically.
- Use arrows or lines to represent processes, interactions, or directional flow.
- Adjust connector styles and positioning to keep the diagram clean and easy to understand.
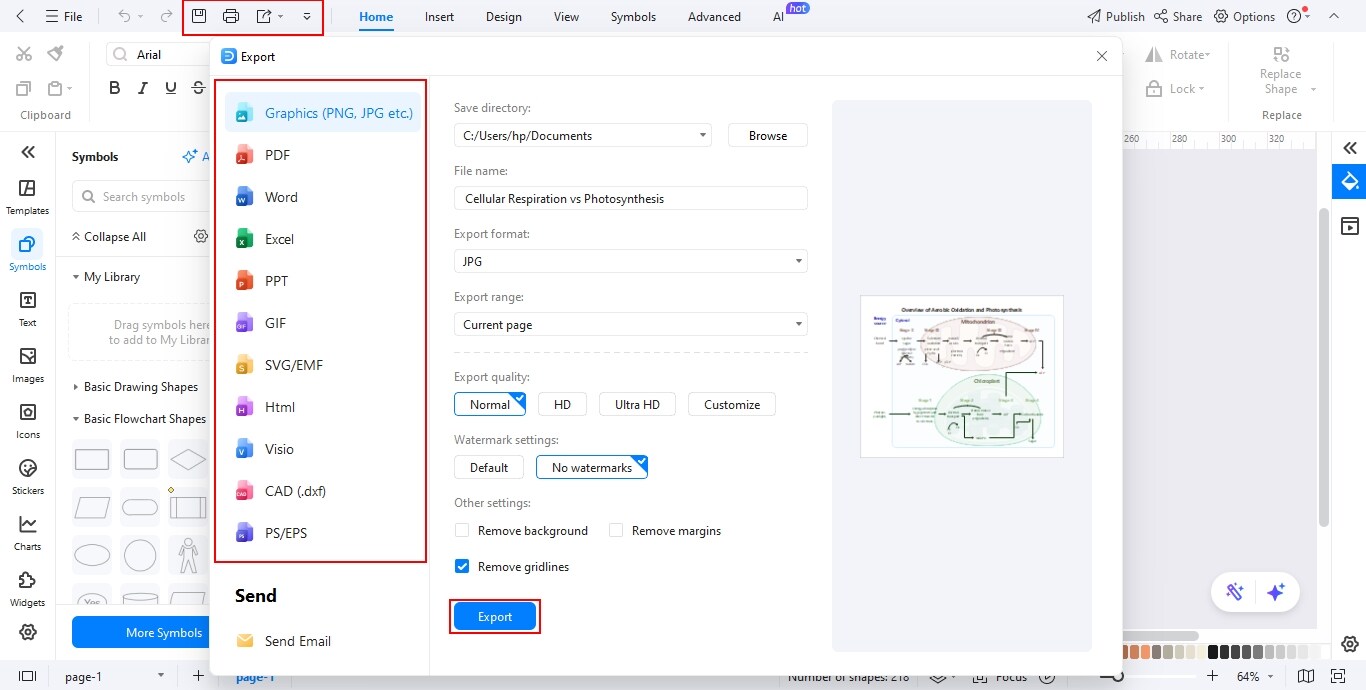
Step5 Export the Diagram
- Review the diagram carefully to ensure correct labeling and proper alignment.
- Click on the Export option and select your preferred file format such as PNG, PDF, or JPG.
- Save or share the final diagram for assignments, presentations, or educational use.
In fact, if you want, you can even export a GIF picture like this one:
Conclusion
Cellular respiration vs. photosynthesis: These are two very important processes occurring within a cell. A clean and detailed metabolism diagram comparing these two processes can help in understanding their relationship, and you can do this with the help of EdrawMax.