You interact with AI almost every day, often without realizing it. Maybe your phone gives you tomorrow’s forecast. Maybe Netflix suggests a show that fits your mood. Or perhaps you chat with a bot and wonder how it understands you so well. AI feels modern, but its roots stretch back decades.
Back then, the machines were massive and slow, but the ideas behind them were daring and uncertain. Yet each success opened new doors. So let’s explore how those steps led to the AI we know today.
In this article
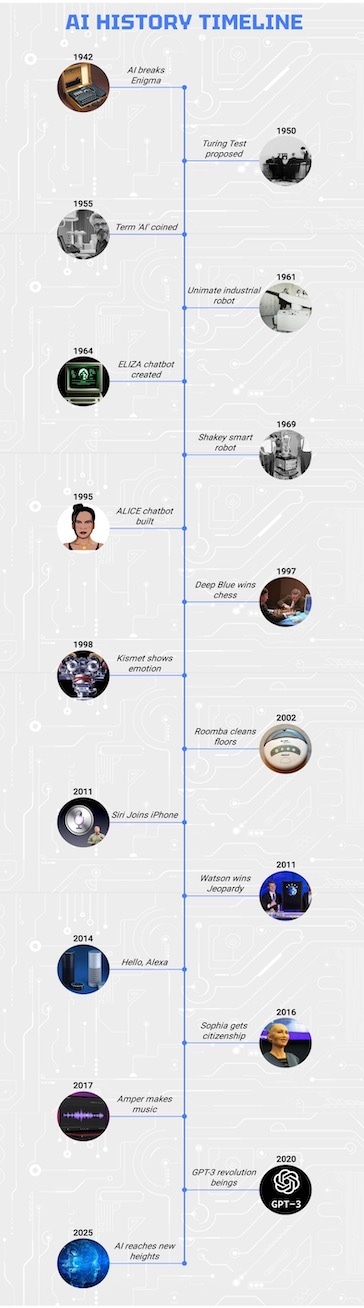
Artificial Intelligence History Timeline
AI has an exciting story. It all started in the 1950s when people like Alan Turing asked a simple question: “Can machines think?” The first programs were very basic, but they got people curious. That curiosity grew into research that’s still going on today.
Since then, AI has come a long way. It’s no longer just simple programs. Now it can drive cars, chat with us, and even make art.
Let’s have a closer look at the most important moments in AI’s history.
1942: Breaking Enigma with AI
During World War II, the Allies had a huge problem. German military codes. They seemed impossible to crack. That’s when Alan Turing showed up with an idea. He built a machine called the Bombe.
Now, it didn’t look anything like a laptop. It was massive and clunky. But wow, it worked. The Bombe could run through thousands of possible codes super fast and helped break the German Enigma machine. This changed the course of the war and proved one thing, machines could outsmart people at certain jobs if built the right way..
1950: Alan Turing and the Turing Test
Turing didn’t stop there. A few years later, he asked one of the coolest questions ever: “Can machines think?”
To test this, he came up with what’s now called the Turing Test. It worked like this: you’d chat with someone through a screen, not knowing if it was a person or a machine. If you couldn’t tell the difference, the machine had passed. Simple, but kind of genius. That idea became the first real way to measure if a machine could act “smart.”
1955-1956: John McCarthy and the Birth of AI
In 1955, John McCarthy came up with the name Artificial Intelligence. A year later, at the Dartmouth Conference, AI was officially born as a field of study.
McCarthy believed machines could one day learn and solve problems like humans. He wasn’t just dreaming, though, he actually built tools to make it happen. In 1958, he created LISP, a programming language still used in AI today. No wonder people call him the “Father of AI.”
1961: Unimate (The First Industrial Robot)
The first real robot worker showed up in 1961. Its name was Unimate.
Unimate worked at a General Motors factory, moving hot metal parts that were dangerous for people to touch. This thing was huge, over 4,000 pounds, and looked like a giant robot arm. Not exactly sci-fi cool, but it did the job. After Unimate, factories everywhere started bringing in robots to handle the risky or boring tasks.
1964: ELIZA (The First Chatbot)
At MIT, Joseph Weizenbaum made a program called ELIZA. It could chat with people by rephrasing what they typed. For example, if someone wrote, “I feel anxious,” ELIZA would reply, “Why do you feel anxious?” It was simple, but it really worked. People were surprised at how human it felt to talk to a machine.
Many users felt the machine understood them, even though it followed scripts. ELIZA proved people could form connections with computers. It opened the door to conversational AI, inspiring chatbots, virtual assistants, and today’s human-like interactions with machines.
1969: Shakey (The First Smart Robot)
In the late 1960s, Stanford engineers built Shakey, the first robot that could perceive and plan. Shakey wasn’t just following commands. It mapped surroundings, analyzed obstacles, and made choices about where to go. For the first time, a machine combined sensors, logic, and movement.
This was a huge leap beyond automation. Shakey showed robots could reason about their actions, not just execute instructions. It laid the foundation for autonomous machines, self-driving cars, and intelligent robotics in the real world.
1995: ALICE (A Chatbot for the 90s)
By the mid-1990s, chatbots had advanced far beyond ELIZA. Richard Wallace created ALICE, a chatbot that used natural language processing to hold surprisingly human-like conversations. It could answer many questions and even show personality through playful responses.
ALICE won awards for its intelligence and charm. It influenced later digital assistants and even inspired movies like Her. This milestone showed AI could be both interactive and engaging, bridging the gap between humans and machines in daily conversation.
1997: Man vs Machine (DeepBlue beats chess legend)
In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue faced Garry Kasparov, the world chess champion. Millions watched as the computer battled the greatest human strategist in an ancient game of skill. To everyone’s shock, Deep Blue won, making history as the first machine to beat a reigning champion.
This victory wasn’t just about chess. It proved AI could handle complex strategy and logic at a level beyond humans. Deep Blue showed machines could outthink people in specific, structured domains.
1998: Kismet (The Robot with Feelings)
At MIT, researchers built Kismet, a robot designed to show emotions. With moving eyes, lips, and eyebrows, Kismet could mimic expressions like happiness, anger, or surprise. It reacted to human voices and facial cues, making interactions feel surprisingly natural.
Kismet wasn’t just a robot; it was a breakthrough in emotional AI. It proved machines could connect with people socially, not just logically. This milestone influenced future technologies in caregiving, customer service, and human-computer interaction.
2002: Roomba (The Vacuum Cleaning Robot)
In 2002, the Roomba rolled into homes as the first popular robotic vacuum. It used sensors to detect walls, avoid obstacles, and clean floors on its own. For many people, it was the first time AI felt useful in daily life.
Roomba wasn’t perfect, but it was practical and fun. It showed that AI could make household tasks easier. This milestone proved intelligent machines could live with us, not just in labs or factories.
2011: Siri (The AI Personal Assistant)
In 2011, Apple introduced Siri on the iPhone. For the first time, millions of people could talk to their devices. Siri could set alarms, answer questions, or even crack jokes. Suddenly, AI became a personal assistant in your pocket.
Siri wasn’t flawless, but it changed how people saw AI. It made technology feel conversational and approachable. This milestone showed that voice-powered AI could enhance everyday communication and become a trusted digital helper.
2011: IBM Watson (The Q&A Genius)
Also in 2011, IBM’s Watson took on champions Brad Rutter and Ken Jennings on Jeopardy!. Watson was fast and understood natural language, scanned huge databases, and delivered correct answers under pressure. Against all odds, the AI won.
Watson’s victory was more than entertainment. It showed AI could process vast information and apply it practically. Later, Watson moved into healthcare and business, proving AI could solve real-world problems far beyond the quiz show stage.
2014: Alexa (Your AI Voice Partner)
Next in the list is Alexa, Amazon’s virtual assistant. You just say “Alexa,” and she lights up, even in a noisy room. She can play music, give you news or weather updates, and control smart devices. Alexa even helps you order from Amazon.
Alexa is everywhere now. You’ll find her on smartwatches, speakers, TVs, and even in cars. Yep, she’s hard to miss!
2016: Sophia (The Humanoid Robot)
Then there’s Sophia, a humanoid robot from Hanson Robotics. She can mimic facial expressions, have conversations, and even share her thoughts on certain topics. Sophia also keeps learning over time.
In 2016, she made headlines for becoming the first robot to get citizenship, granted by Saudi Arabia. She was also named the UNDP’s first Innovation Champion. Her face was inspired by Audrey Hepburn, Queen Nefertiti, and the creator’s wife.
2017: Amper (The AI Music Composer)
Amper was the first AI to write, produce, and release music. Musicians use it to create original tracks using AI and music theory.
Amper teamed up with singer Taryn Southern for an album called I AM AI. Their song “Break Free” was the first human-AI music collaboration. Amper is changing the way music gets made.
2020: GPT-3 (The Game-Changer for Conversations)
GPT-3.. The turning point in AI history. In 2020 OpenAI introduced GPT-3. This wasn’t your usual chatbot. GPT-3 could write essays, answer questions, translate languages, and even code, all from just a few words. For the first time, it really felt like AI understood us.
GPT-3 stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3. It was trained on massive amounts of text from the internet. Unlike older chatbots, it doesn’t just repeat phrases. It responds with context. Suddenly, talking to AI felt natural. From emails to stories, GPT-3 opened a whole new world of AI-powered creativity. And now you can experience it too.
2015: AI Today
By 2025, AI is no longer experimental. It’s everywhere. It writes, designs, codes, diagnoses, and powers self-driving cars. From chatbots to medical scans, AI has woven itself into daily routines across industries and homes.
Tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney let people bring ideas to life instantly. AI is no longer just a tool, it’s a partner. The journey from Turing’s Bombe to today’s assistants reflects human ambition and the endless potential of intelligence.
How to Create an AI History Timeline in EdrawMax?
Artificial intelligence has evolved through decades of research, discoveries, and innovations. Keeping track of these milestones can be complex, and visualizing connections is not always easy. But EdrawMax simplifies the process. Its templates and tools let you create a structured, professional AI history timeline in minutes.
Follow these steps to make your AI history timeline:
Step1Start with a Blank Canvas
Open EdrawMax and sign using Wondershare ID or a social account.
Or, create an account if you're a new user.
Click New on the left panel and choose Blank Drawing to start fresh.
Step2Add a Background Image
To add a background image, go to the Insert tab in the top menu bar and select Picture.
Upload a relevant AI-themed background from Local Pictures.
To adjust the brightness, contrast, or transparency, select the image and use the Adjust options in the customization panel.
Step3Add a Timeline Heading
You can add a title using either a text box or an image. Let’s use text here.
Click Text and then Click to Add Title to add your heading.
You can also add icons or symbols related to AI to enhance the title.
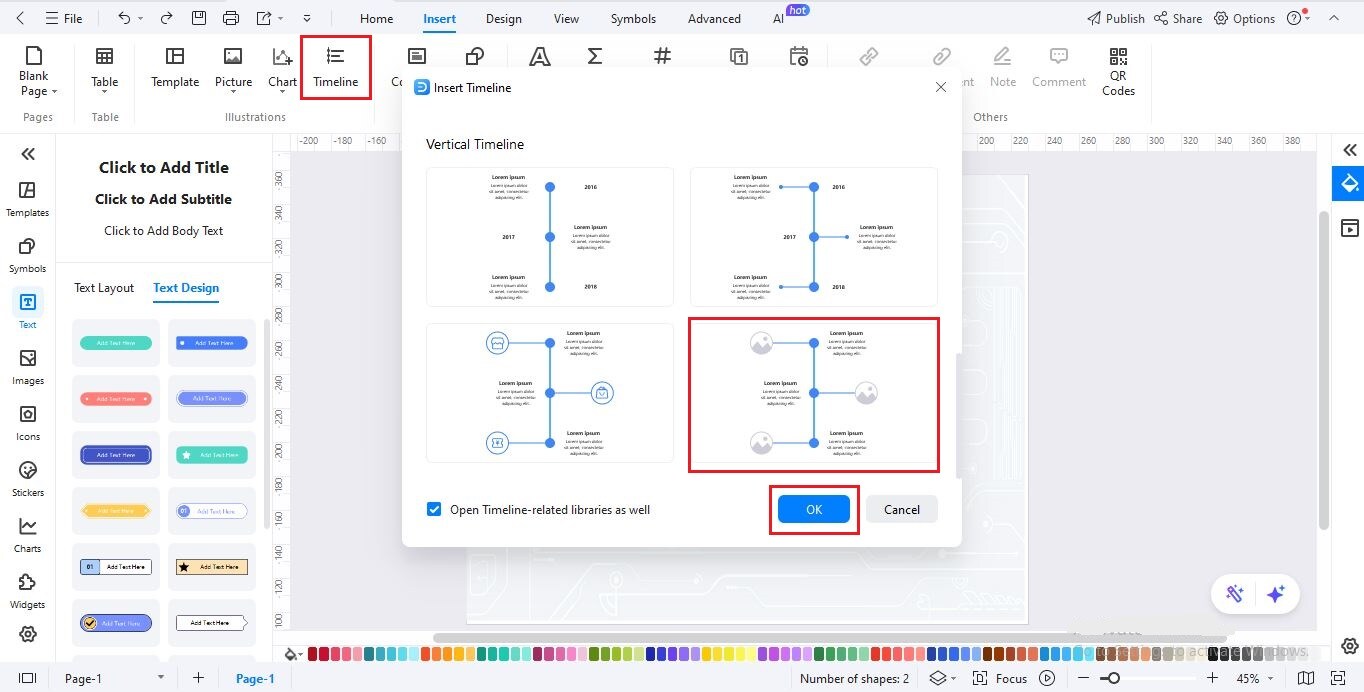
Step4Insert the Timeline Layout
Click Insert in the top menu and select Timeline.
Choose Horizontal Timeline and select a layout that includes images.
Click OK to add it to your canvas.
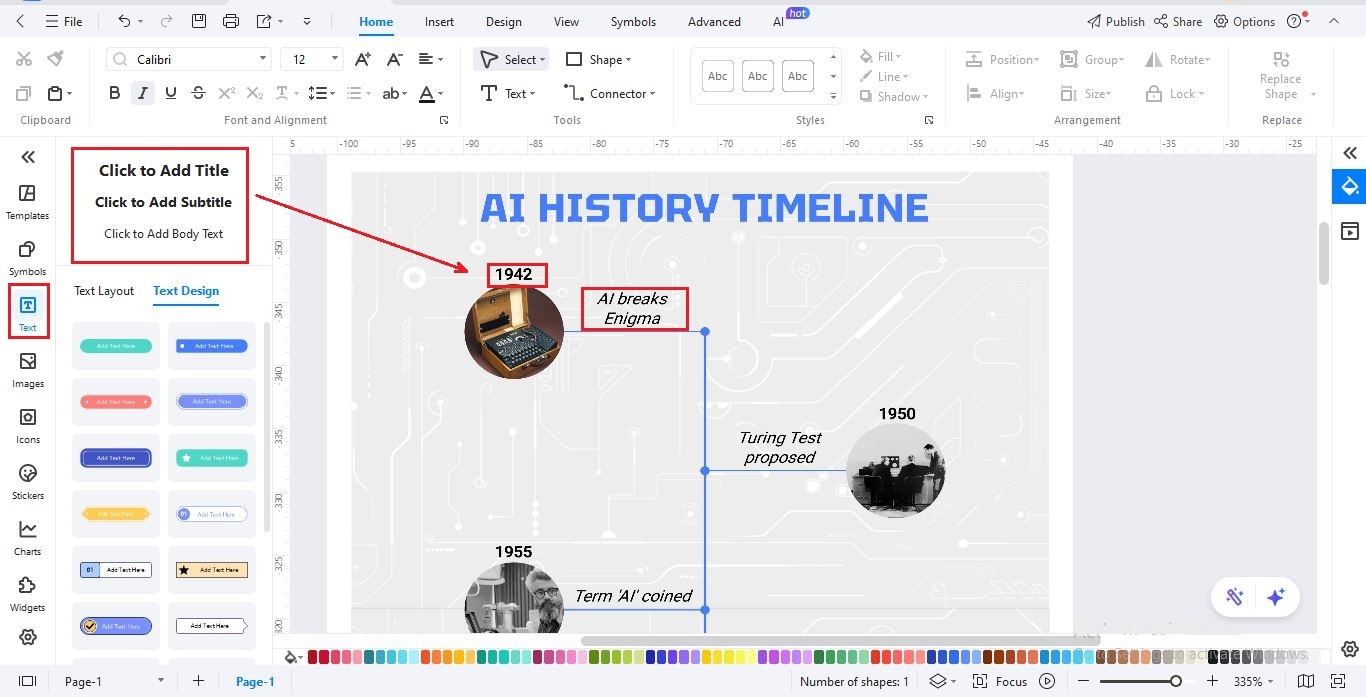
Step5Add Text to the Timeline
In the left panel, click Text.
Use Click to Add Subtitle for the year of each AI milestone.
Use Click to Add Body to briefly describe the event.
Repeat for all key events in AI history.
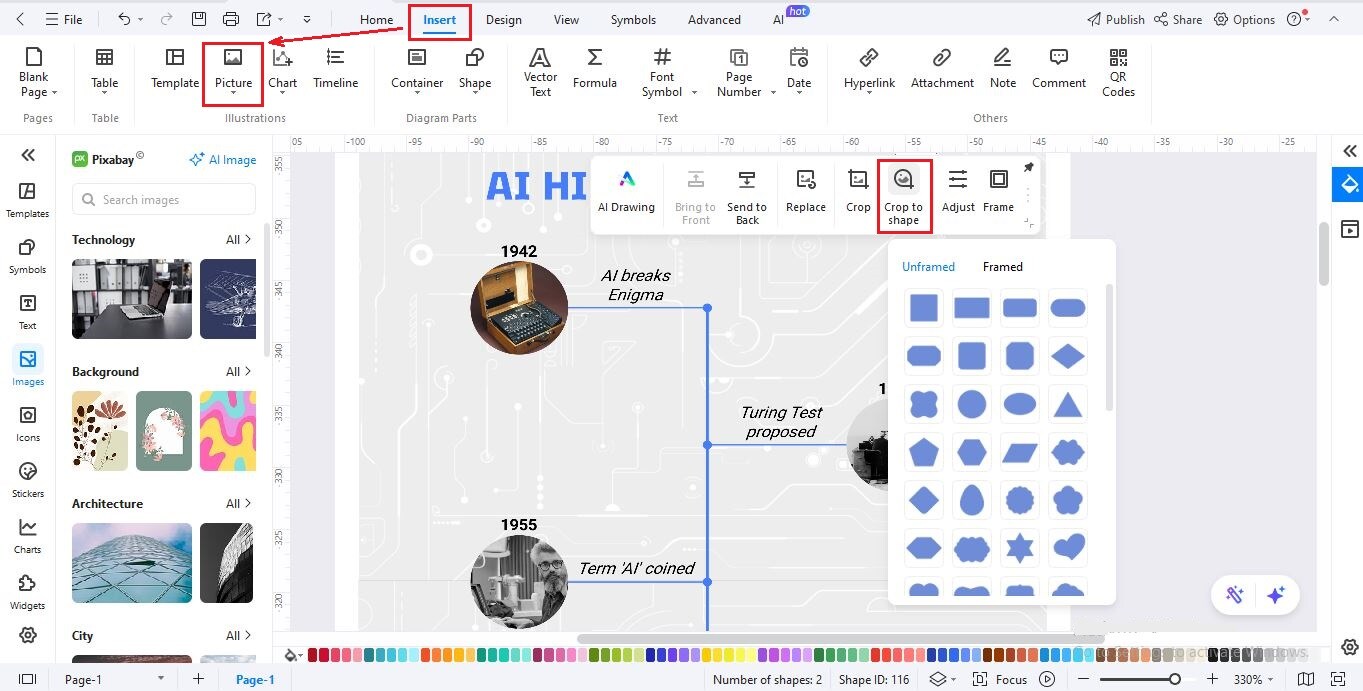
Step6Insert Thumbnail Images
Go to Insert > Picture > Local Pictures to add images for each milestone, such as photos of researchers, robots, or AI systems.
Select a thumbnail, choose Crop to Shape, and apply a frame style.
Repeat for all events to make your timeline more engaging.
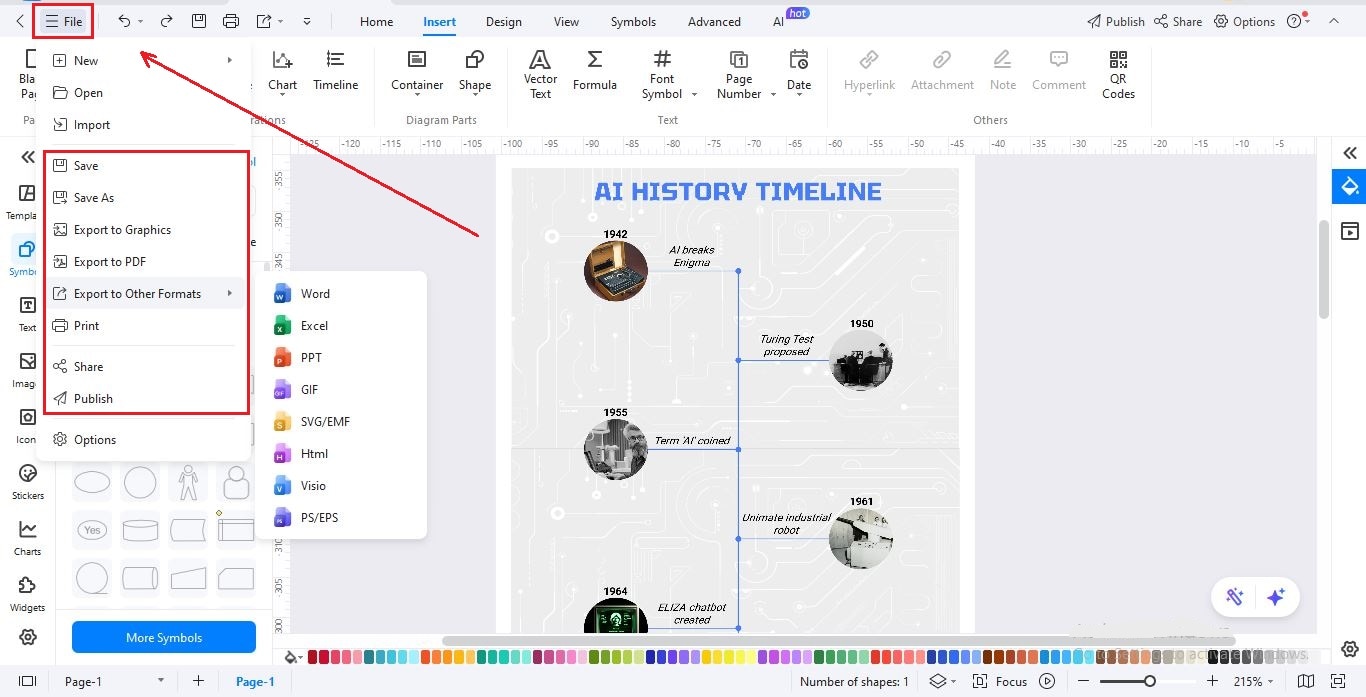
Step7Save, Export, and Share
Once your timeline is ready, save it using File > Save to keep it editable.
You can also share it directly by clicking the Share button.
If you want to export in different formats, click File > Export, and choose formats like PNG, PDF, SVG, HTML, or Excel.
The Future of AI
The future of AI is full of promise. Smarter systems will assist doctors, personalize learning for students, and help businesses automate tasks. In short, AI will make our life more easier and creative.
But it also brings challenges. Ethics, privacy, and jobs need careful thought. The key is building AI that supports humans responsibly.
If you’re planning for what’s next, you need a clear vision. And EdrawMax can help with that. It turns your thoughts into smart visual maps with the power of AI. So, are you ready? Give it a try today.