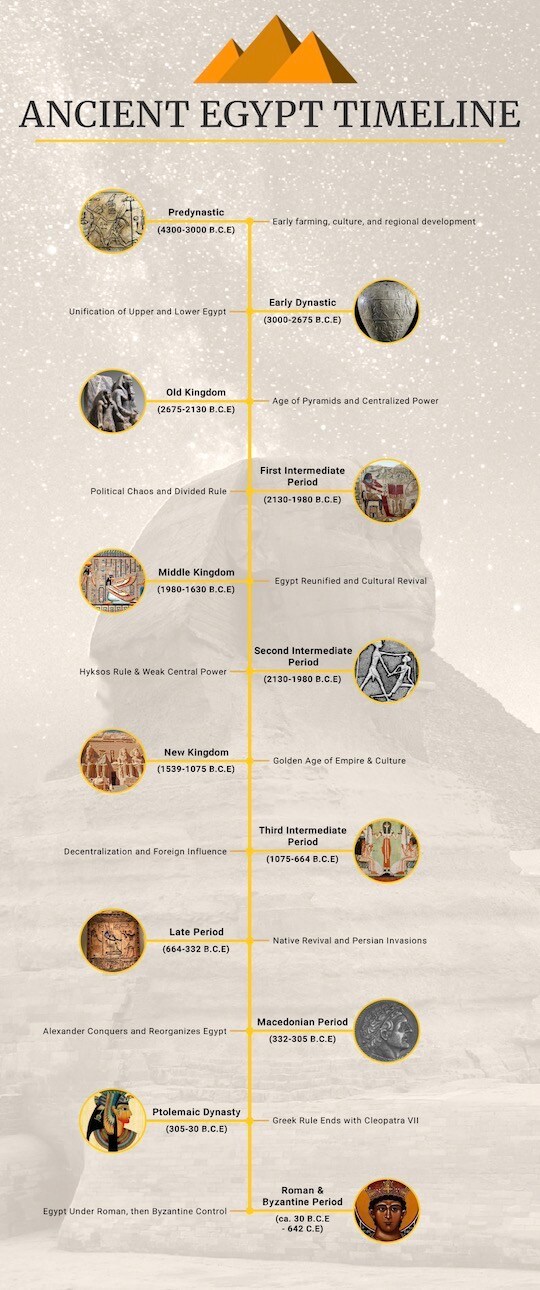
When we think of Ancient Egypt, images of grand pyramids, mighty pharaohs, and the Nile River come to mind. This incredible civilization thrived for over 3,000 years, shaping art, religion, and politics in ways that still fascinate us. To understand its vast history, experts usually divide it into the Old, Middle, and New Kingdom.
Between 4300 BC and 642 CE, Egypt experienced great victories as well as tough challenges. Invasions, innovations, and cultural growth all played a role in its journey. This timeline makes it easy to follow Egypt’s rise, decline, and lasting legacy.
In this article
Timeline of Ancient Egypt
The story of Ancient Egypt is almost 5,000 years long. It begins around 4300 BC and goes all the way to 642 CE. In that time, the Egyptians built those famous pyramids we still talk about today. They came up with their own way of writing and made big progress in art and science. And we all know about their rules. The Pharaohs. Well, they were seen not just as kings but also as gods.
Of course, Egypt’s history wasn’t always smooth. There were wars, invasions, and hard times. But there were also golden ages filled with peace, creativity, and growth.
To better understand this long journey, let’s explore its timeline step-by-step.
Predynastic Period (4300-3000 BC)
Before the age of pharaohs, life along the Nile was simple. Small farming villages grew crops, made pottery, and traded with nearby lands like Nubia. The river’s floods taught people how to work together. It was just the start of Egypt’s long story.
Then came the Naqada culture. They made better tools, used metal, and painted pottery with bold designs. This is also where the first writing symbols showed up, and the idea of kings started to form.
Early Dynastic Period (3000-2675 BC)
This is when Egypt truly came together as one land. King Narmer, also called Menes, united Upper and Lower Egypt and built a strong foundation for the future. He chose Memphis as the capital, giving Egypt a political and cultural heart.
Even though Memphis was now in charge, Abydos remained sacred for religious life. With unity, Egypt developed order and stability. These early steps made it possible for pharaohs to dream big in the centuries ahead.
Old Kingdom (2675-2130 BC)
The Old Kingdom is often called the “Age of Pyramids”, and for good reason. Pharaohs like Djoser and Khufu built incredible pyramids that still tower over the desert today. Egypt’s rulers had huge power, and their monuments showed off their wealth and ambition.
Life thrived under strong leadership, but cracks appeared as local officials gained power. Over time, the pharaoh’s control weakened, leading to unrest. Egypt’s first golden age slowly slipped away into turmoil.
First Intermediate Period (2130-1980 BC)
After the Old Kingdom collapsed, Egypt entered its first real “dark age.” The country broke apart, with rival rulers in Thebes and Heracleopolis fighting for control. Without unity, life became harder, and temples and statues were often damaged or destroyed.
Still, Egypt wasn’t finished. Thebes grew stronger, and its leaders worked to restore order. Eventually, they succeeded, pulling the land back together and opening the door to the Middle Kingdom.
Middle Kingdom (1980-1630 BC)
The Middle Kingdom brought Egypt back to life. Pharaohs like Amenemhat I reunited the country, strengthened borders, and expanded into Nubia. They invested in farming, trade, and building projects, making Egypt rich and stable again. Art and writing flourished during this time.
This era also gave us Sobekneferu, Egypt’s first female pharaoh. She proved women could rule with authority. But after her reign, Egypt once again faced division and growing outside threats.
Second Intermediate Period (1630-1539 BC)
Egypt broke apart again. Different rulers controlled different regions. The most famous newcomers were the Hyksos, who ruled northern Egypt. They brought new ideas, like horse-drawn chariots and weapons the Egyptians had never seen.
At first, it seemed like Egypt had lost control. But in the south, the rulers in Thebes were growing stronger. They learned from the Hyksos while planning to fight back and restore Egypt’s greatness.
New Kingdom (1539-1075 BC)
This was Egypt at its best, its real golden age. Pharaohs like Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, and Ramses II led armies, grew the empire, and filled the land with wealth. Big temples and tombs, like the Valley of the Kings, showed off their power.
Life in Egypt was full of trade and culture. The country was one of the strongest in the world. But over time, invasions and weak rulers took their toll. Slowly, the empire began to fall.
Third Intermediate Period (1075-656 BC)
After Ramses XI died, Egypt fell apart again. Power was split between priests in Thebes and pharaohs in the north. Without a strong leader, the country became unstable and open to attack.
Eventually, the Nubians stepped in and reunited Egypt under the 25th Dynasty. They brought back old traditions and rebuilt monuments. But danger was never far. When the Assyrians invaded, Egypt faced yet another period of trouble.
Late Period (664-332 BC)
Egypt tried to rebuild under Psamtik I. He brought unity back, strengthened trade with Greece, and invested in farming and canals. For a moment, life felt steady, and Egypt reconnected with the wider world.
But outside powers never stayed away for long. Persia conquered the land, and although Egyptians briefly fought back, they couldn’t hold on. Then Alexander the Great marched in, changing Egypt’s path forever.
Macedonian Period (332-305 BC)
When Alexander the Great entered Egypt, people welcomed him as a liberator from Persian rule. He founded Alexandria, which quickly became a hub of learning, trade, and culture. The city would later shine as one of the greatest in the ancient world.
But Alexander didn’t stay long. After his death, Egypt passed to his general, Ptolemy. With this shift, Egypt moved into a brand-new era under Greek leadership.
Ptolemaic Dynasty (305-30 BC)
The Ptolemies ruled Egypt for nearly three centuries. Though Greek by birth, they took on pharaonic traditions, blending cultures. Alexandria thrived, boasting its famous library and becoming a center for trade, art, and science. Egypt was wealthy, but cracks were forming.
Family rivalries and Roman influence weakened the dynasty. Cleopatra VII made a final effort to protect Egypt, but after her defeat, Rome took control, ending Egypt’s independence.
Roman & Byzantine Period (30 BC-642 CE)
Under Rome, Egypt became a vital province, supplying grain to feed the empire. Life blended Roman, Greek, and Egyptian traditions, though the old pharaonic system was gone. The land remained wealthy, but independence was lost.
Later, Egypt shifted into Byzantine control, holding its role as a key crossroads of trade and culture. In 642 CE, Arab Muslim forces conquered the land, closing the chapter on Ancient Egypt’s long story.
How to Make a Similar Timeline Using EdrawMax?
Ancient Egypt’s history is full of pharaohs, pyramids, and big moments. But with thousands of years to cover, it’s easy to lose track. A timeline makes the story much clearer.
The good news is you don’t need design skills to build one. EdrawMind has ready-made templates and easy tools to help you. Here’s how to make your own Ancient Egypt timeline with EdrawMax:
Step1Start with a Blank Canvas
- Open EdrawMax on your desktop and log in, or register if you’re a new user.
- Click New on the left panel, then choose Blank Drawing to open a fresh canvas for your Ancient Egypt timeline.
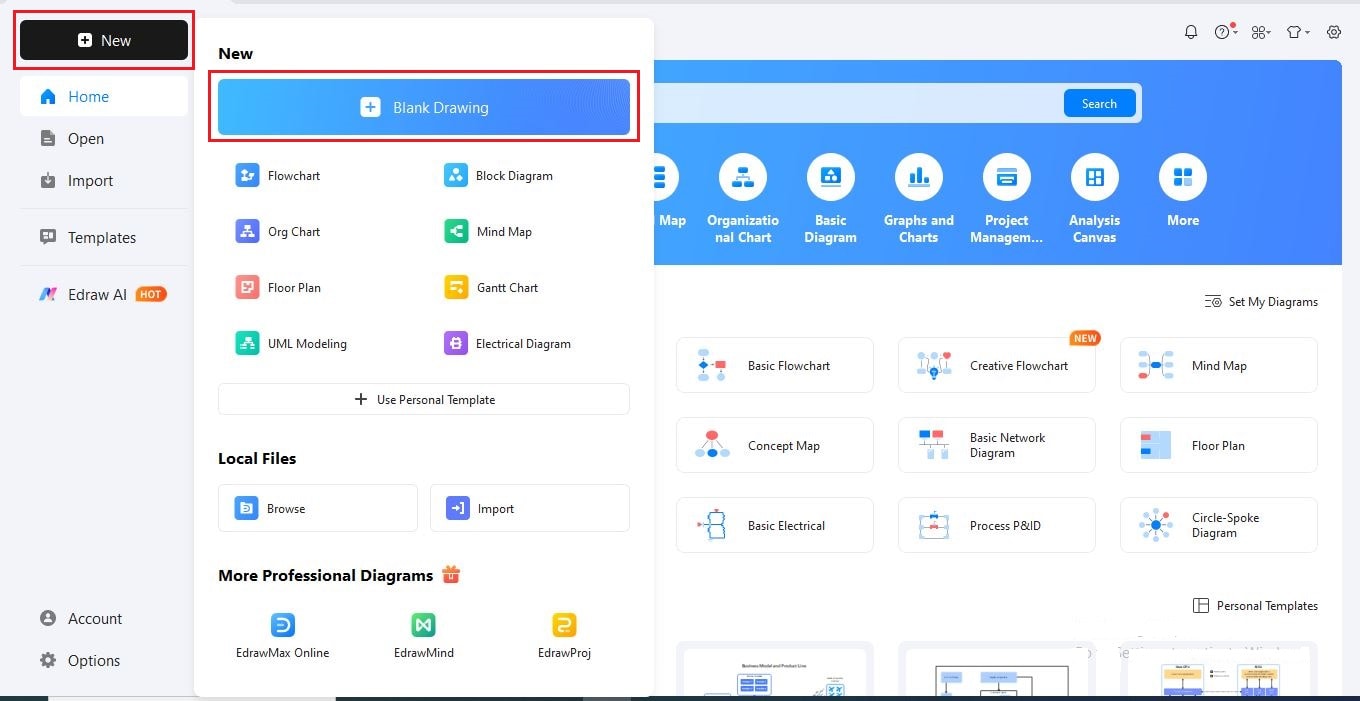
Step2Add a Background Image
- Go to the Insert tab and click Picture.
- Choose Local Pictures to upload a background image..
- Use the Adjust option on the floating toolbar to change brightness, contrast, or transparency so it blends well with your design.
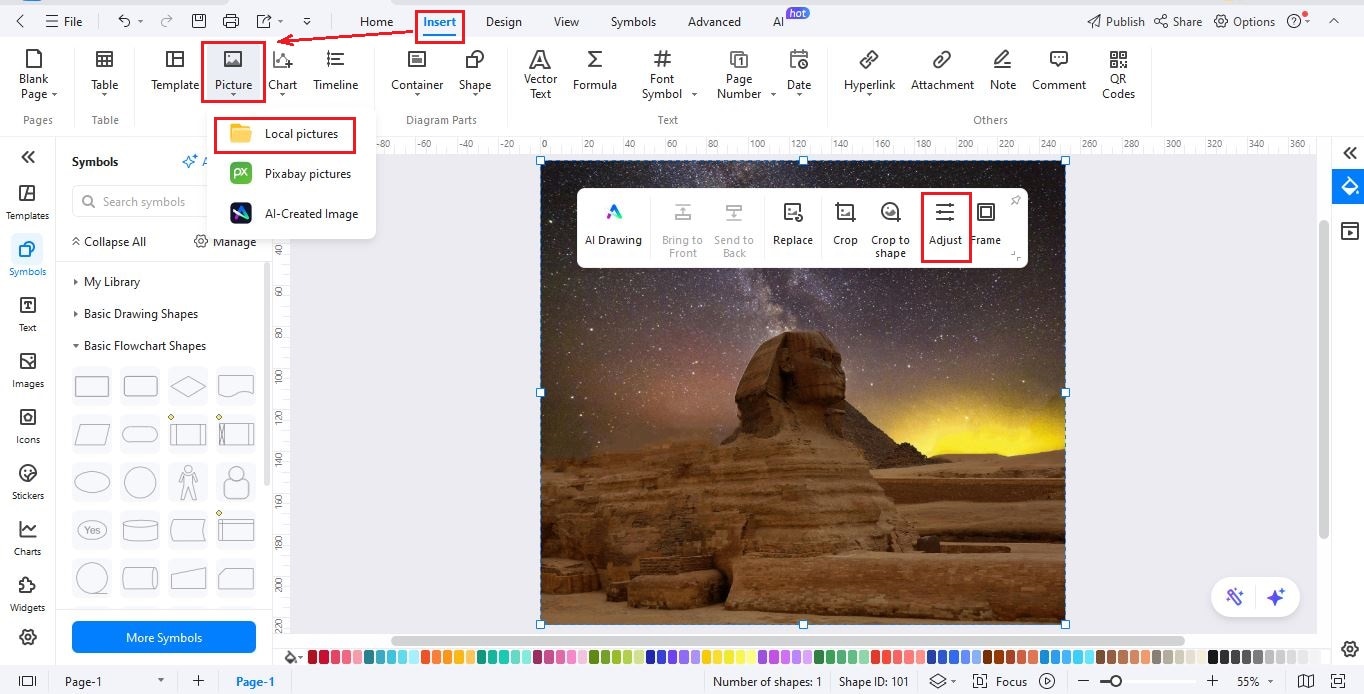
Step3Insert a Timeline Title
- Add a title such as “Ancient Egypt Timeline” using text or image. Here we'll use an image. We'll use text here.
- Click Text and then Click to Add Title to add your heading.
- You can also insert icons like scarabs, pyramids, or ancient symbols to make it interesting.
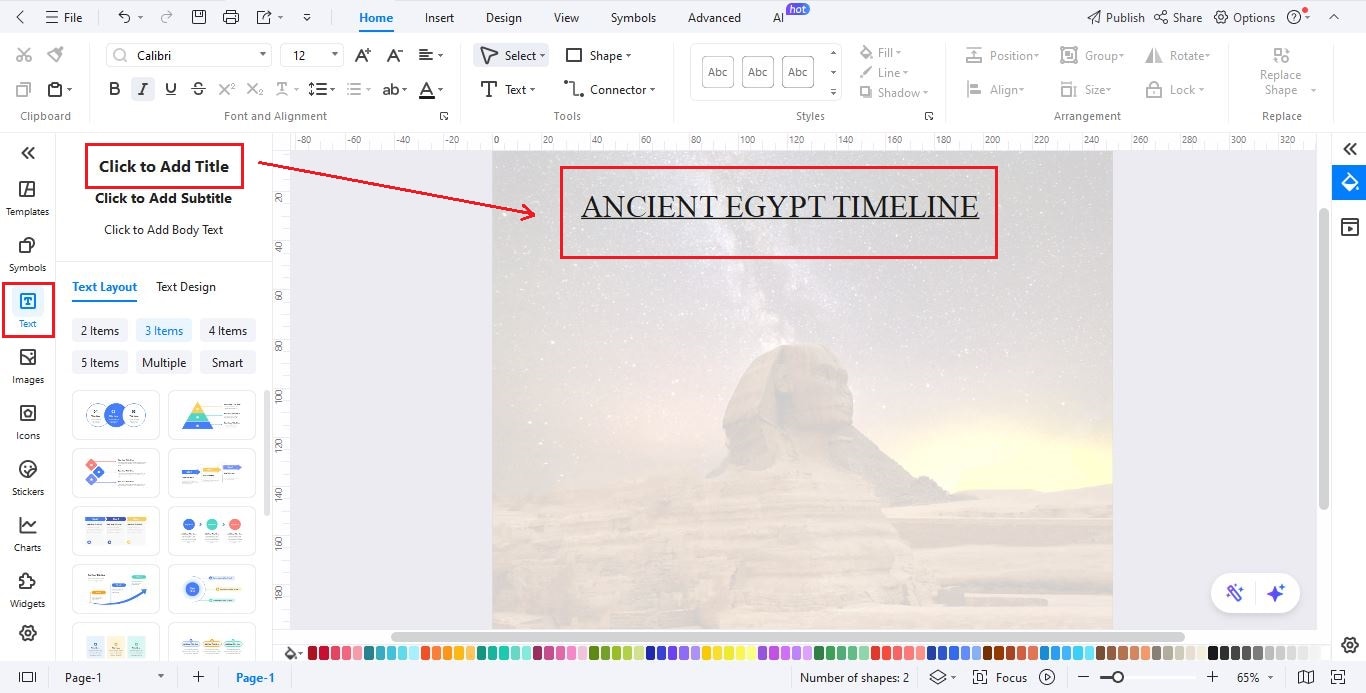
Step4Insert the Timeline Layout
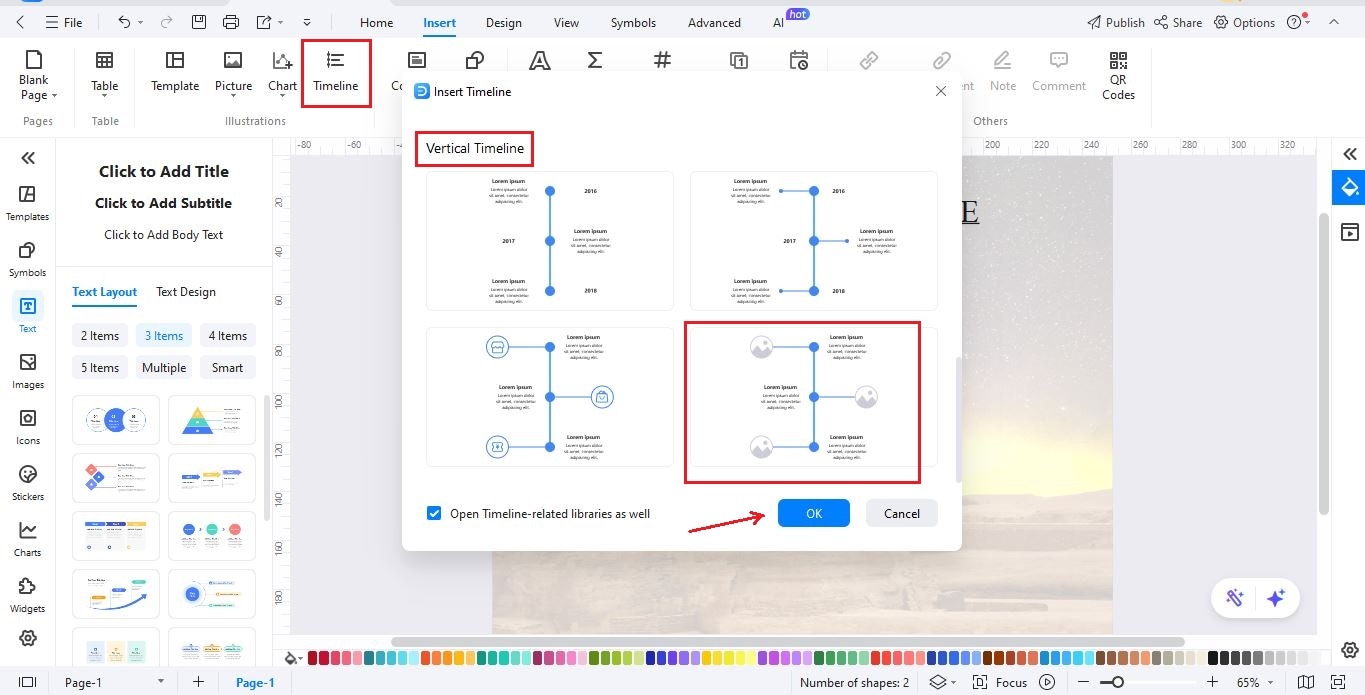
- On the top menu, go to Insert and select Timeline.
- Pick a Vertical Timeline with image placeholders, then click OK to add it to your canvas.
- Click on the timeline to open a toolbar where you can adjust its structure to fit Ancient Egypt’s chronology.
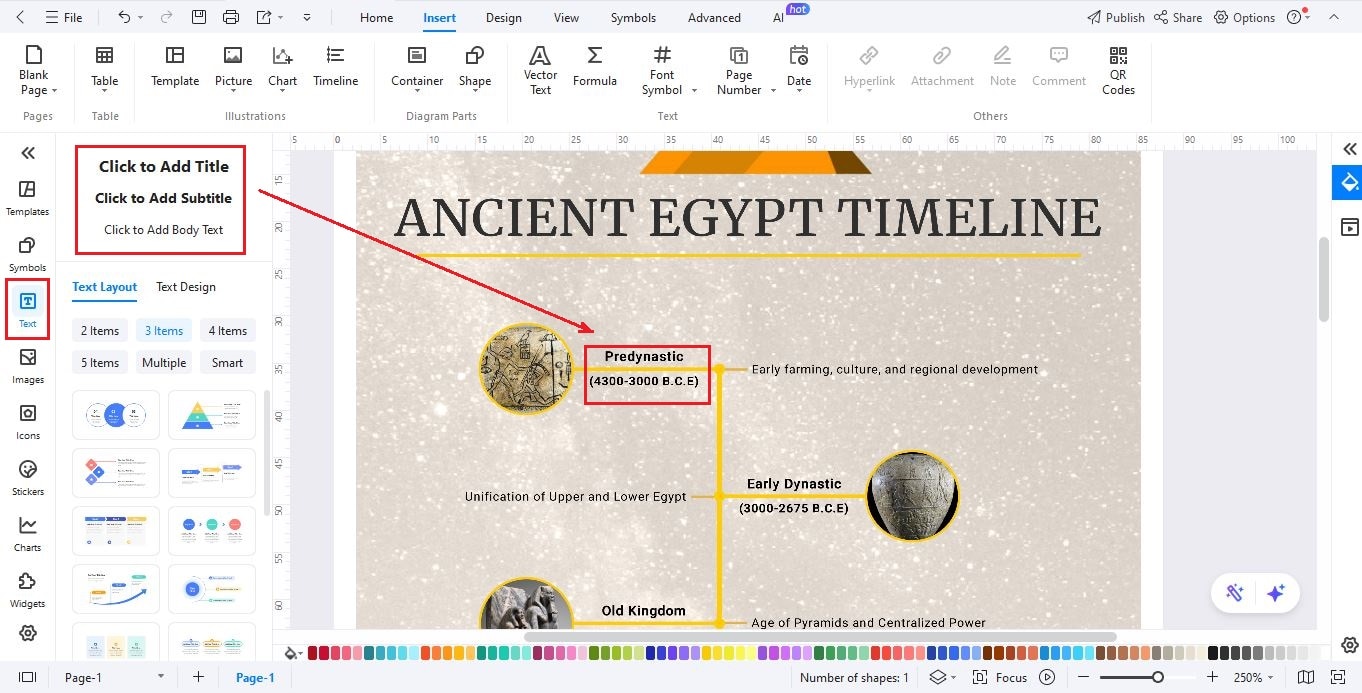
Step5Add Key Ancient Egypt Events
- Click Text on the left editing panel.
- Use Click to Add Subtitle for each era.
- Then use Click to Add Body to add short descriptions of each major event or dynasty.
- Continue until your full Ancient Egypt history is mapped.
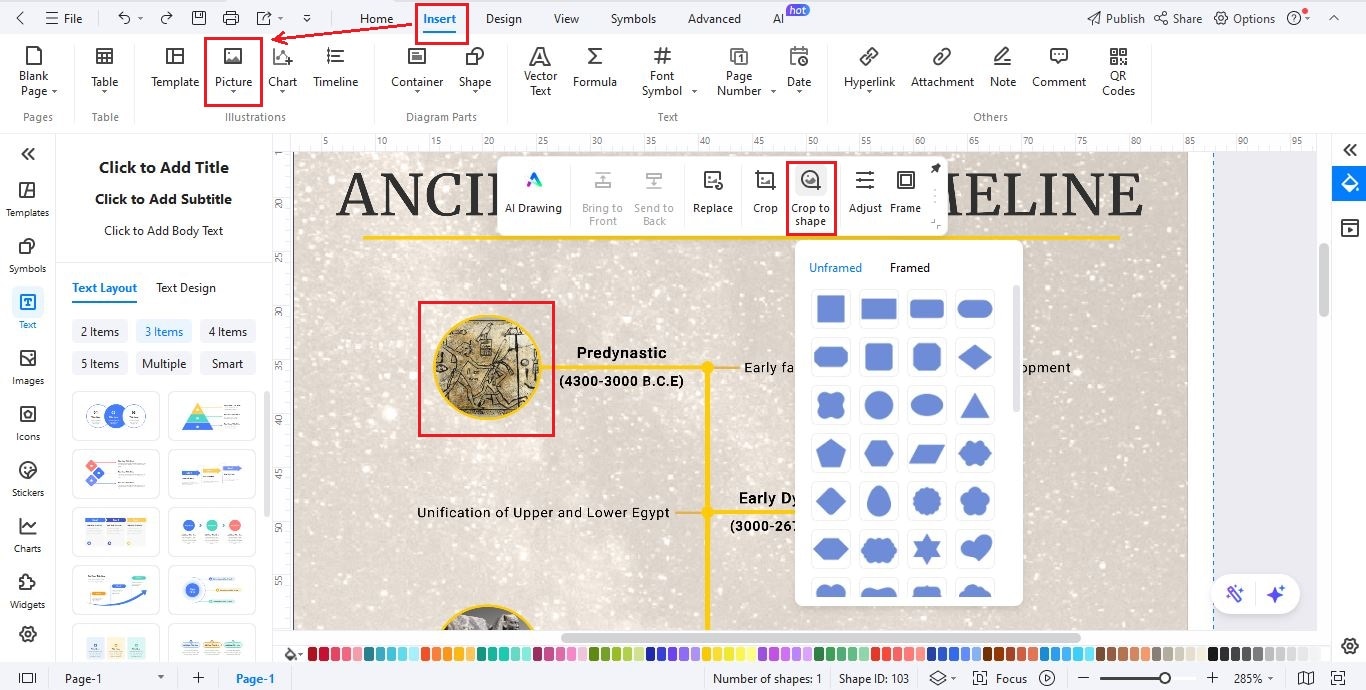
Step6Insert Milestone Images
- Go to Insert > Picture > Local Pictures and upload images like pyramids, temples, pharaohs, or artifacts.
- Click an image, choose Crop to Shape, and select a frame style to match your layout.
- Repeat for each key milestone to make your timeline more visual and engaging.
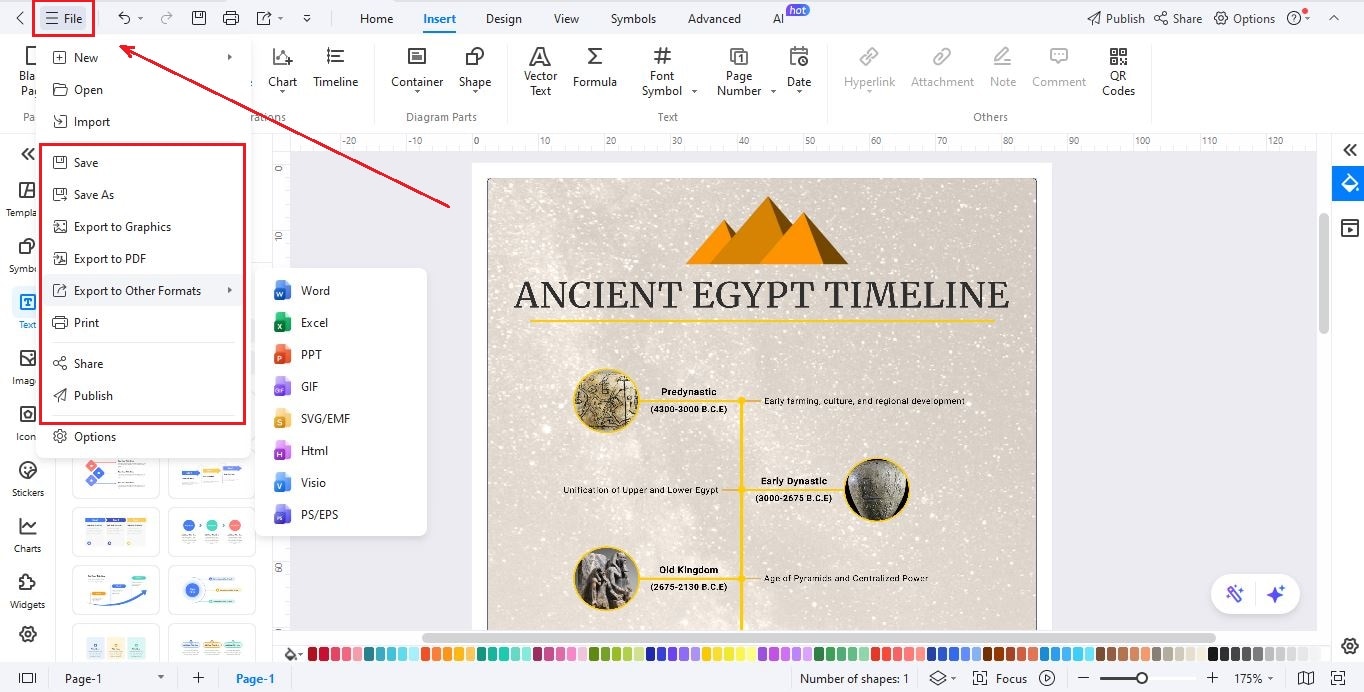
Step7Save and Share Your Timeline
- When your timeline is complete, click File > Save to keep an editable version.
- To share it, go to File > Export and choose PNG, PDF, SVG, HTML, Visio, or Excel.
- Want to inspire others? Click Publish to share your timeline with the EdrawMax community.
Wrapping Up
This journey through Ancient Egypt shows how strong and resilient the civilization was. Pharaohs built temples and pyramids that still amaze the world. Foreign invasions came and tested Egypt’s power, yet the culture always found a way to survive. Each era left its own mark, adding a new chapter to a story that lasted thousands of years. Even today, Egypt’s legacy continues to inspire curiosity and wonder.
You can share your own country’s story in a similar way. EdrawMax can make it simple to create timelines that are clear, colorful, and fun. It’s a creative way to bring history back to life and share it with others.