An organizational structure is a framework that defines the hierarchy and arrangement of elements within an organization. It provides clarity on roles and responsibilities, streamlines workflows, and promotes effective communication and coordination. Organizational charts visually represent the structure, depicting positions, reporting relationships, departments, and lines of communication. In this article, you will get a comprehensive outlook on organizational structures. You will also learn how you can create an organizational chart for your own organization here.
Contents of this article
What is an Organizational Structure?
An organizational structure refers to the framework that delineates the hierarchy and arrangement of various elements within an organization. It outlines the reporting lines, authority levels, and communication channels prevalent throughout the entity. While some organizations may adopt a hierarchical model, others may opt for a flatter structure, emphasizing decentralization and increased autonomy for employees.
Why is an Organizational Structure Important?
There are many reasons why an organizational structure is significant. Some of the main reasons why organizational structures are important are discussed below:
1) Ensures clarity and defines the reporting relationships
Organizational structures play a pivotal role in promoting several key aspects within organizations. Firstly, they ensure clarity and define the reporting relationships, enabling employees to understand their roles and responsibilities. By delineating formal lines of authority, organizational structures establish a clear chain of command, facilitating decision-making processes and reducing ambiguity.
2) Enhances efficiency
A well-designed org structure enhances efficiency by streamlining workflows and optimizing resource allocation. Through proper division of labor and specialization, organizations can capitalize on the unique skills and knowledge of their employees. This leads to increased productivity and minimizes duplication of efforts.
3) Facilitates effective communication and coordination
A business organizational structure also facilitates effective communication and coordination among employees. By creating clear channels for information flow, such as vertical reporting lines or cross-functional teams, organizations foster collaboration and synergy. This, in turn, enhances problem-solving abilities, teamwork, and innovation.
Components of Organizational Charts
Organizational charts visually represent the various components of an organizational structure. These charts illustrate the hierarchy, reporting relationships, and functional divisions within an organization. The key components often depicted in organizational charts include:
1) Positions and Job Titles
Organizational charts highlight different positions within the hierarchy, including top-level executives, middle management, and frontline employees. These positions are labeled with corresponding job titles to provide clarity regarding each role's rank and authority.
2) Reporting Relationships
Organizational charts showcase the reporting relationships between different positions in the entity. This information clarifies whom each employee reports to and assists in understanding the chain of command. It aids in decision-making processes as well as in establishing accountability and responsibility.
3) Departments and Divisions
To depict the functional divisions within an organization, organizational charts include distinct departments and divisions. By visualizing these divisions, organizational charts help employees identify their place within the broader organizational structure and understand how their department aligns with others.
4) Lines of Communication
Organizational charts often include lines of communication to indicate formal channels for information flow. These lines help employees understand the routes through which communication and decision-making processes occur, fostering efficiency and reducing confusion.
Types of Organizational Structure
There are various types of organizational structure. Some of the most common types of organizational structures are discussed below:
1) Hierarchical Organizational Structure
The hierarchical organizational structure follows a top-down approach, where authority and decision-making power flow from the executive level downward through various levels of management. Each level has its own specific responsibilities and reporting lines, creating a clear chain of command.
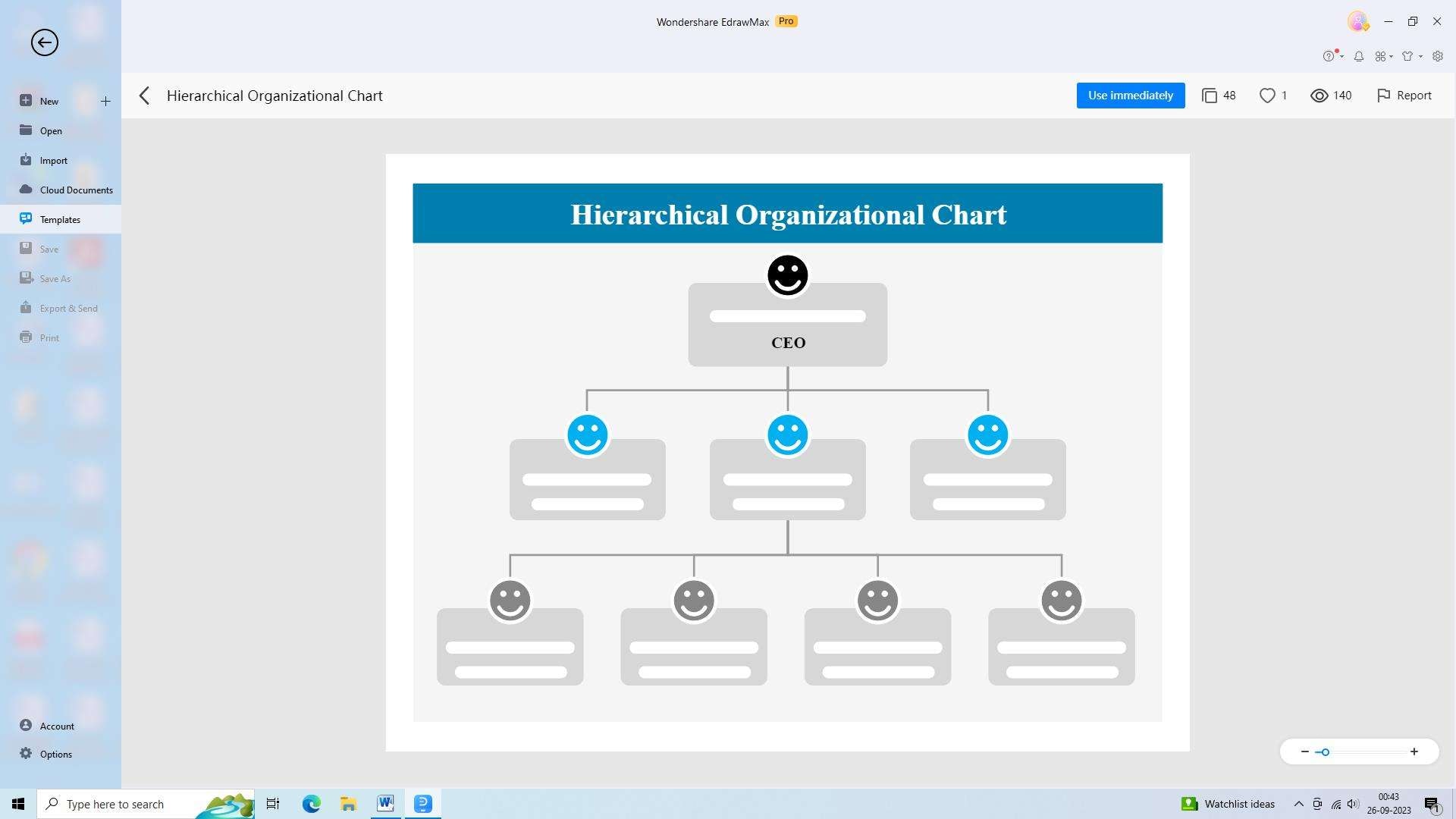
Pros:
- Clear reporting lines and well-defined authority prevent confusion and provide employees with a sense of direction.
- Efficient decision-making process, as decisions are made at higher levels and cascaded down.
- Favorable for larger organizations that require strict control and coordination.
Cons:
- Lack of flexibility due to the rigid nature of the structure.
- Can lead to communication barriers, as information may be slow to reach lower-level employees.
- Reduced autonomy for employees, which may impact motivation and creativity.
2) Functional Organizational Structure
A functional organizational structure groups employees based on their expertise or specialization. Departments such as marketing, finance, human resources, and operations are created, each headed by a functional manager who oversees their respective domain.
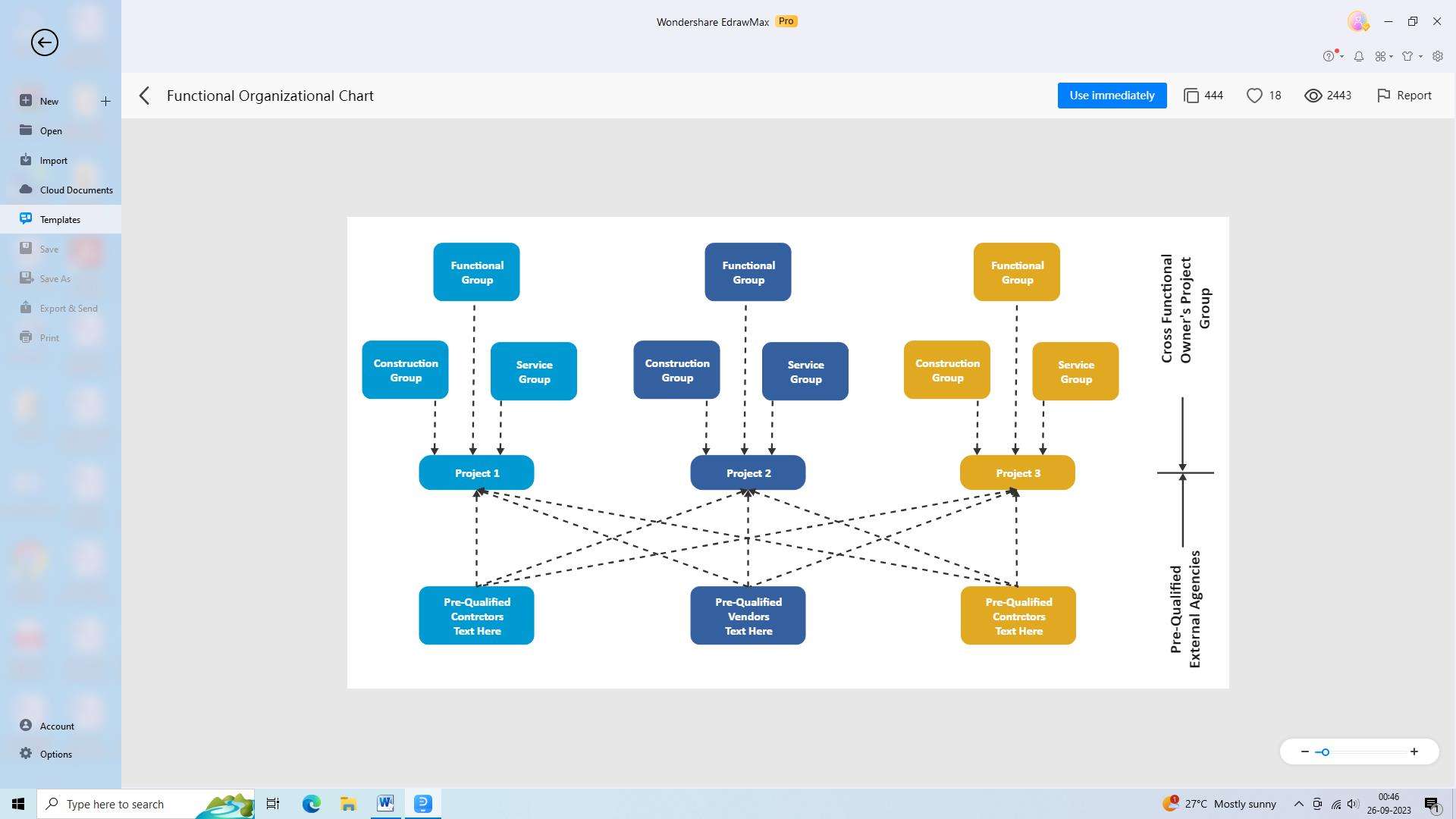
Pros:
- Expertise-based departmentalization allows employees to focus on their specialized tasks.
- Efficient use of resources, as individuals with similar skill sets are grouped together.
- Promotes knowledge sharing within functional units, fostering deeper expertise.
Cons:
- Limited communication and coordination between different functional units.
- May struggle to adapt to a rapidly changing business environment.
- Potential for an inward focus, disregarding the overall organizational goals.
3) Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structure
A horizontal or flat organizational structure minimizes layers of management, creating a wide span of control. Power and decision-making authority are decentralized, and there is a focus on collaboration and teamwork.

Pros:
- Enhanced communication and collaboration among employees due to open lines of interaction.
- Quick decision-making process, as there are fewer levels of management to consult.
- Encourages employee empowerment and autonomy.
Cons:
- Potential for role ambiguity due to fewer managerial positions.
- Requires strong self-discipline and self-motivation from employees.
- May lead to a lack of career progression opportunities, as there are limited hierarchical positions.
4) Divisional Organizational Structure
A divisional organizational structure groups employees based on products, services, customers, or geographic locations. Each division operates independently and functions as a self-contained entity with its own resources and decision-making capabilities.
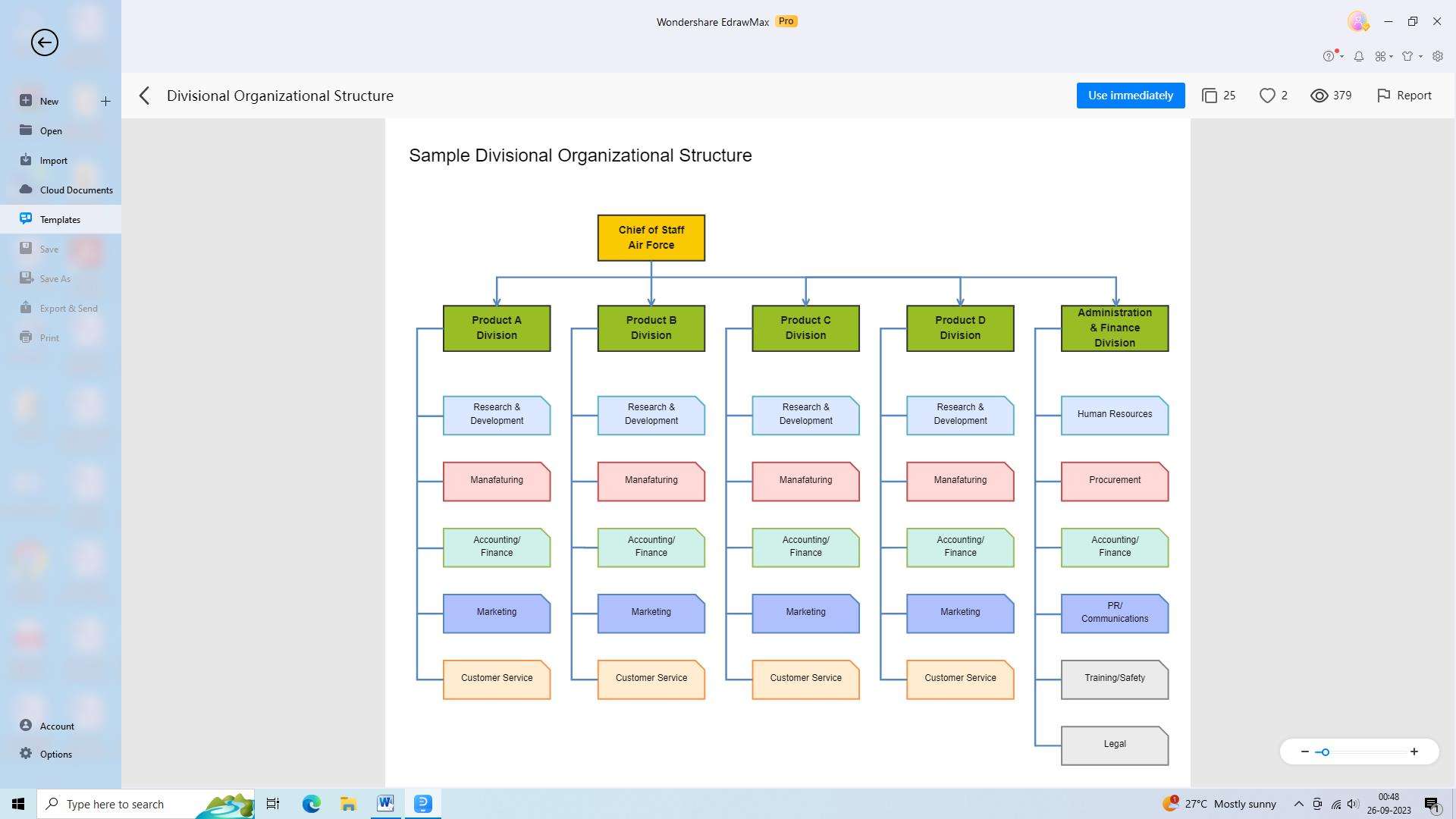
Pros:
- Enhances focus and specialization within each division.
- Allows for greater flexibility and adaptability to specific market needs.
- Encourages innovation and entrepreneurial spirit within each division.
Cons:
- Potential for duplication of efforts and inefficiencies across divisions.
- May hinder knowledge sharing and collaboration between divisions.
- Can lead to internal competition and conflicts between divisions.
5) Matrix Organizational Structure
A matrix organizational structure combines both functional and divisional structures, aiming to leverage the benefits of both. It involves cross-functional teams that are created for specific projects and are led by project managers.
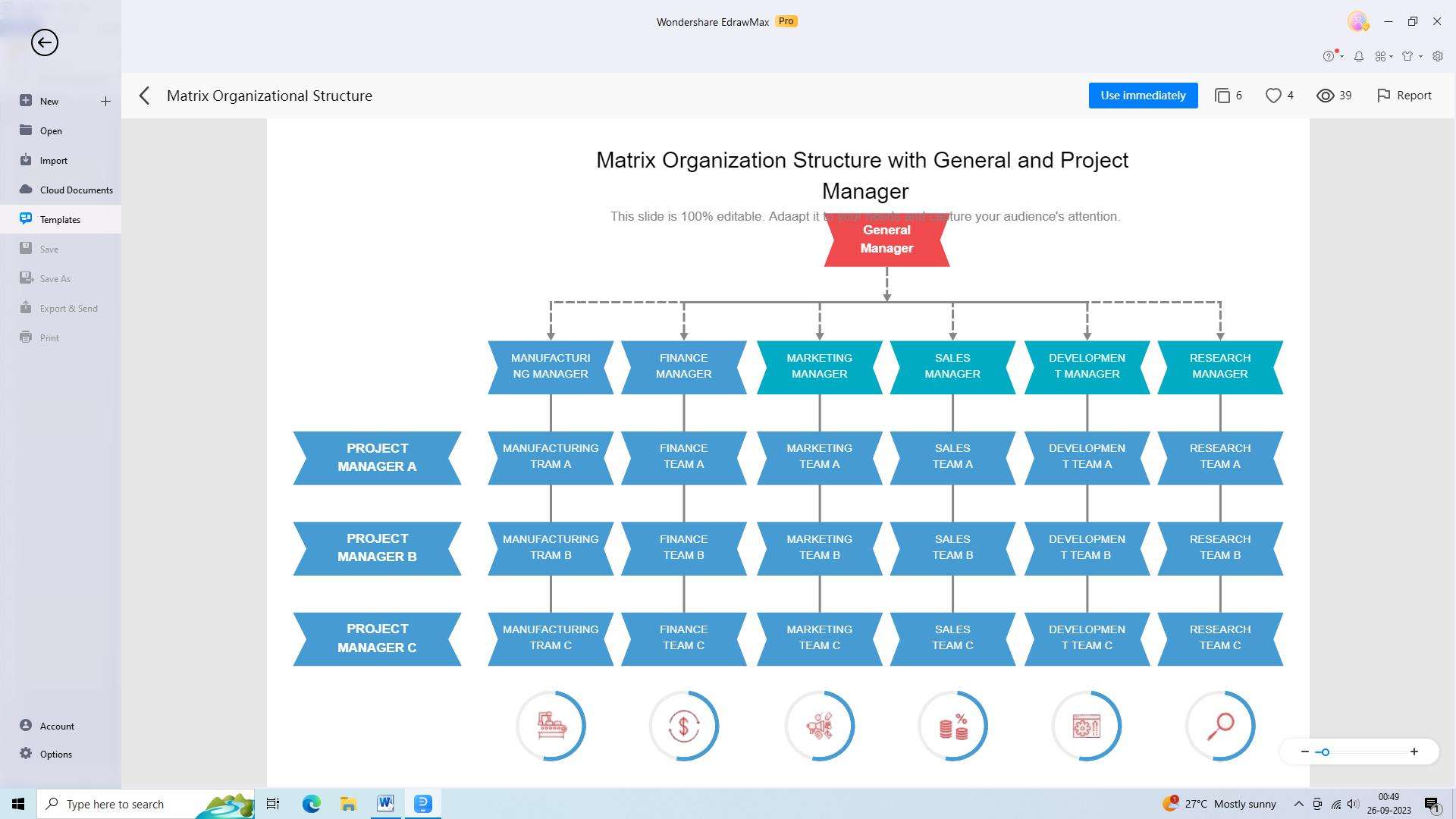
Pros:
- Enables efficient resource allocation and sharing of expertise across projects.
- Promotes collaboration and communication across different functional areas.
- Provides opportunities for employee development and learning through participation in diverse projects.
Cons:
- Dual reporting lines can cause confusion and potential conflicts.
- Requires strong coordination and communication skills to ensure smooth operations.
- May lead to increased bureaucracy and decision-making complexities.
How to Make an Organizational Chart?
Making organizational charts does not have to be stressful or time-consuming. One can use an online tool to make an organizational chart easily. Wondershare EdrawMax is the best online tool available for creating organizational charts. Given below are the steps to create an organizational chart using the tool:
Step 1: Launching EdrawMax and Selecting the Organizational Chart Template
After conducting a preliminary analysis of the organization, launch EdrawMax on your computer. EdrawMax offers a wide range of visually appealing templates to choose from. Search for an "Organizational Chart" template to initiate the process.
Step 2: Customizing the Chart Layout
Once the organizational chart template is selected, tailor it to suit the specific needs and requirements of your organization. EdrawMax provides a variety of customization options, including layout styles, shapes, colors, and fonts. Ensure consistency and clarity in visually representing the various departments, roles, and reporting relationships.
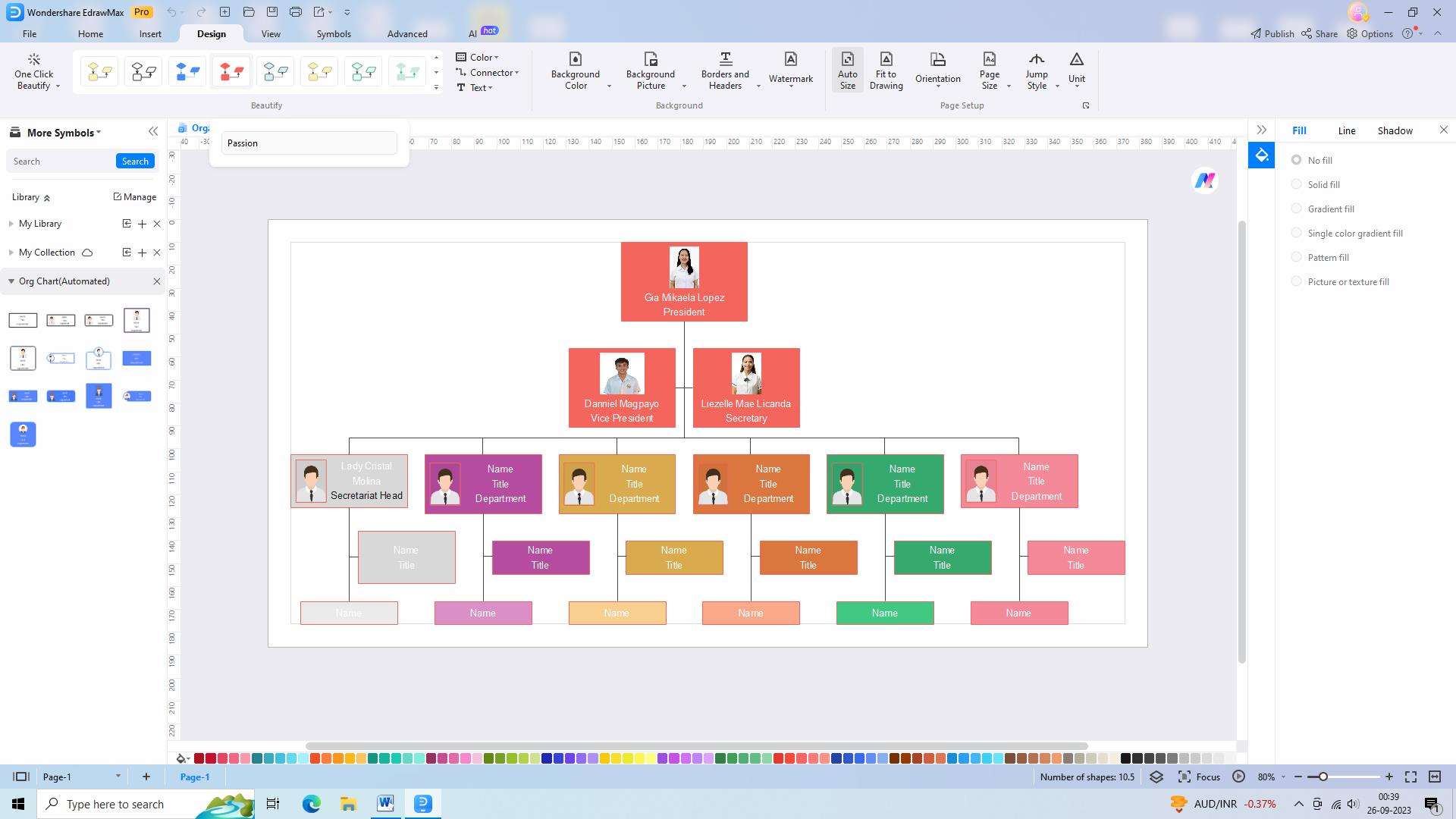
Step 3: Adding Organizational Units and Divisions
Begin by adding the highest-level organizational units, such as departments, divisions, or branches. Use the drag-and-drop feature in EdrawMax to create the necessary shapes and connect them appropriately. Customize these units with names and titles, ensuring accuracy and clarity.
Step 4: Inserting Roles and Employees
Subsequently, insert the roles and employees within each organizational unit. EdrawMax allows you to add shapes, lines, and connectors to designate reporting relationships, positions, and levels of authority. Be sure to include job titles, position descriptions, and relevant employee information while maintaining consistency with the organization's current structure.
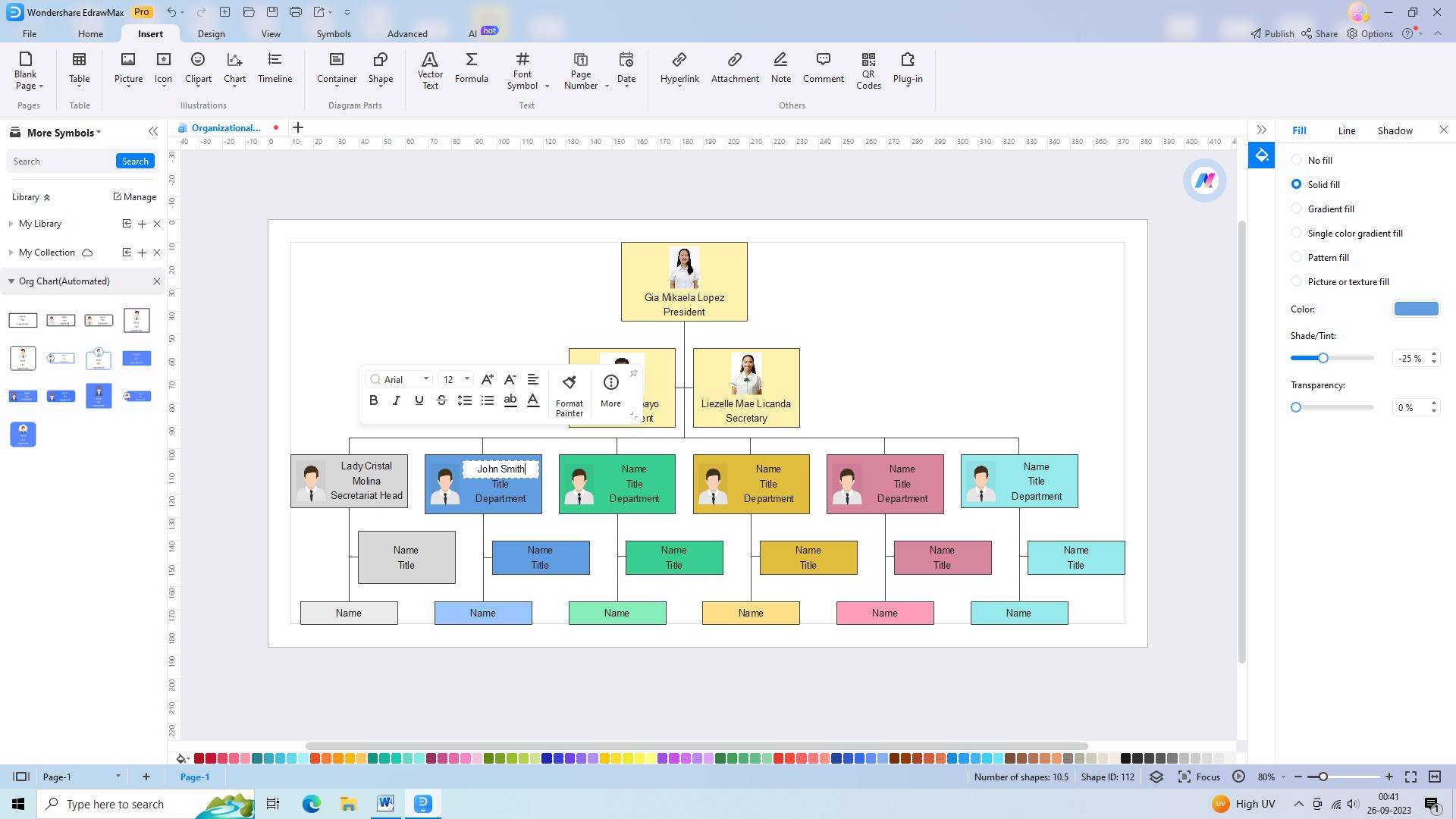
Step 5: Sharing and Collaborating on the Organizational Chart
Once the organizational chart is finalized, sharing it with key stakeholders and team members is crucial. EdrawMax offers seamless options for exporting the chart in various formats, such as PDF or image files. Collaborative features allow multiple users to work simultaneously and make real-time adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
An organizational structure is essential for establishing clear reporting lines, optimizing resource allocation, and fostering collaboration and innovation within an organization. By understanding the different types of organizational structures and using a tool like EdrawMax, organizations can create effective organizational charts that enhance clarity, efficiency, and productivity.




