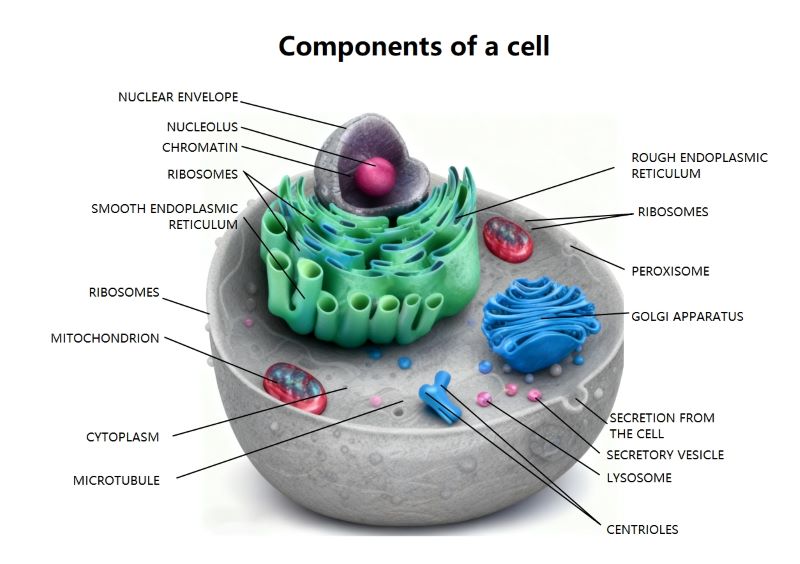
About this animal cell labelled diagram template
This template offers a high-definition view of an animal cell. It is designed to help students and educators visualize the spatial arrangement of organelles. Use it to study cellular functions, create posters, or enhance biology presentations. It serves as a perfect foundation for learning eukaryotic anatomy.
The Control Center
The nucleus is the most critical part of an animal cell. It holds the genetic data needed for growth and reproduction. This section highlights the structures that protect and organize our hereditary material effectively.
- Nuclear Envelope
- Nucleolus
- Chromatin
The Assembly Line
Proteins and lipids are created and processed in this complex network. The endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes work together to build the building blocks of life. These structures ensure the cell operates at peak efficiency.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Ribosomes
Processing and Transport
Once molecules are made, they must be sorted and shipped. This system handles the modification and movement of materials. It ensures that nutrients and waste products reach their proper destinations inside or outside the cell.
- Golgi Apparatus
- Secretory Vesicle
- Secretion from the cell
- Lysosome
Energy and Framework
Every cell needs energy to function and a physical structure to maintain its shape. These components provide the power and the skeleton for the cell. They are essential for movement, metabolism, and maintaining stability.
- Mitochondrion
- Cytoplasm
- Microtubule
- Centrioles
- Peroxisome
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the main function of the nucleus in an animal cell?
The nucleus acts as the control center for the animal cell. It contains the genetic material or DNA, which provides instructions for all cellular activities. The nucleolus inside produces ribosomes, while the nuclear envelope protects this delicate information. Without a functioning nucleus, the cell would not be able to replicate or coordinate complex chemical reactions required for life.
-
How do the Golgi apparatus and Endoplasmic Reticulum work together?
These two organelles work like a factory and shipping center. The Endoplasmic Reticulum produces proteins and lipids. These materials are then sent to the Golgi apparatus for further processing and sorting. Once the Golgi modifies these molecules, it packages them into secretory vesicles. These vesicles then transport the finished products to their final destinations inside or outside the cell.
-
Why is the mitochondrion called the powerhouse of the cell?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they perform cellular respiration. During this process, they convert nutrients like glucose into energy. This energy is stored in a molecule called ATP. The cell uses ATP to power movement, growth, and chemical reactions. Without mitochondria, animal cells would lack the fuel necessary to survive and perform their biological duties.