About this Animal Taxonomy Chart template
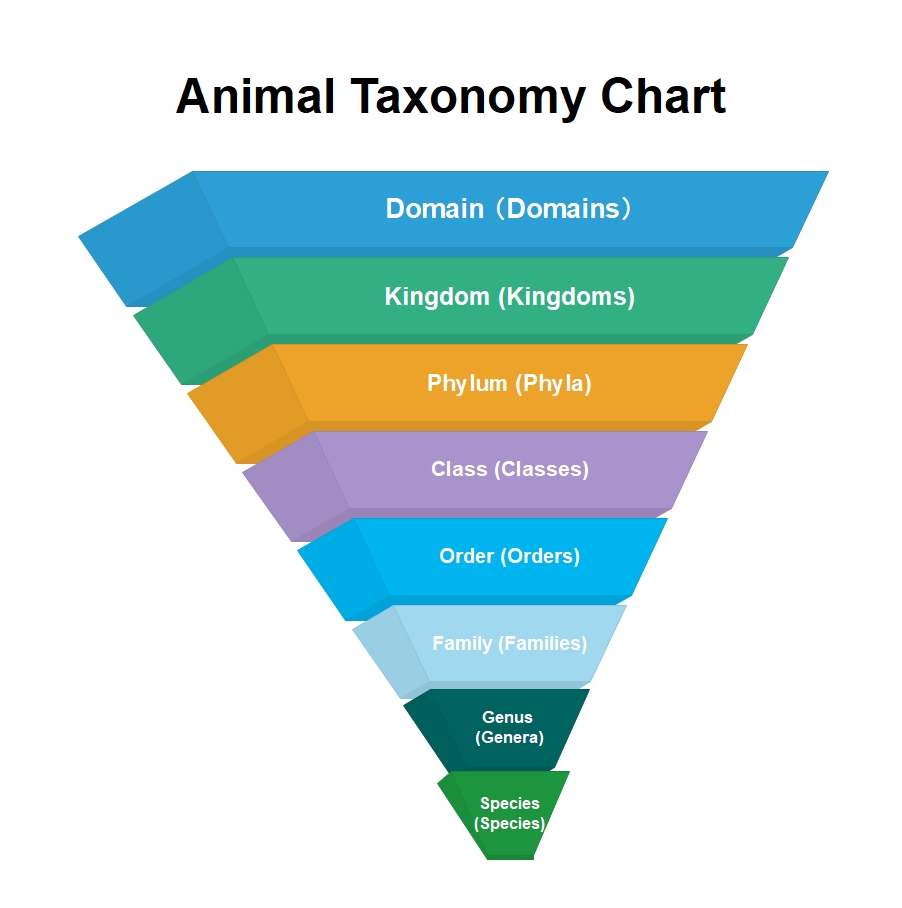
This template provides a clear visual hierarchy of the biological classification system. It uses an inverted pyramid to show how categories narrow down from broad domains to specific species. It is an ideal tool for biology students, educators, and researchers to organize complex taxonomic data.
Domain (Domains)
The domain is the highest and broadest level of biological classification. It categorizes life into three primary groups based on cellular structure. These groups include Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya, encompassing all known living organisms on Earth.
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Eukarya
Kingdom (Kingdoms)
Kingdoms divide domains into large groups with similar fundamental characteristics. In the Eukarya domain, common kingdoms include Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, and Protista. This level helps scientists group organisms based on how they obtain nutrients and their cell types.
- Animalia (Animals)
- Plantae (Plants)
- Fungi
- Protista
Phylum (Phyla)
Phylum groups organisms within a kingdom based on their general body plan or structural features. For example, the phylum Chordata includes all animals with a backbone. This level helps distinguish major structural differences between various groups of living things.
- Chordata
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca
- Annelida
Class, Order, and Family
These middle levels further refine groups based on more specific physical traits and behaviors. A class like Mammalia shares characteristics like fur and milk production. Orders and families then group these animals into even more closely related biological units.
- Class (e.g., Mammalia)
- Order (e.g., Carnivora)
- Family (e.g., Felidae)
Genus and Species
The genus and species levels provide the most specific classification for an individual organism. This binomial nomenclature creates a unique two-part scientific name. For instance, Panthera leo identifies a lion, ensuring scientists globally refer to the exact same animal.
- Genus (e.g., Panthera)
- Species (e.g., leo)
- Binomial Nomenclature
FAQs about this Template
-
Why is the animal taxonomy chart shaped like an inverted pyramid?
The inverted pyramid shape represents the narrowing scope of biological classification. At the top, the Domain category is very broad and includes millions of diverse organisms. As you move down through levels like Kingdom and Phylum, the criteria become more specific. By the time you reach the bottom Species level, only one unique type of organism remains in the group.
-
What is the importance of binomial nomenclature in taxonomy?
Binomial nomenclature is a formal system of naming species using two parts: the genus and the species name. This system is crucial because it provides a universal language for scientists across different countries. It prevents confusion caused by local common names, which can vary significantly. By using Latin names, researchers ensure they are always discussing the exact same biological entity globally.
-
How do scientists decide which category an animal belongs to?
Scientists classify animals based on shared physical characteristics, genetic similarities, and evolutionary history. Modern taxonomy relies heavily on DNA sequencing to determine how closely related different species are. They also look at anatomical structures, such as skeletal arrangements or reproductive methods. This multi-layered approach ensures that the taxonomy chart accurately reflects the natural relationships and history of life on our planet.