About this Brain diagram template
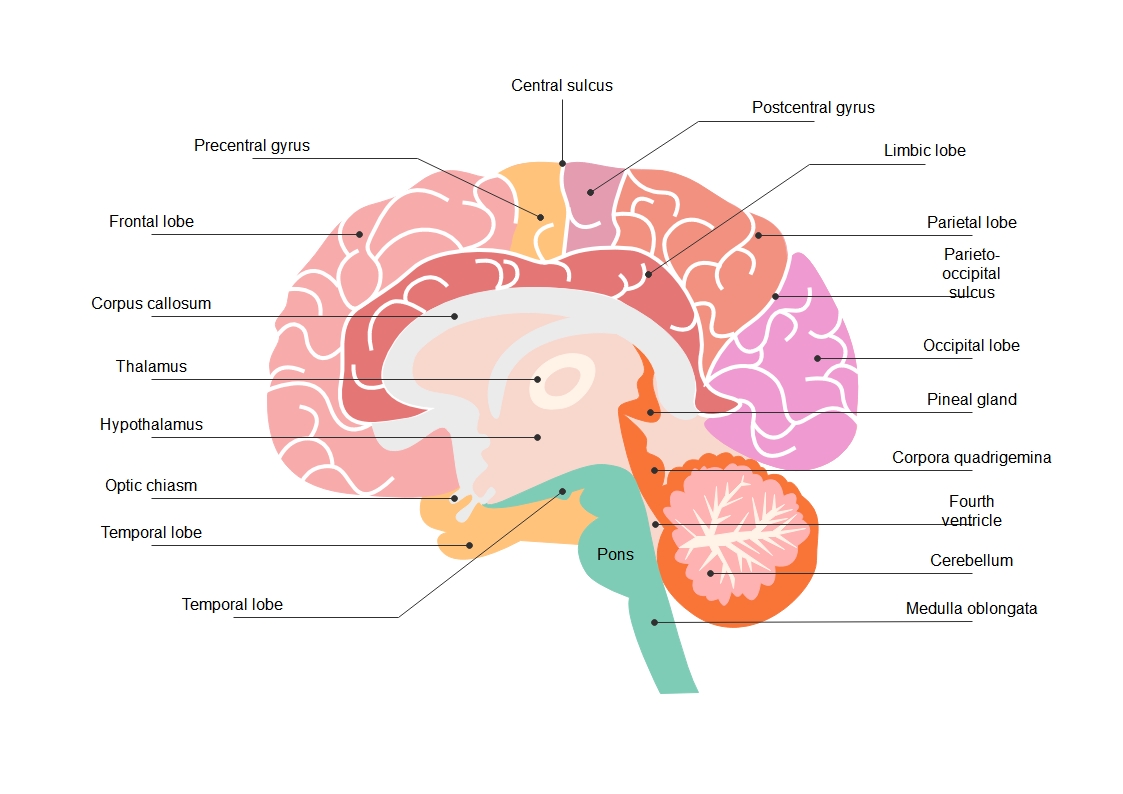
This brain diagram template provides a clear cross-section of the human brain. It accurately labels key parts such as the lobes and deep internal structures. Use this visual tool to study anatomy or create educational posters for science projects.
Cerebral Lobes and Gyri
The outer layers of the brain control complex reasoning and motor skills. These regions include the frontal and parietal lobes. Specific grooves called sulci help define these zones, allowing different parts of the brain to specialize.
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Precentral gyrus
- Postcentral gyrus
- Central sulcus
- Parieto-occipital sulcus
Internal Brain Structures
Deep within the brain lie structures that regulate hormones and process sensory data. These parts connect the hemispheres and manage vital needs like sleep and thirst. They also ensure that neural signals reach the correct destination quickly.
- Corpus callosum
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Limbic lobe
- Pineal gland
- Optic chiasm
Brainstem and Cerebellum
The lower regions of the brain coordinate physical movement and basic life support. This section includes the cerebellum for balance and the brainstem. The brainstem connects to the spinal cord to manage automatic body functions like breathing.
- Cerebellum
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Fourth ventricle
FAQs about this Template
-
What are the four main lobes of the human brain shown in the diagram?
The four main lobes are the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. The frontal lobe handles planning and movement, while the parietal lobe processes sensory information. The occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision. Finally, the temporal lobe manages auditory processing and memory. Each lobe works together to ensure the body functions correctly and responds to the environment around you.
-
What is the function of the cerebellum in this brain diagram?
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, just above the brainstem. Its primary role is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements and maintain posture and balance. Without the cerebellum, simple tasks like walking or reaching for an object would become very difficult. It ensures that your movements are smooth, precise, and well-timed during all of your daily physical activities.
-
Why is the corpus callosum important for brain function?
The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain. It allows the two sides to communicate and share information instantly. This coordination is vital for complex tasks that require both logical and creative processing. It ensures that sensory input from one side of the body is understood and processed by the whole brain.