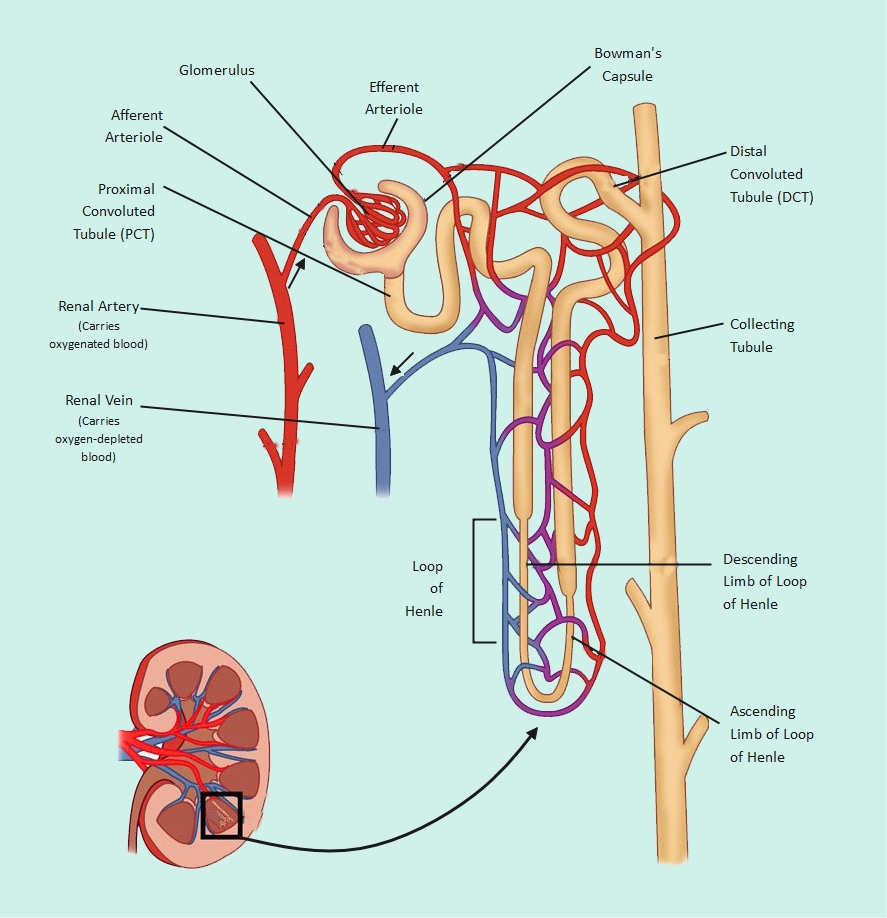
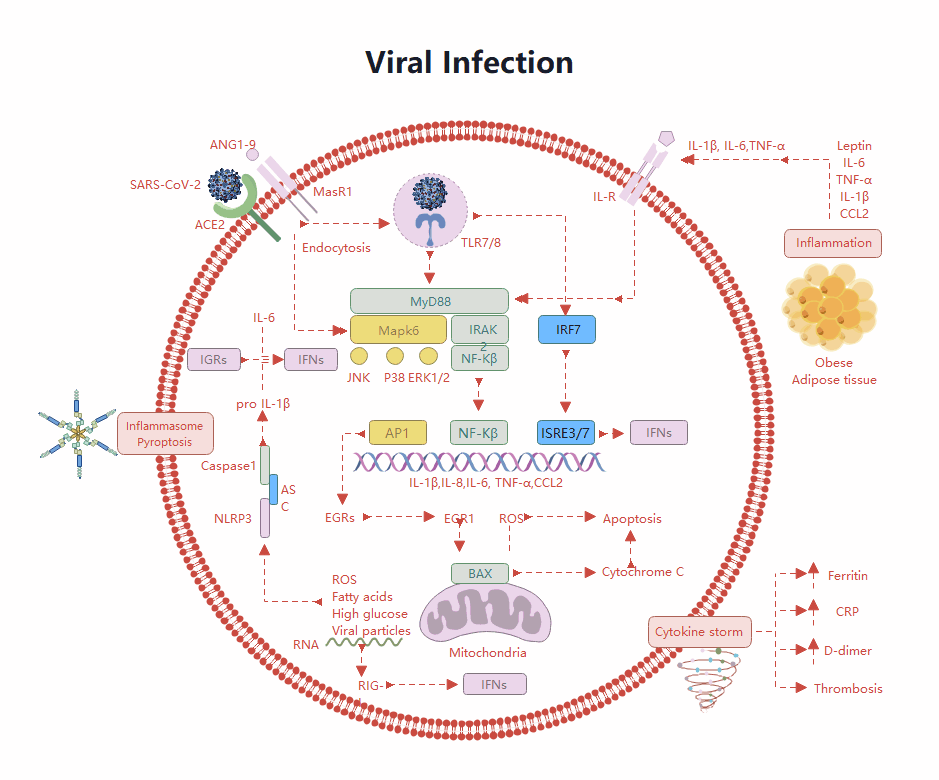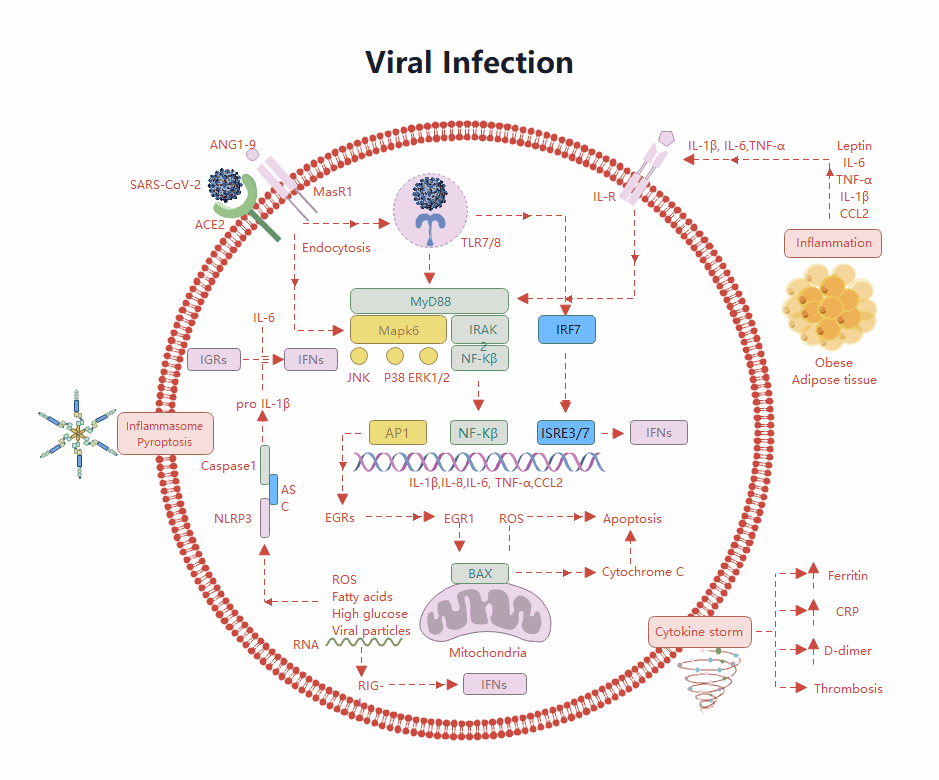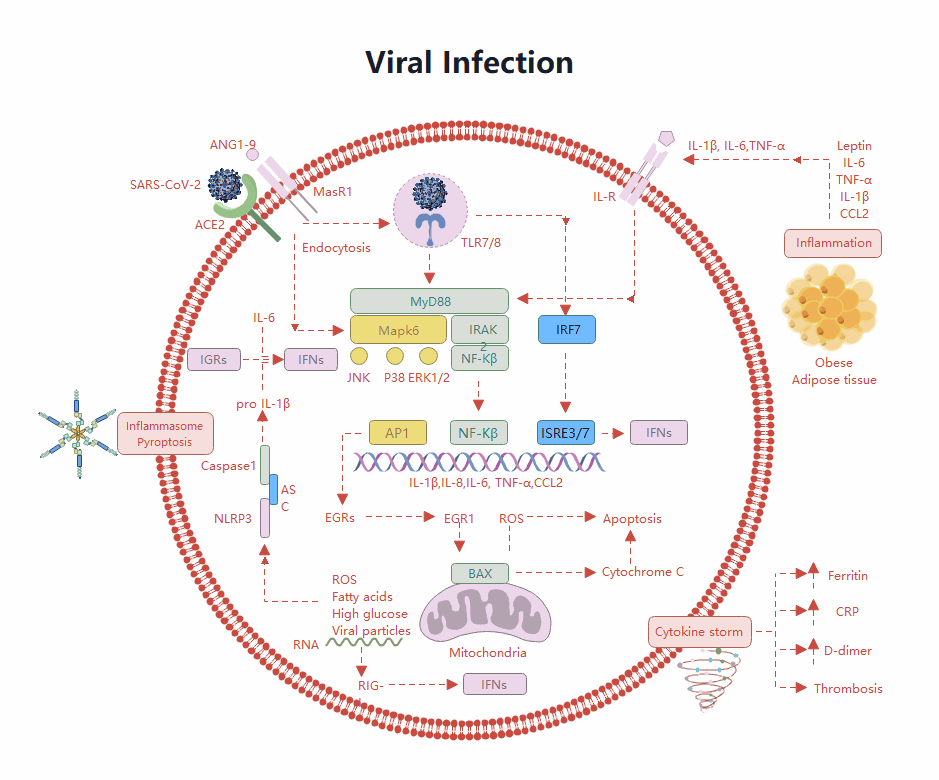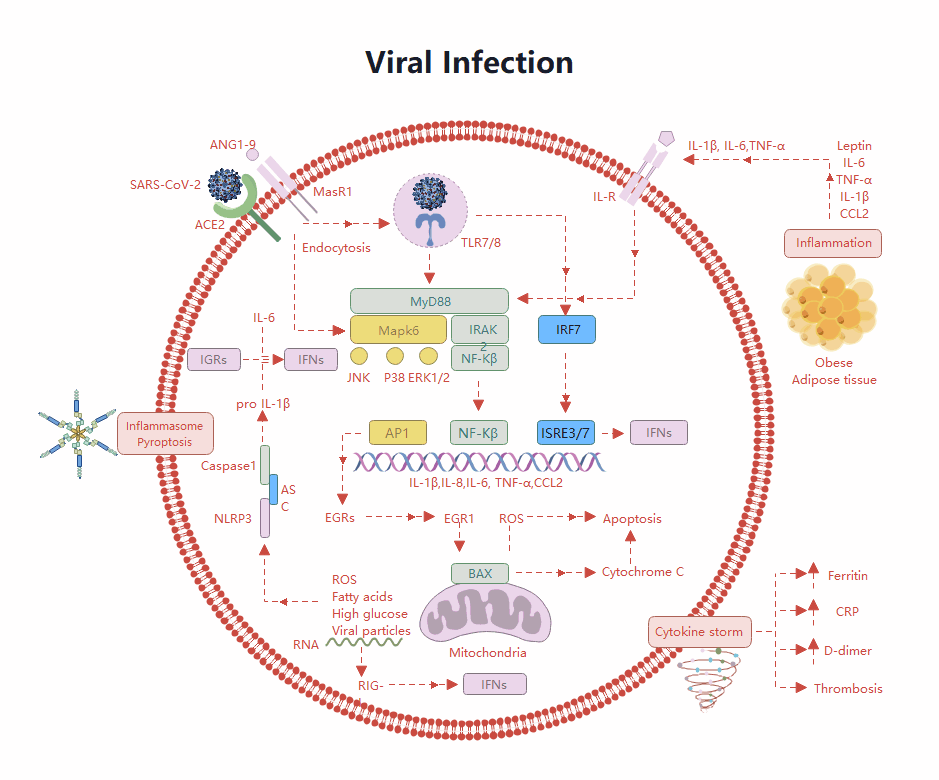
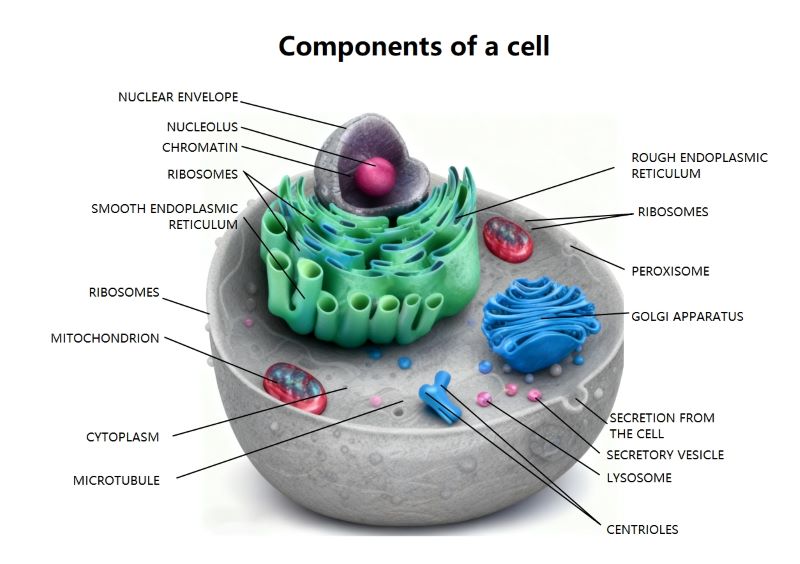
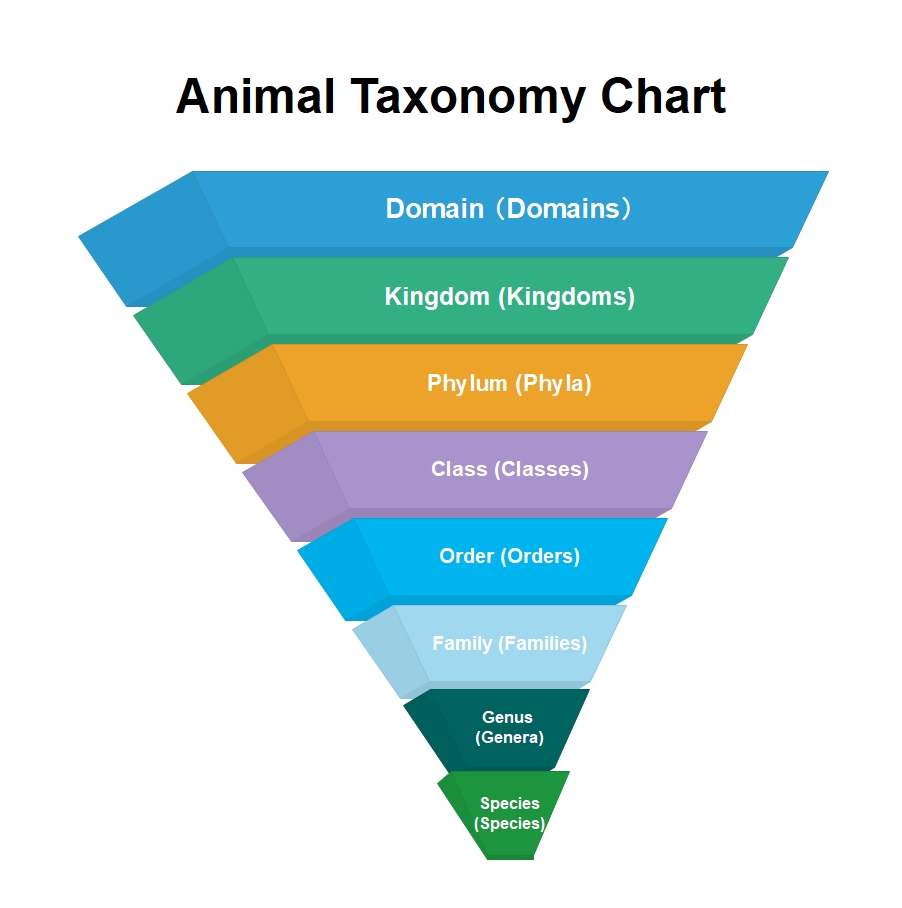
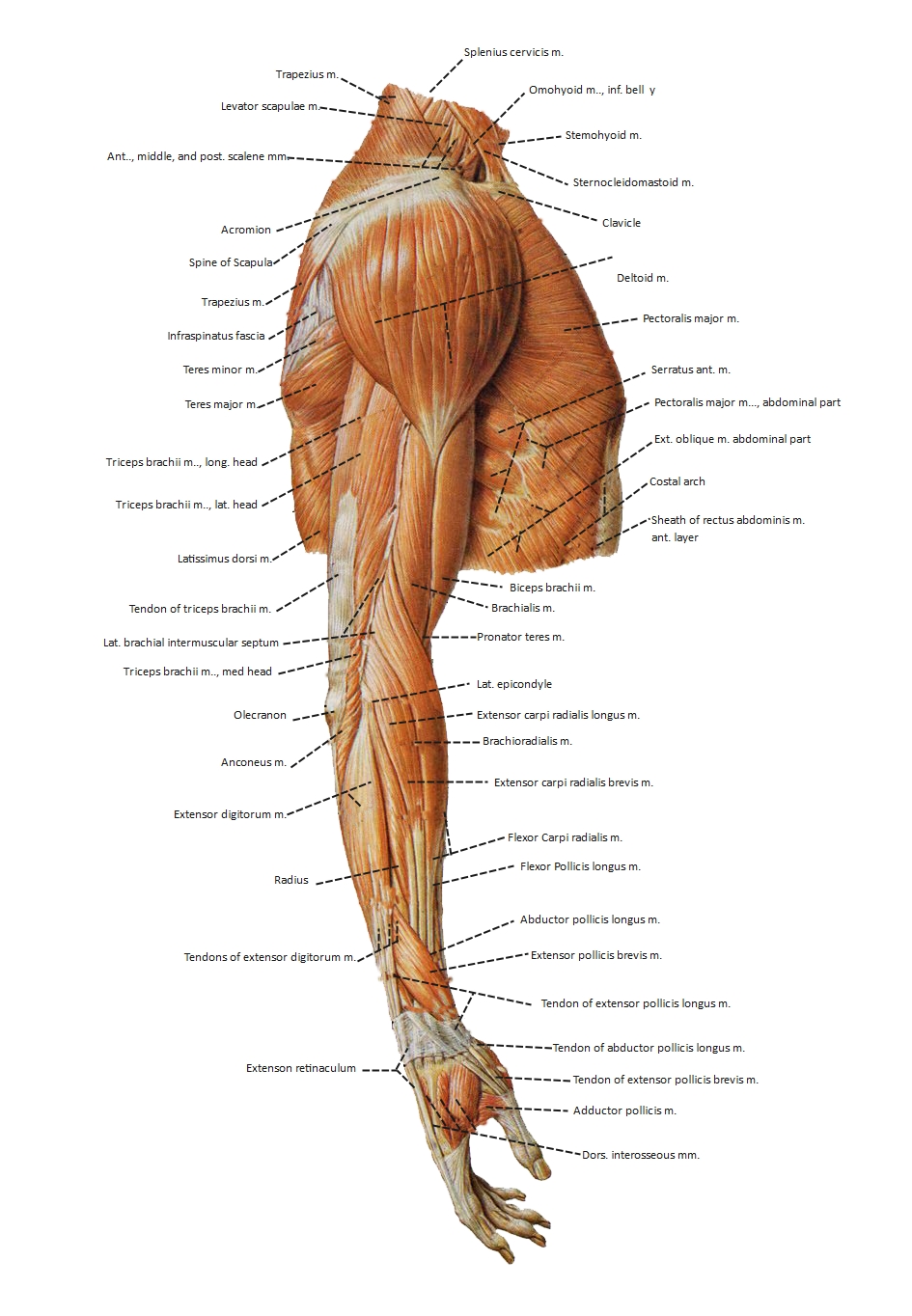
About this nephron labelled diagram template
This detailed nephron diagram provides a clear visual map of the kidney's filtration system. It highlights the connections between blood vessels and renal tubules. This template is an essential tool for biology students and medical educators to explain complex renal functions clearly.
Renal Blood Circulation
Blood enters and exits the nephron through specialized vessels to facilitate filtration. This process ensures metabolic waste is removed. Meanwhile, oxygenated blood continues to circulate throughout the body to support vital organ health and daily biological function.
- Renal Artery (Carries oxygenated blood)
- Renal Vein (Carries oxygen-depleted blood)
- Afferent Arteriole
- Efferent Arteriole
Renal Corpuscle Structure
The renal corpuscle is the initial site of blood filtration within the nephron. It consists of a cluster of capillaries and a surrounding capsule. This part captures the filtrate before it moves into the complex renal tubule system.
- Glomerulus
- Bowman's Capsule
The Tubular System
The tubular system processes the filtrate by reabsorbing nutrients and secreting waste. As liquid travels through these distinct sections, its concentration changes. It eventually forms urine for excretion from the body to maintain internal chemical stability and balance.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- Loop of Henle (Descending and Ascending limbs)
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- Collecting Tubule
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the main job of the nephron in the human body?
The nephron serves as the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its primary role is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts. It filters the blood, reabsorbs what is needed, and excretes the rest as urine. This complex process is vital for maintaining homeostatic balance, controlling blood pressure, and managing the body's overall fluid volume levels.
-
How do the Glomerulus and Bowman's Capsule work together?
The Glomerulus is a high-pressure capillary network where the actual filtration of blood occurs. In contrast, the Bowman's Capsule is a cup-like sac that surrounds the Glomerulus. Its function is to collect the primary filtrate that passes through the glomerular walls. Together, they form the renal corpuscle, which is the essential starting point for urine formation within every nephron structure in your kidneys.
-
Why is the Loop of Henle important for urine concentration?
The Loop of Henle plays a critical role in creating a concentration gradient in the kidney's medulla. By utilizing a countercurrent multiplier system, it allows the kidney to reabsorb water and ions effectively. This process is essential for producing concentrated urine when the body needs to conserve water. Without this specific structure, the body would lose excessive amounts of fluid and vital electrolytes every single day.