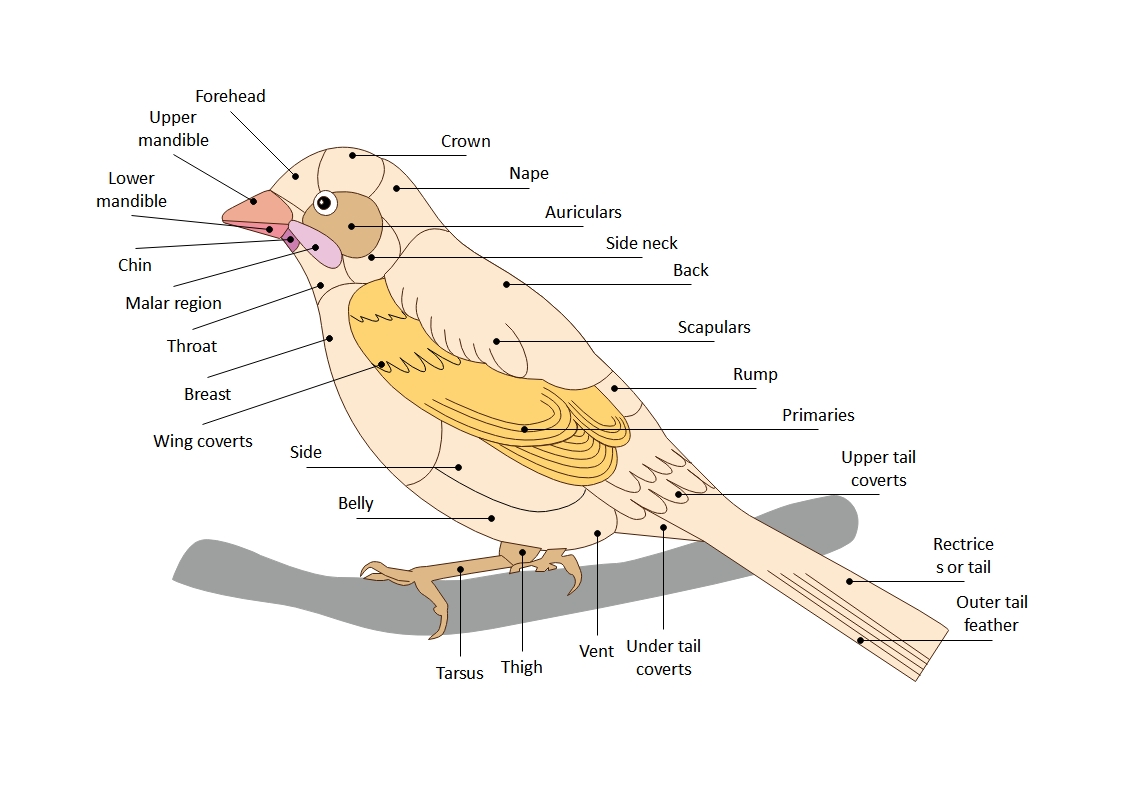
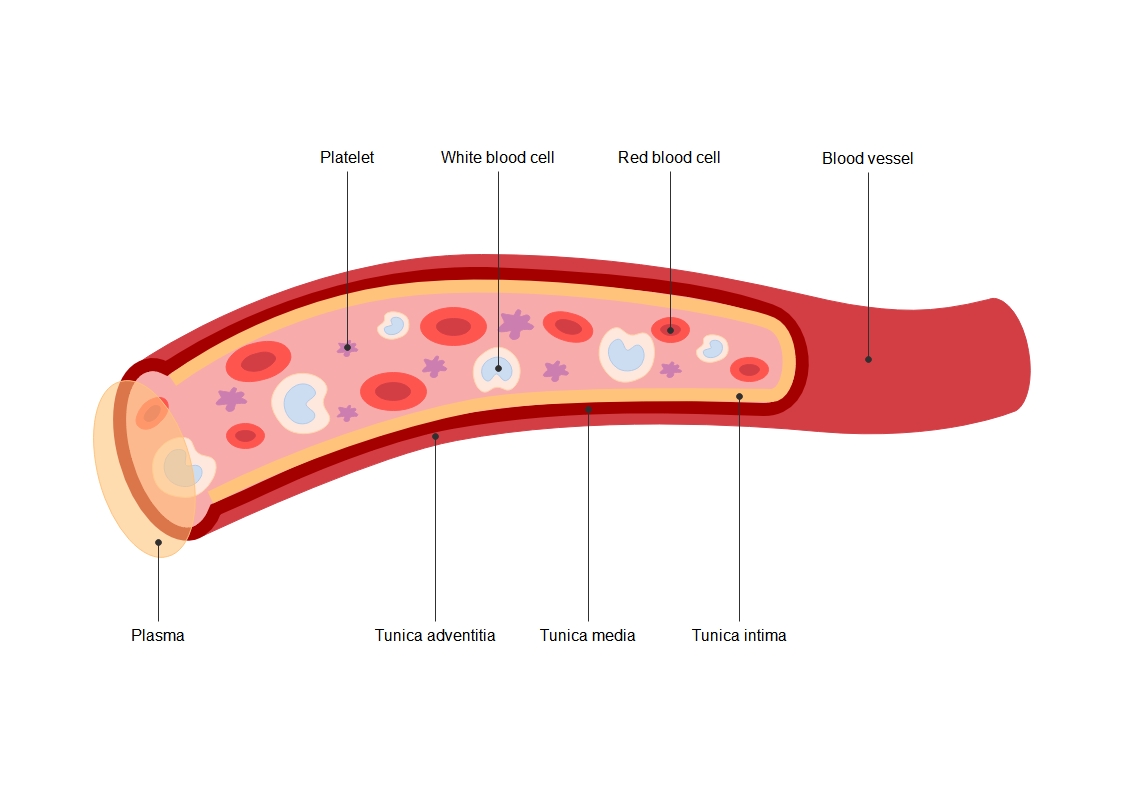
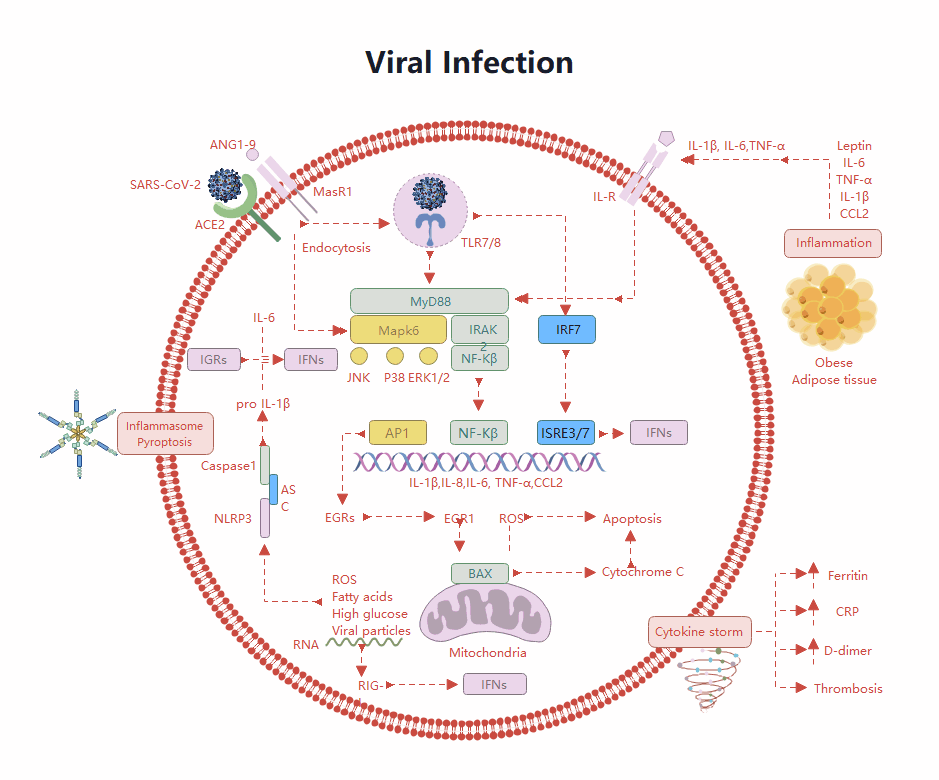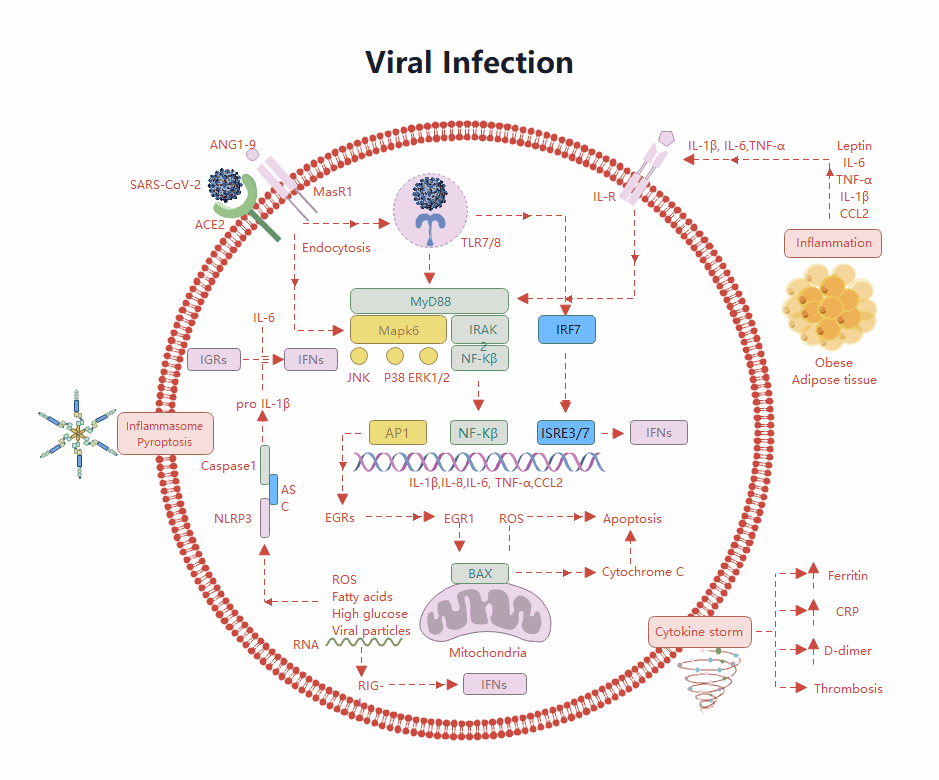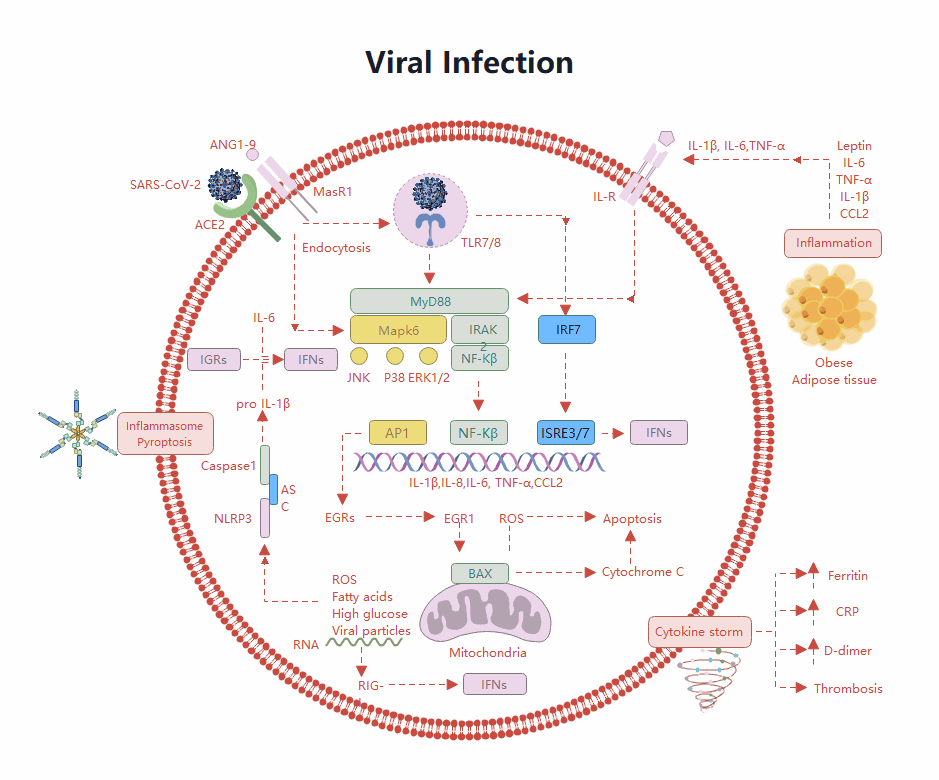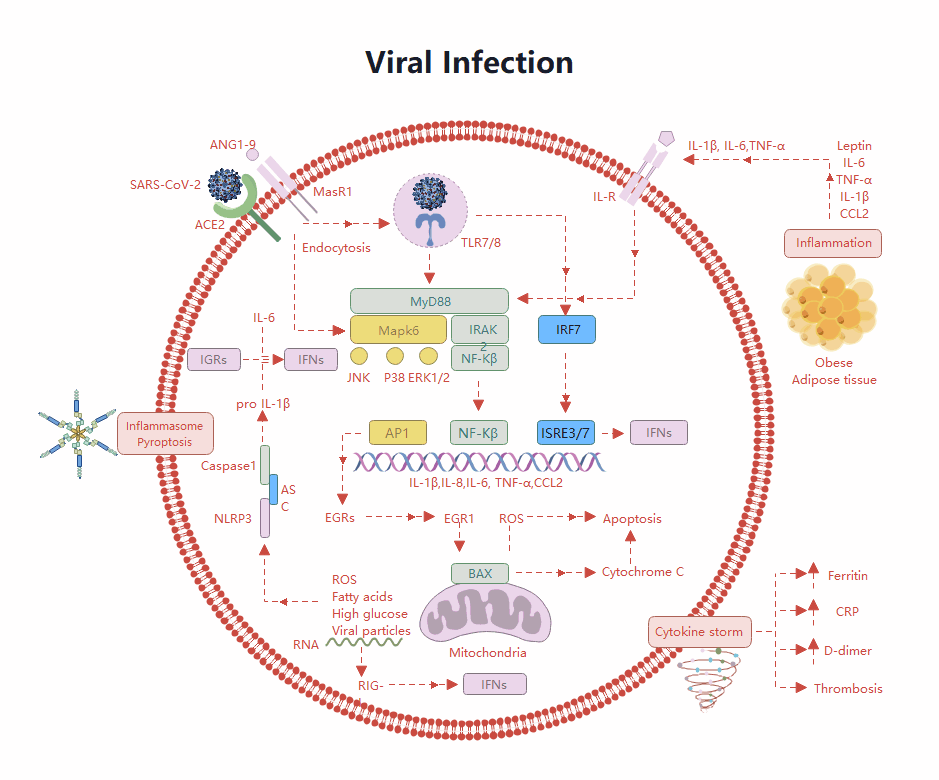
About this elbow joint anatomy template
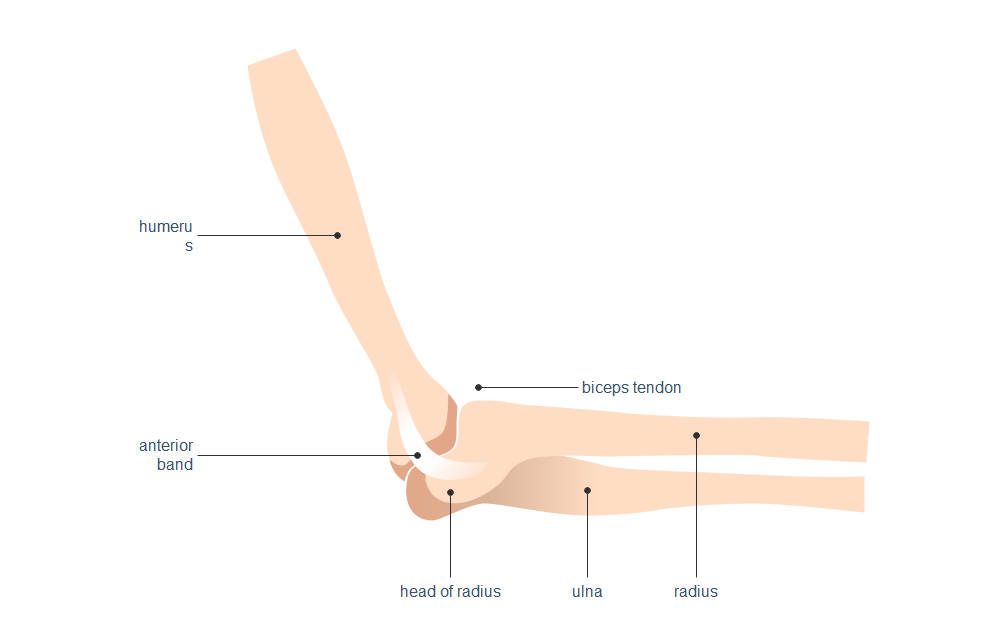
This template offers a clear visual breakdown of the human elbow's primary components. It is designed to help students and healthcare professionals identify the specific bones and soft tissues that ensure the arm remains stable and functional during movement.
Bony Structures of the Elbow
The union of three major bones forms the elbow joint. These provide the structural framework for the arm's movement. Understanding how the humerus connects with the forearm bones is essential for medical study.
- Humerus
- Ulna
- Radius
- Head of radius
Connective Tissues and Tendons
Connective tissues like tendons and ligaments are vital for joint stability and strength. They anchor muscles to bones and hold the joint together during intense physical activities, preventing injuries like dislocations or painful ligament tears.
- Biceps tendon
- Anterior band
FAQs about this Template
-
What are the primary bones that form the elbow joint?
The human elbow joint is composed of three primary bones: the humerus, the radius, and the ulna. The humerus is the long bone of the upper arm, while the radius and ulna make up the forearm. These bones meet to form a complex hinge that allows for bending, straightening, and the essential rotation of the forearm and hand.
-
What is the function of the biceps tendon at the elbow?
The biceps tendon at the elbow, known as the distal biceps tendon, connects the biceps muscle to the radius bone. Its main function is to allow for powerful elbow flexion and forearm supination, which is the rotation of the palm upward. This tendon is crucial for activities that require lifting or turning movements, such as using a screwdriver.
-
Why is the anterior band significant for elbow stability?
The anterior band is the most critical part of the medial collateral ligament complex in the elbow. It acts as the primary stabilizer against valgus stress, which is the outward force applied to the joint. This band is particularly important for athletes like baseball pitchers, as it helps maintain joint integrity during high-speed overhead throwing motions.