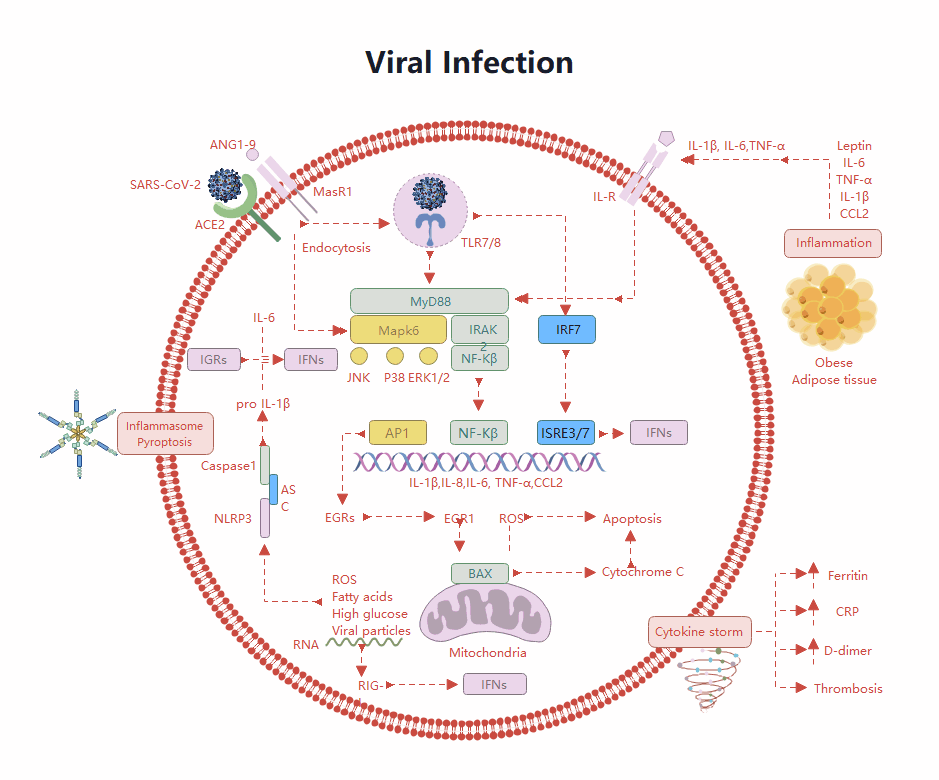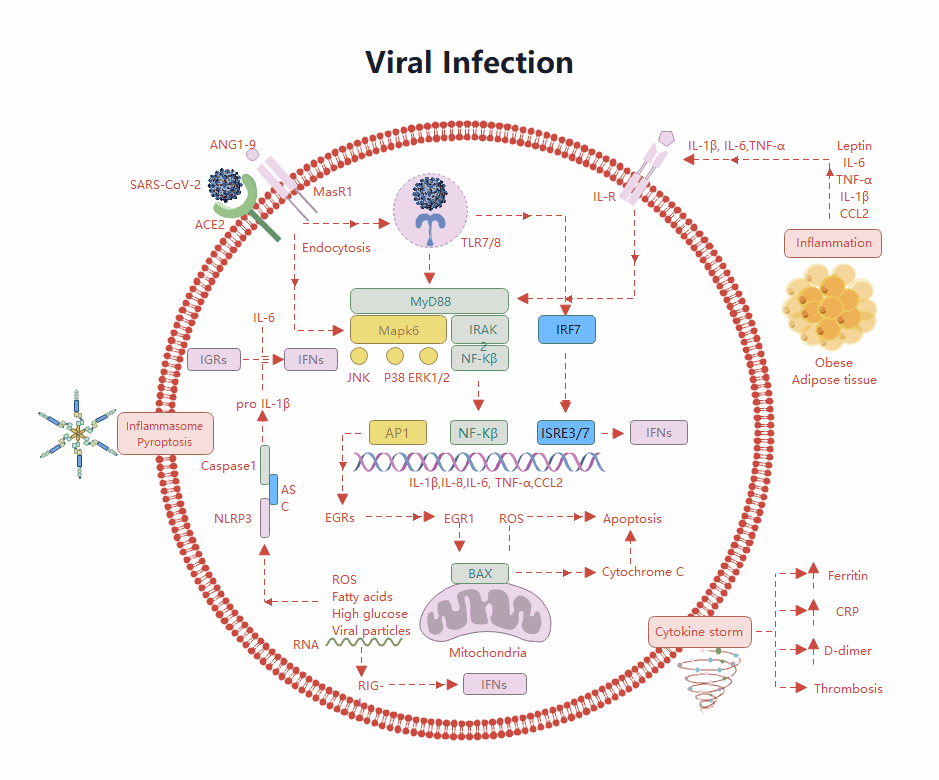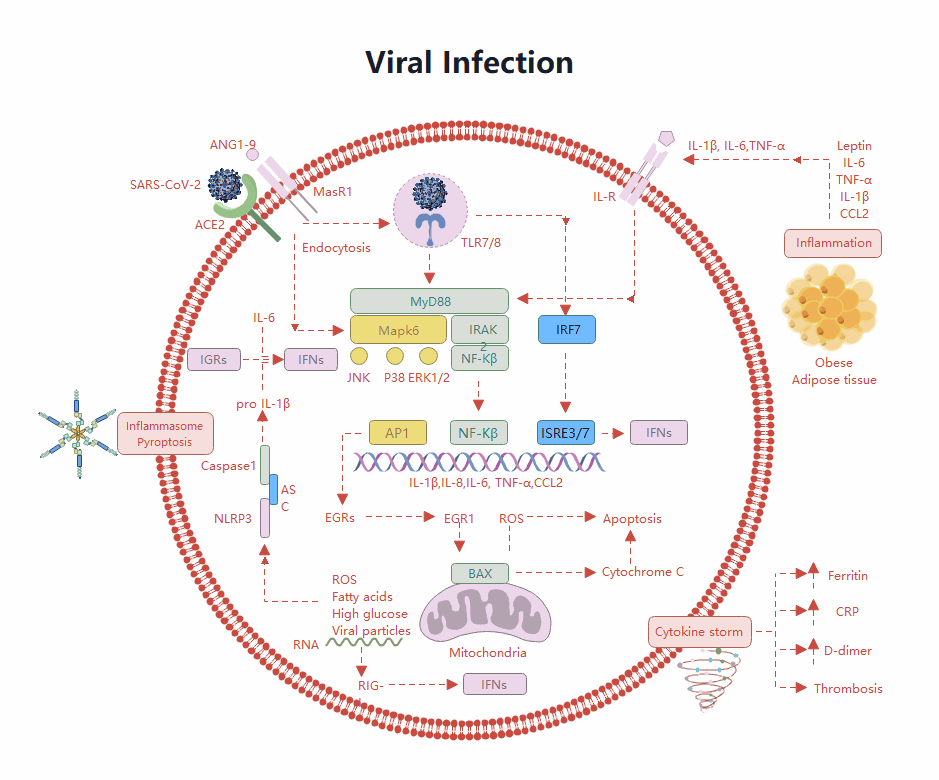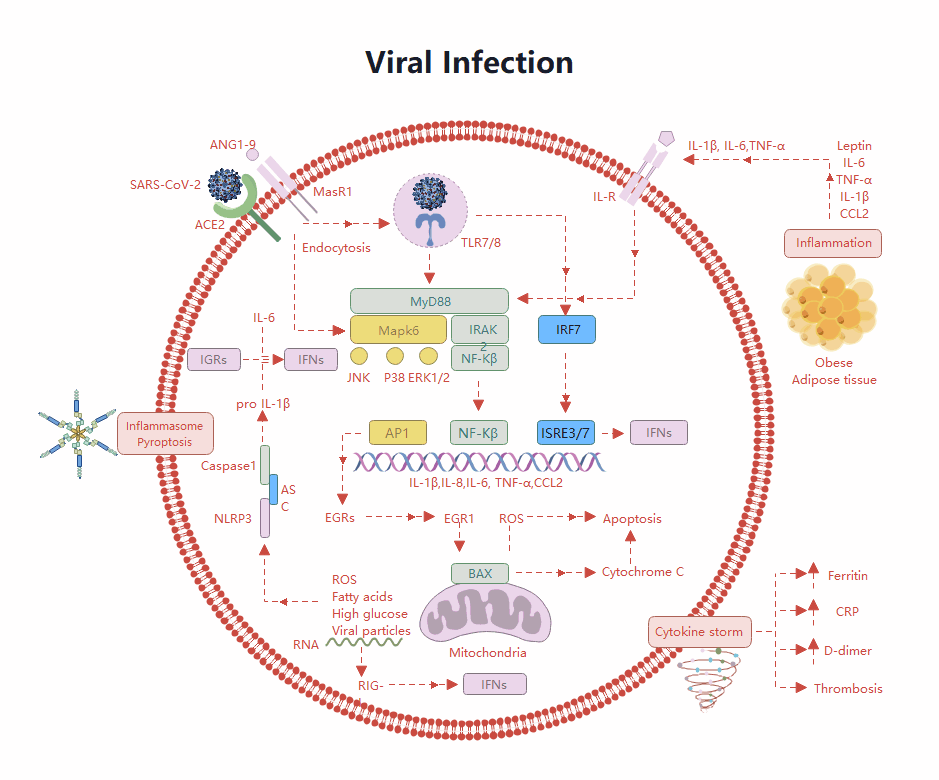
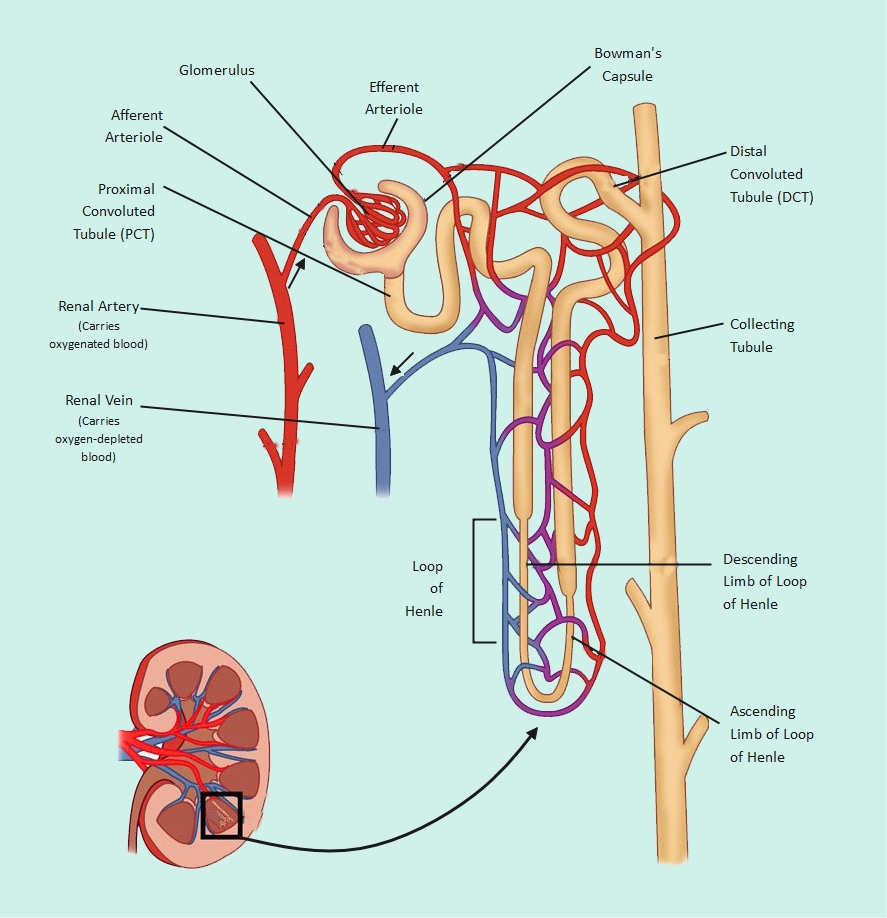
About this human lung diagram template
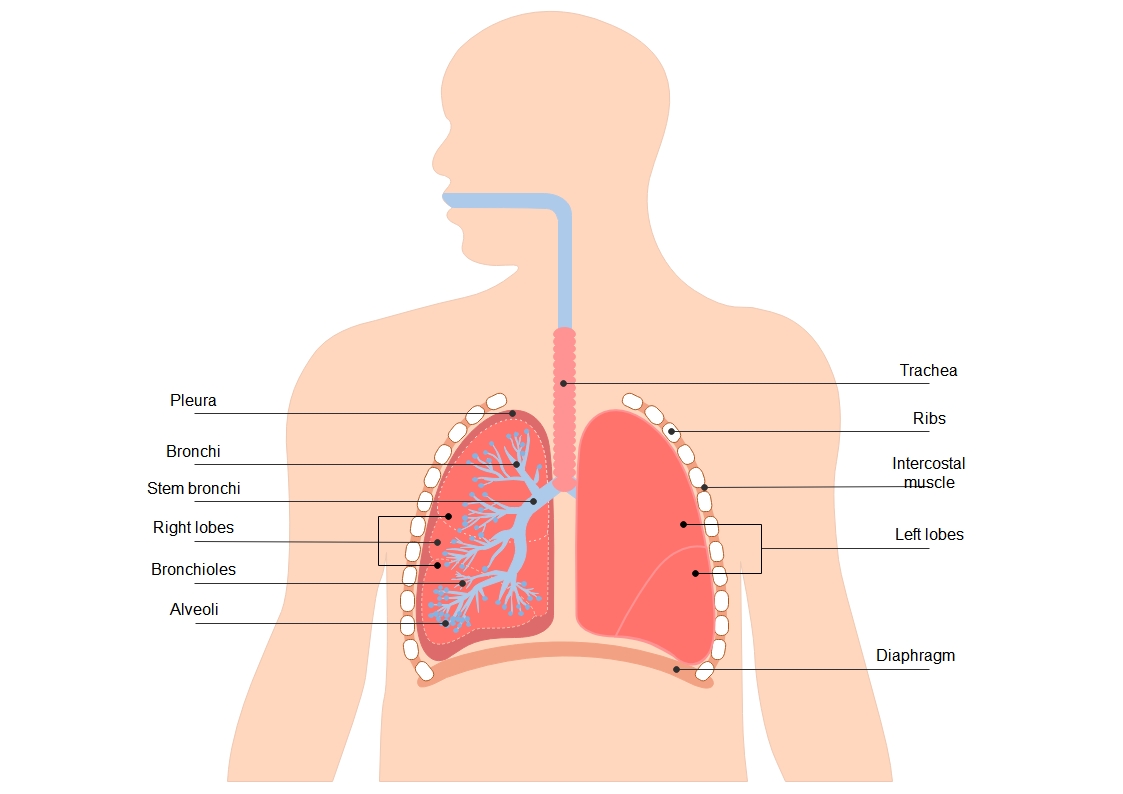
This human lung diagram template provides a clear visual breakdown of the respiratory system. It is designed for students, teachers, and medical professionals. You can easily customize labels and colors to fit your specific educational needs.
Upper Respiratory Structures
The upper respiratory structures act as the main gateway for air entering the body. These parts filter, warm, and moisten the air before it reaches the sensitive tissues deeper inside the chest cavity for gas exchange.
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Stem bronchi
Lung Anatomy and Lobes
The lungs are the primary organs of respiration located in the thoracic cavity. They are divided into distinct sections called lobes. These structures expand and contract efficiently to facilitate the vital process of continuous breathing.
- Right lobes
- Left lobes
- Pleura
Bronchial Tree and Alveoli
Inside the lungs, the airways branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles. These lead to tiny air sacs where oxygen enters the bloodstream. This complex network is essential for maximizing the surface area available for gas transfer.
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
Protective and Functional Muscles
The lungs are protected and supported by several external structures. These parts work together to create the pressure changes needed for inhalation and exhalation. They also provide a physical shield against impact and external injury.
- Ribs
- Intercostal muscle
- Diaphragm
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the main function of the human lung?
The primary function of the human lung is to facilitate gas exchange through a process called respiration. When you inhale, your lungs take in oxygen from the air and pass it into the bloodstream. Simultaneously, they collect carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, from the blood and expel it from the body when you exhale.
-
How do the diaphragm and ribs help with breathing?
The diaphragm and ribs work together to change the volume of the chest cavity. When the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, and the intercostal muscles pull the ribs upward and outward, the chest cavity expands. This creates a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs. Relaxing these muscles allows the chest to shrink and push air out.
-
Why are the alveoli so important in the respiratory system?
Alveoli are tiny, grape-like air sacs located at the end of the bronchial tubes. They are the exact site where gas exchange occurs. Their thin walls allow oxygen to diffuse easily into the surrounding capillaries while carbon dioxide moves out. Without these millions of tiny sacs, the body could not get enough oxygen to survive.