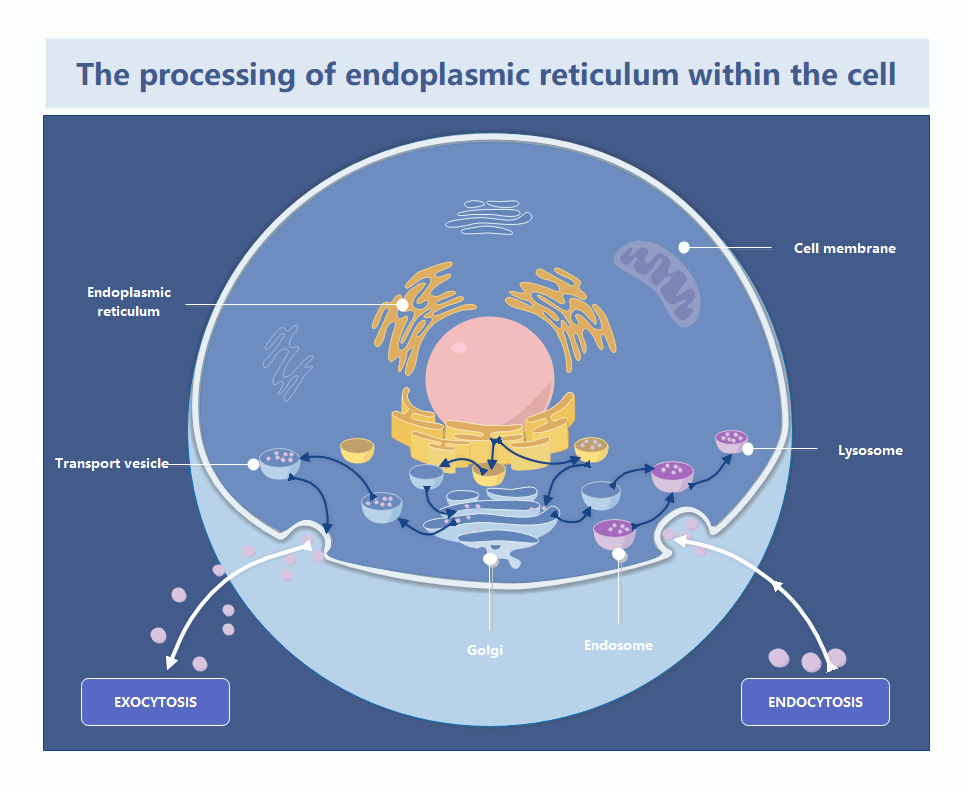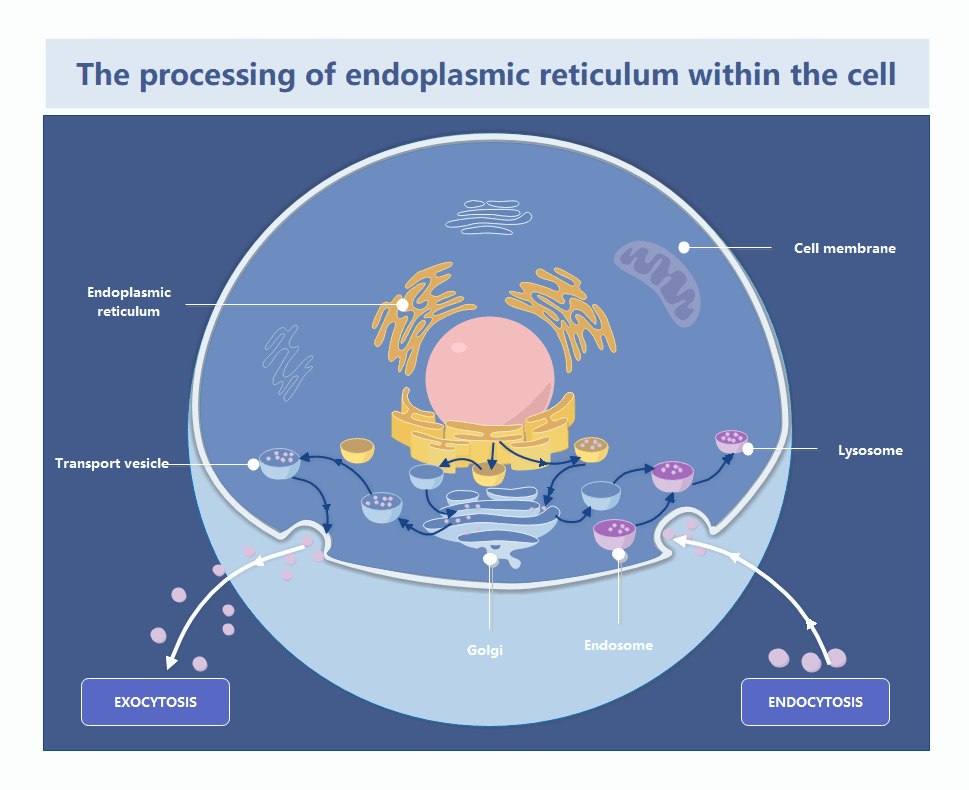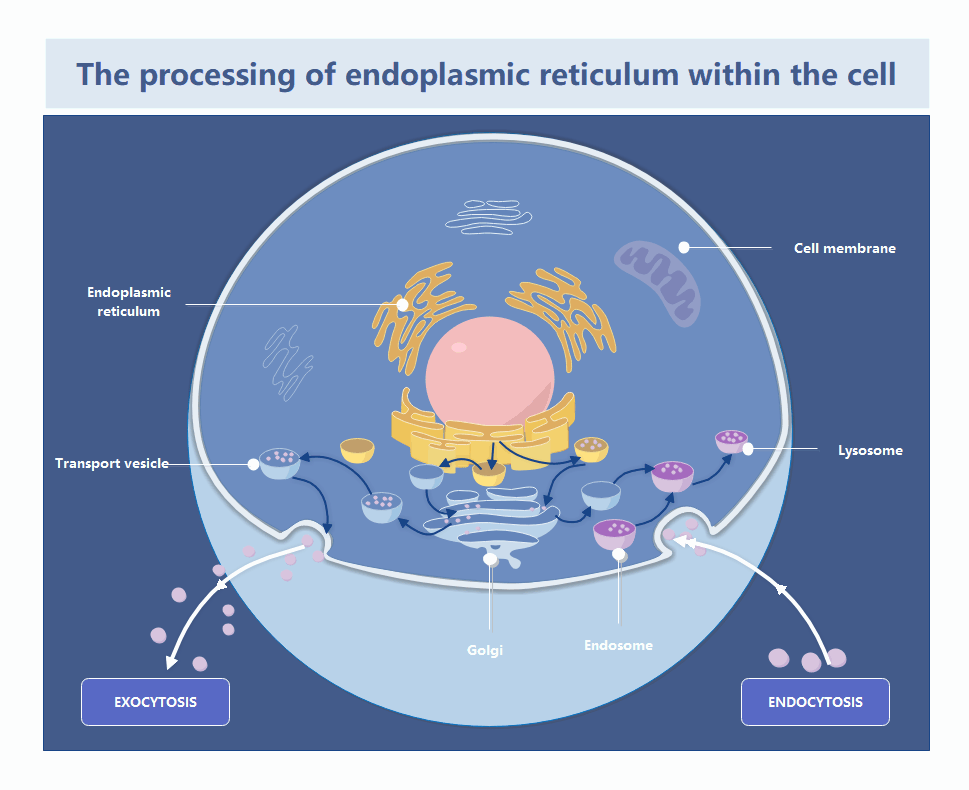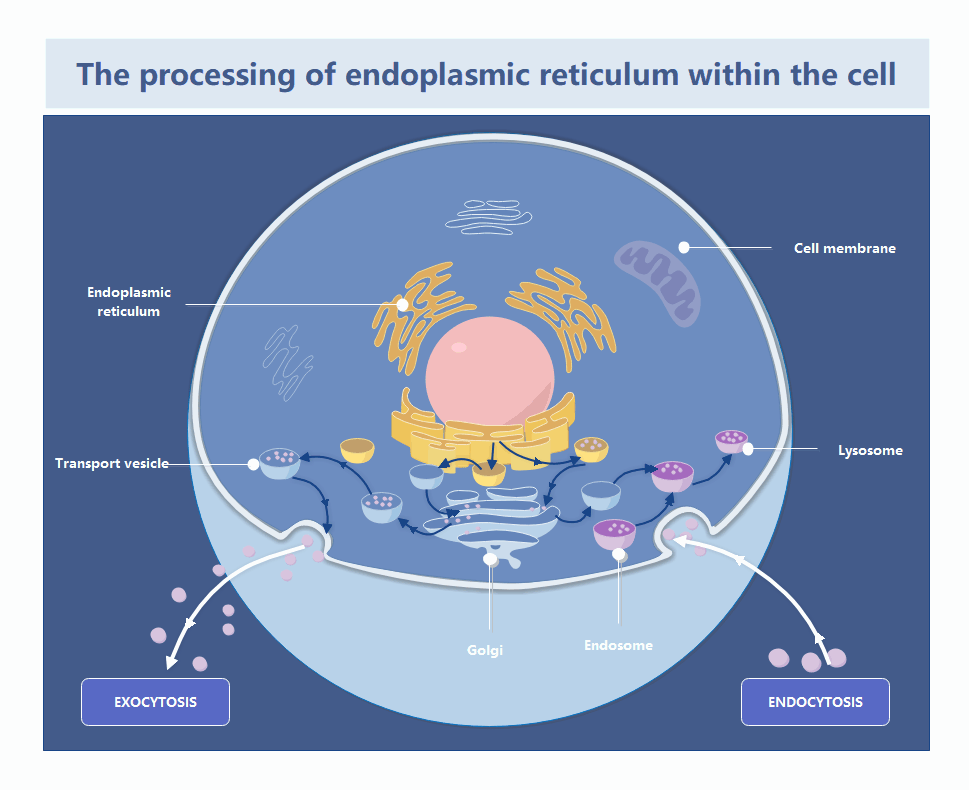
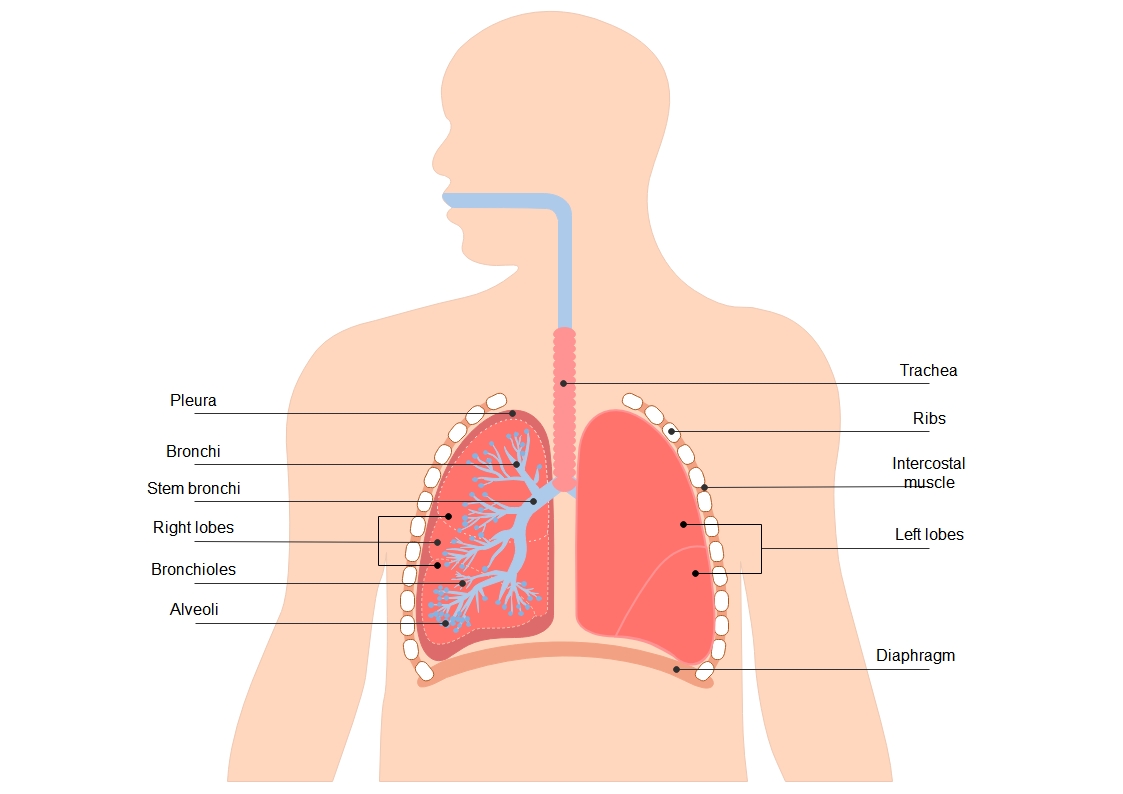
About this Flower parts diagram template
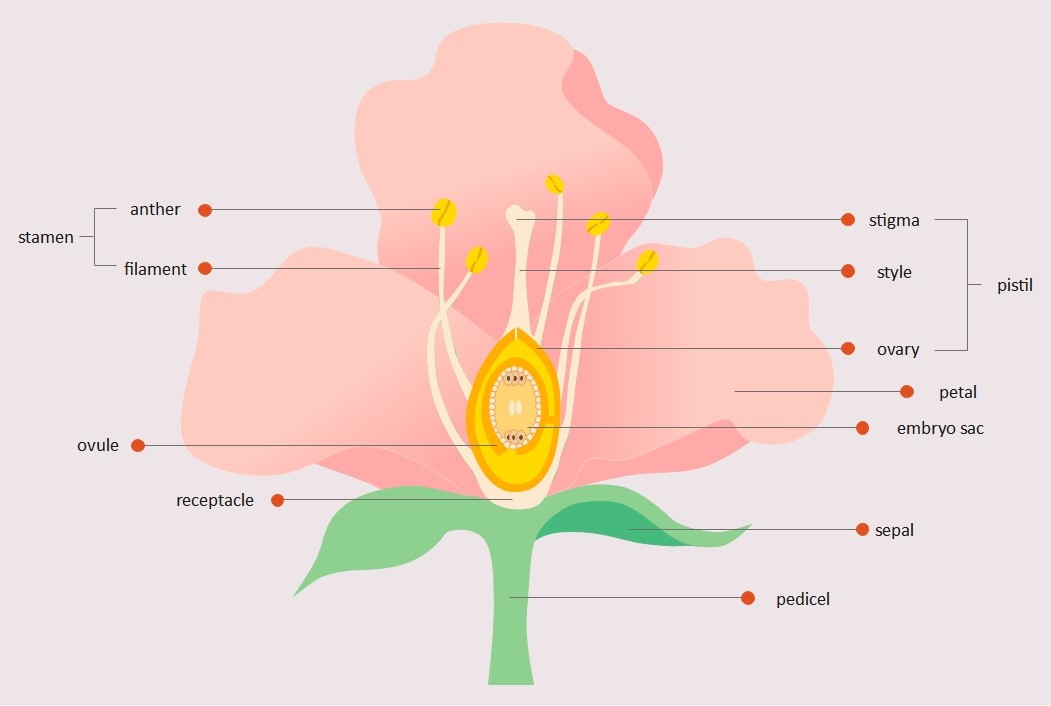
This flower parts diagram template is a professional educational resource designed to illustrate the internal and external anatomy of a typical flower. It highlights key reproductive organs and supporting structures, making it an ideal tool for teaching plant science and pollination concepts.
Stamen (Male Parts)
The stamen represents the male reproductive organ of a flower. It consists of two primary components that work together to produce and deliver pollen, which is necessary for the fertilization process in plants.
- Anther
- Filament
Pistil (Female Parts)
The pistil is the central female reproductive part of a flower. It is composed of three main structures that receive pollen and facilitate the development of seeds within the protected environment of the ovary.
- Stigma
- Style
- Ovary
Internal Reproductive Structures
Inside the flower, several critical parts support the development of future seeds. These internal elements house the genetic material and provide the nutrients required for the initial stages of a new plant's life cycle.
- Ovule
- Embryo sac
Supporting and Accessory Parts
Flowers also contain non-reproductive parts that play vital roles in protection and attraction. These components support the flower's structure and help attract pollinators like bees or butterflies to ensure successful reproduction occurs.
- Petal
- Sepal
- Receptacle
- Pedicel
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the primary function of the stamen and pistil in a flower?
The stamen and pistil are the essential reproductive organs of a flower. The stamen serves as the male part, producing pollen in the anther. The pistil is the female part, which collects pollen on the stigma and facilitates fertilization in the ovary. Together, these structures allow plants to produce seeds and continue their species through the process of sexual reproduction.
-
Why are petals usually bright and colorful in most flowers?
Brightly colored petals serve a specific biological purpose to ensure the plant's survival. They act as visual signals to attract pollinators, such as birds, bees, and butterflies. These animals visit the flower for nectar and inadvertently move pollen between plants. Without colorful petals to grab their attention, many flowering plants would struggle to achieve successful pollination and produce healthy seeds.
-
What role does the pedicel play in the anatomy of a flower?
The pedicel is a small stalk that supports an individual flower within an inflorescence or on a stem. Its main job is to hold the flower in an optimal position for pollination by wind or animals. Additionally, the pedicel acts as a transport channel, moving water and essential nutrients from the rest of the plant to the developing floral parts.