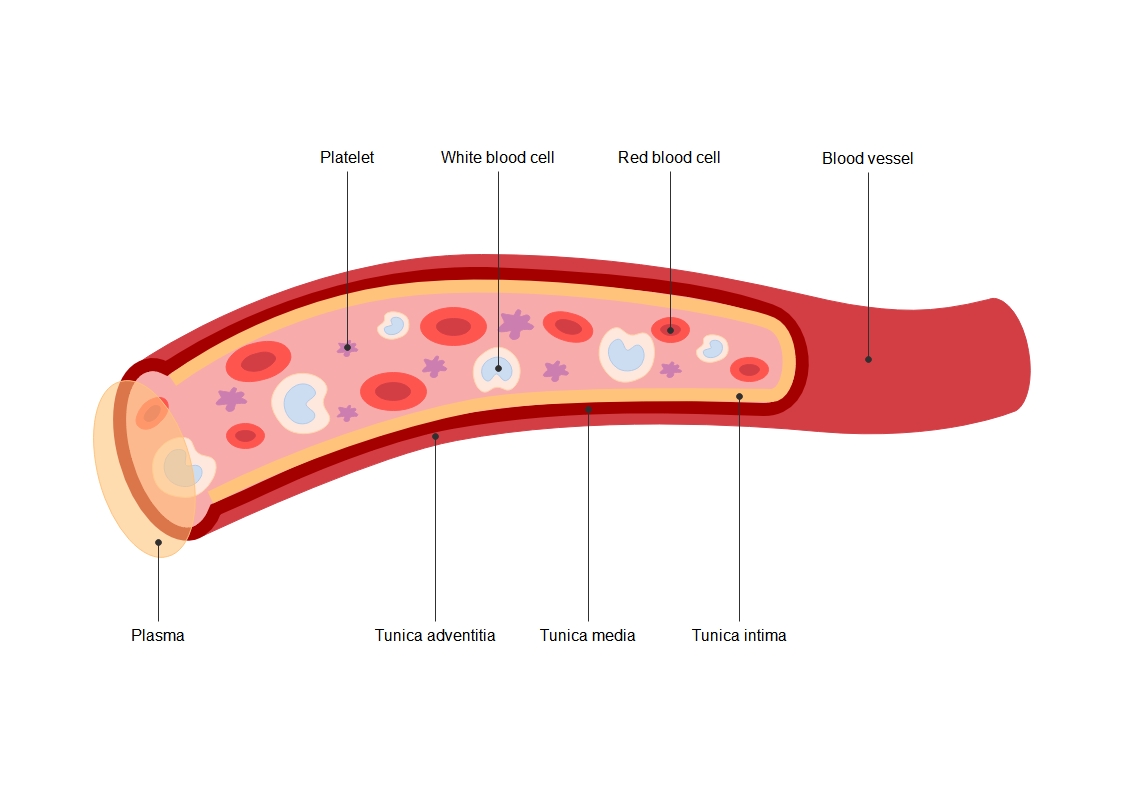
About this Embryo implantation template
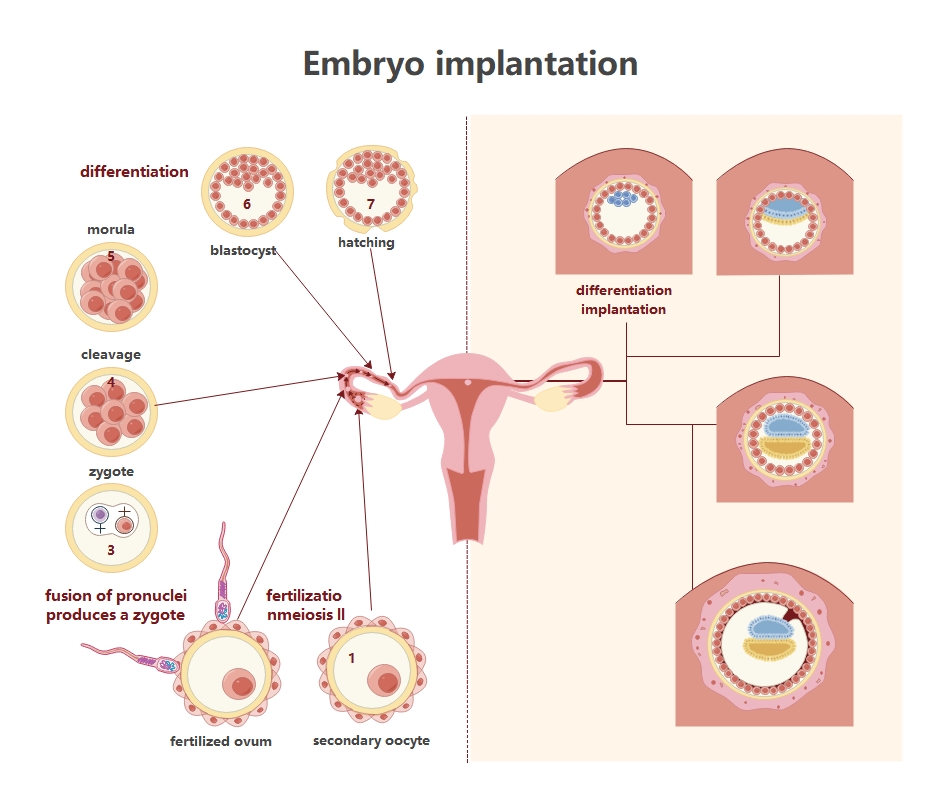
This diagram visualizes the biological journey from fertilization to implantation. It provides a clear map of cellular development and anatomical transitions within the female reproductive system for educational or medical presentations.
Early Fertilization and Zygote Formation
This initial phase captures the moment sperm meets the egg to create life. It includes the secondary oocyte stage and the fusion of pronuclei, which eventually results in a single-celled zygote.
- Secondary oocyte
- Fertilized ovum
- Fusion of pronuclei
- Zygote formation
Cleavage and Morula Stages
After fertilization, the zygote begins rapid cell division known as cleavage. These divisions transform the single cell into a solid ball of cells called a morula as it travels toward the uterus.
- Rapid cell cleavage
- Development of the morula
- Transportation through the fallopian tube
Blastocyst Development and Hatching
The morula becomes a hollow blastocyst, allowing for early cellular differentiation. Before the embryo can attach to the uterine wall, it must undergo hatching to break free from its outer protective layer.
- Blastocyst formation
- Cellular differentiation
- Embryo hatching
Differentiation Implantation Phase
In the final stage, the hatched blastocyst embeds itself into the vascularized uterine lining. This critical connection allows the embryo to receive nutrients and oxygen, ensuring the pregnancy continues to develop successfully.
- Attachment to the endometrium
- Trophoblast invasion
- Early placental development
FAQs about this Template
-
How long does the embryo implantation process usually take?
Embryo implantation typically occurs about six to twelve days after ovulation and fertilization. The process itself is not instantaneous; it involves a complex sequence of physical and chemical signals between the embryo and the uterine wall. Most women find that successful implantation happens around day nine, marking the definitive beginning of a clinical pregnancy.
-
What are the signs that implantation has successfully occurred?
While many women experience no symptoms at all, some may notice light spotting known as implantation bleeding. This occurs when the embryo disrupts tiny blood vessels in the uterine lining. Other early signs include mild cramping, breast tenderness, or subtle mood swings. These physical changes result from shifting hormone levels as the body prepares for pregnancy.
-
Why is the hatching stage vital for successful implantation?
The hatching stage is mandatory because the embryo is encased in a tough outer shell called the zona pellucida. For the blastocyst to interact with and stick to the uterine lining, it must first break out of this shell. If hatching fails, the embryo cannot attach to the endometrium, preventing a successful pregnancy from starting.