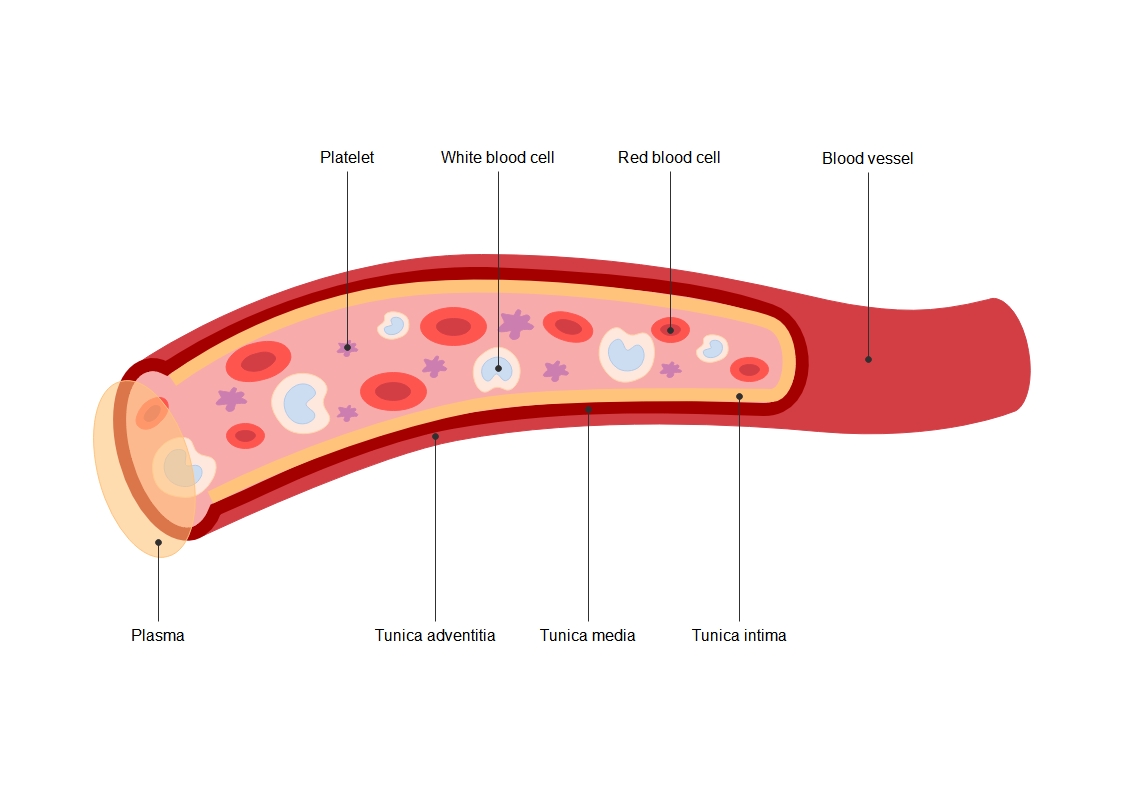
About this Endoplasmic reticulum diagram template
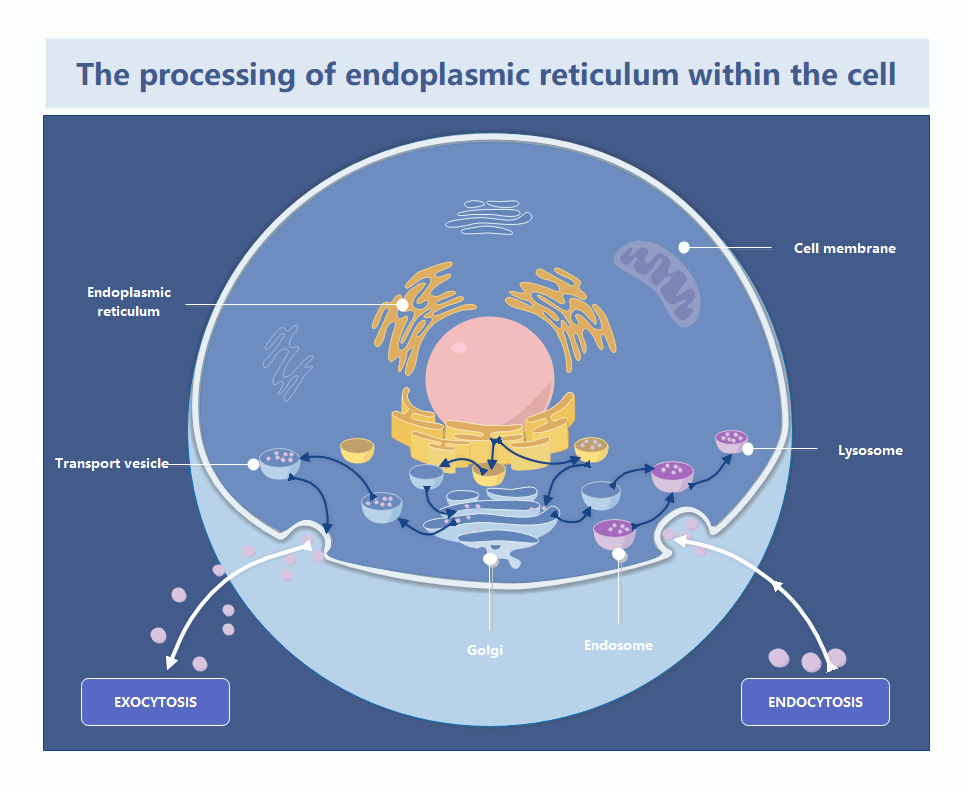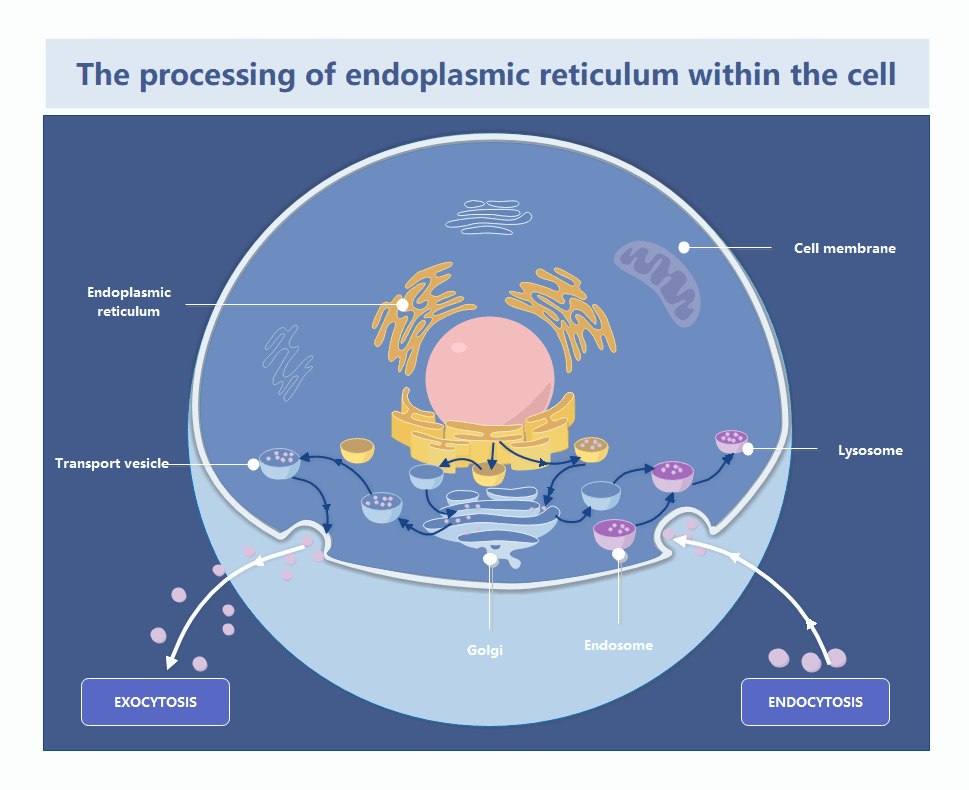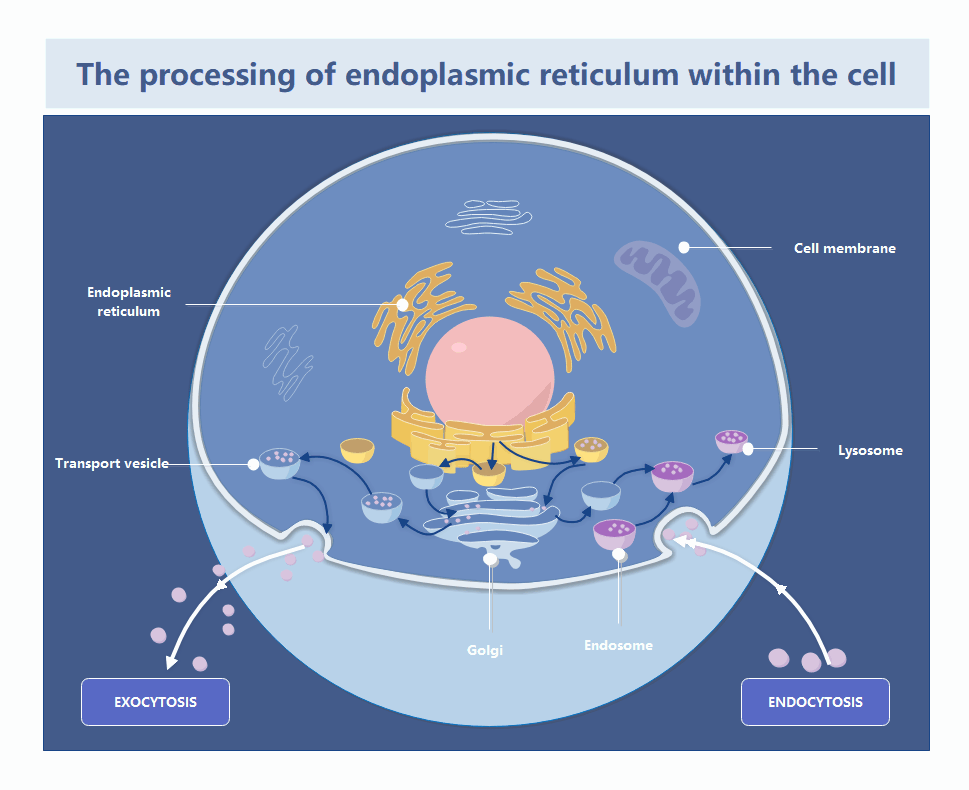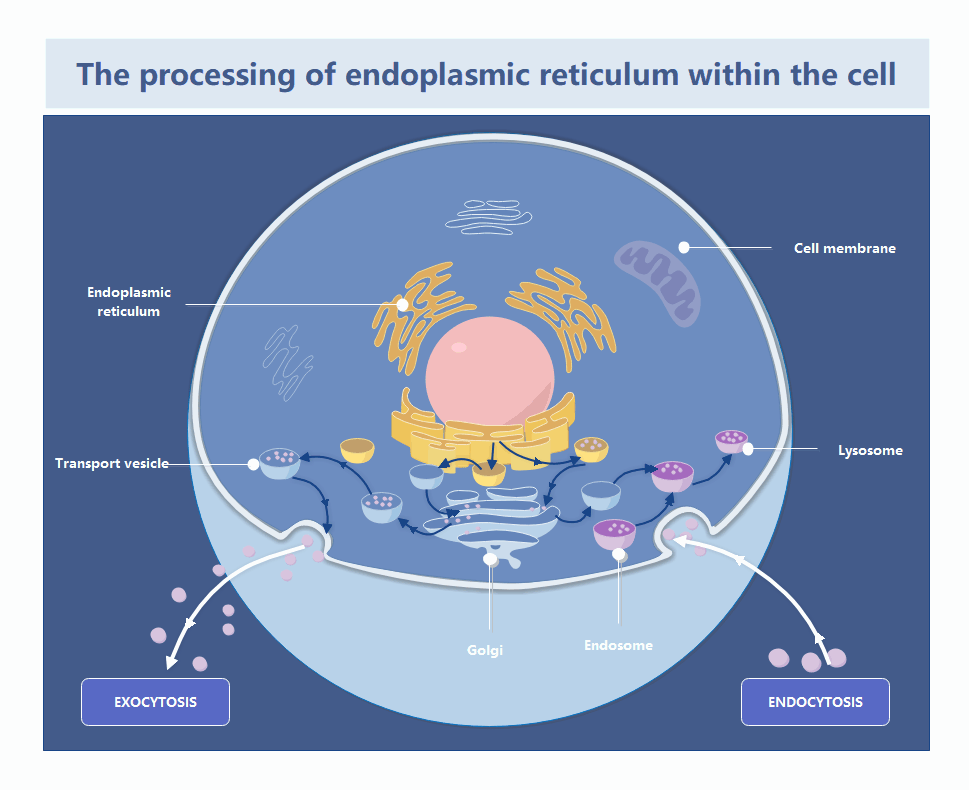
This template illustrates the complex journey of materials within a cell. It highlights how the endoplasmic reticulum interacts with the Golgi apparatus and cell membrane. Users can easily customize it to teach biological processes or study cellular transport mechanisms effectively.
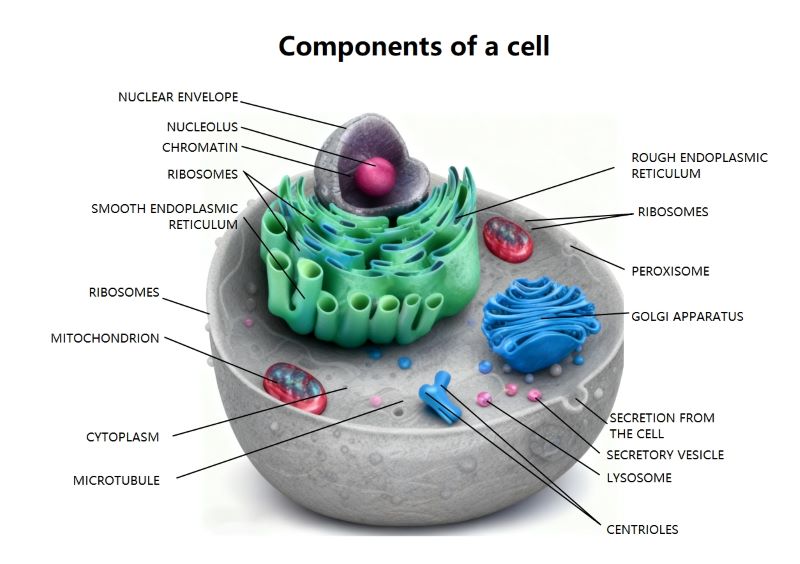
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a vast network of folded membranes located near the nucleus. It serves as the primary site for protein and lipid synthesis. These materials are then packaged for transport throughout the cell.
- Rough ER for proteins
- Smooth ER for lipids
- Membrane synthesis
- Calcium storage
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus functions as the cell's post office by receiving proteins from the ER. It modifies, sorts, and packages these molecules into vesicles. This ensures they reach the correct destination inside or outside the cell.
- Protein modification
- Lipid transport
- Vesicle formation
- Polysaccharide synthesis
Vesicular Transport
Transport vesicles move substances between organelles and the cell membrane. This process includes exocytosis for secreting materials and endocytosis for bringing them in. It maintains the cell's internal balance and allows for efficient communication with the environment.
- Exocytosis secretion
- Endocytosis intake
- Lysosome digestion
- Endosome sorting
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the main difference between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
The main difference lies in the presence of ribosomes on the surface. Rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes, making it essential for synthesizing and folding proteins. In contrast, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks these ribosomes. It focuses primarily on creating lipids, storing calcium ions, and detoxifying harmful chemicals within the cell, providing a smooth appearance under a microscope.
-
How does the endoplasmic reticulum interact with the Golgi apparatus?
The endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus work together through a coordinated transport system. Once the ER synthesizes proteins or lipids, it packages them into small transport vesicles. These vesicles travel to the Golgi apparatus, where the molecules undergo further modification and sorting. This partnership ensures that cellular products are correctly labeled and shipped to their final functional destinations.
-
Why is vesicular transport important for the survival of a cell?
Vesicular transport is critical because it allows the cell to move large molecules across its membrane and between organelles. Without this system, the cell could not secrete hormones, digest nutrients, or remove waste products. It also facilitates endocytosis and exocytosis, which are vital for maintaining the cell's shape, acquiring energy, and responding to signals from the surrounding environment.