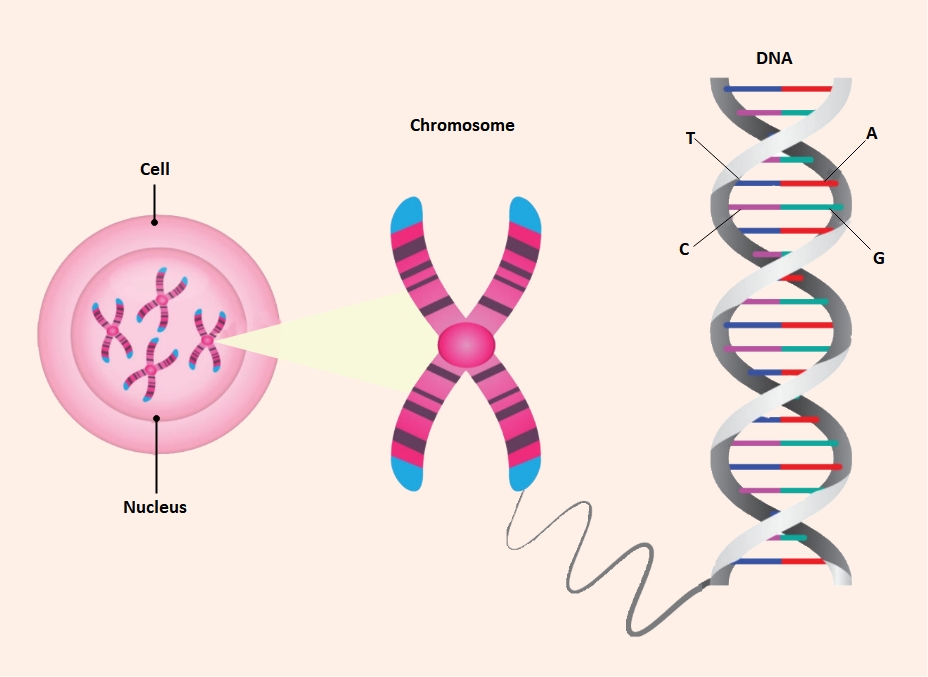
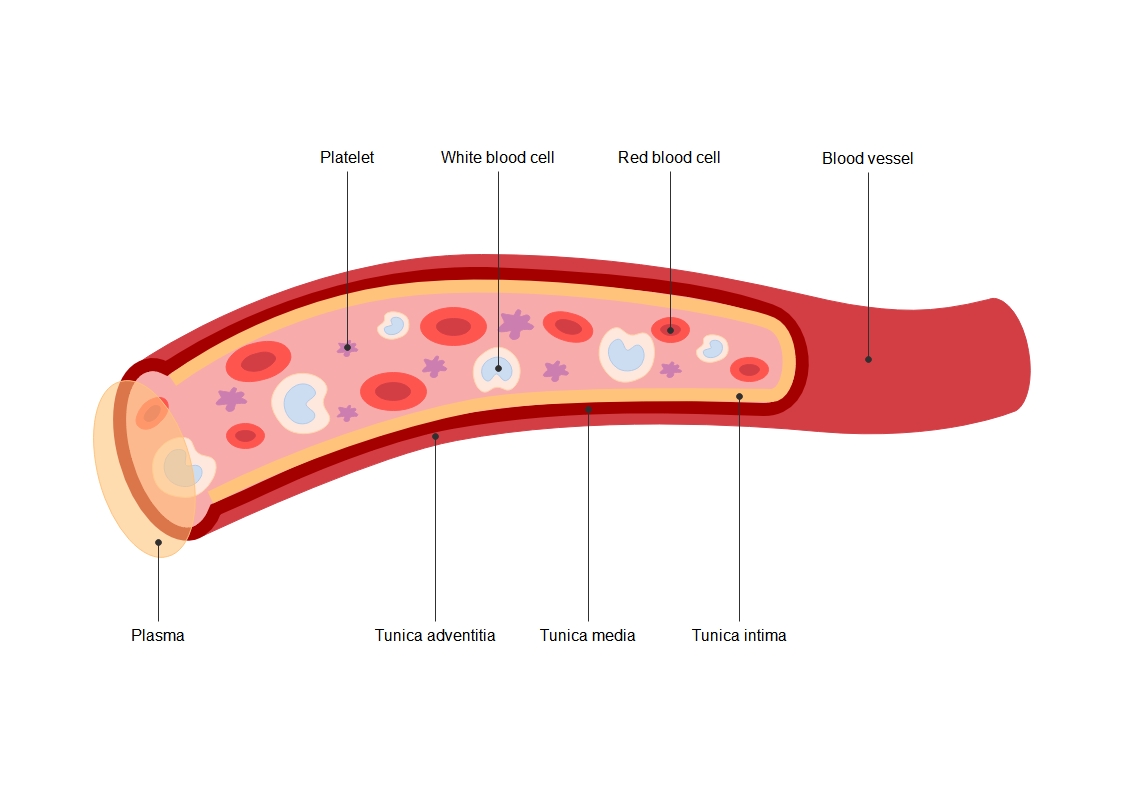
About this Chromosome Labeled template
This chromosome labeled template provides a clear visual representation of genetic hierarchy. It tracks the path from the entire cell down to the molecular level of DNA. This makes complex biological concepts easier to grasp for students.
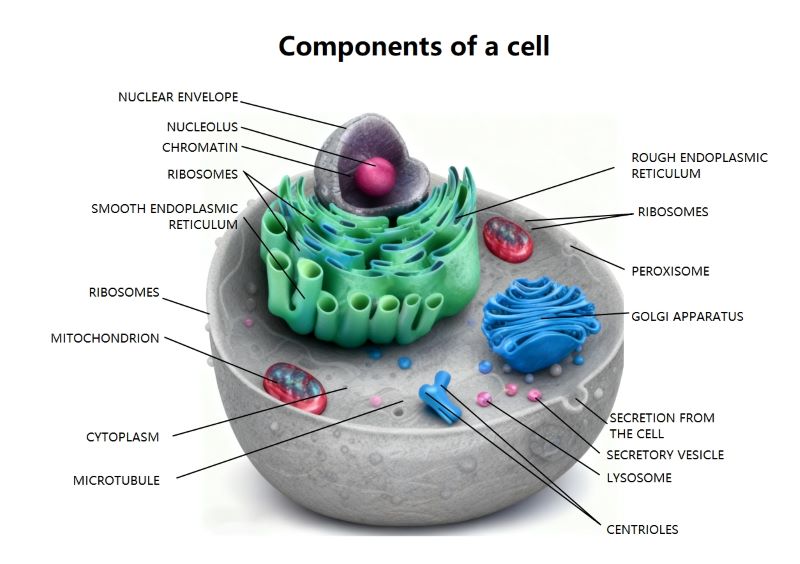
Cell and Nucleus
The cell serves as the basic functional unit of all living organisms. Within the cell lies the nucleus, which acts as the control center. It safely stores the genetic material necessary for growth and reproduction.
- Cell membrane protection
- Nucleus core location
- Housing genetic data
Chromosome Structure
Chromosomes are highly organized structures consisting of DNA and proteins. They appear as distinct X-shaped bodies during cell division. This compact form ensures that DNA is accurately distributed to new daughter cells during the replication process.
- Chromatid arms
- Centromere connection
- Gene storage units
DNA and Nitrogenous Bases
DNA is the long molecule that contains our unique genetic code. It is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. The rungs of this ladder are formed by specific pairs of nitrogenous base molecules.
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the main function of a chromosome in the human body?
Chromosomes act as the primary carriers of genetic information in the human body. Each chromosome consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones. This structure ensures that DNA stays compact and organized. During cell division, chromosomes facilitate the accurate replication and distribution of DNA, which is essential for healthy growth, development, and the repair of body tissues.
-
How do DNA and chromosomes relate to one another?
Chromosomes and DNA are different levels of the same genetic material. A chromosome is essentially a long, continuous strand of DNA that has been tightly packed for storage. While DNA provides the specific chemical instructions for building proteins, the chromosome provides the physical framework. Think of DNA as the text in a book and the chromosome as the entire bound volume.
-
Why are the nitrogenous bases A, T, C, and G important?
Nitrogenous bases are the building blocks of the genetic code. Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T), while Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G). The specific sequence of these base pairs functions like a biological alphabet. This sequence provides the instructions needed for cells to build proteins, which determine an organism’s physical traits and vital biological functions.