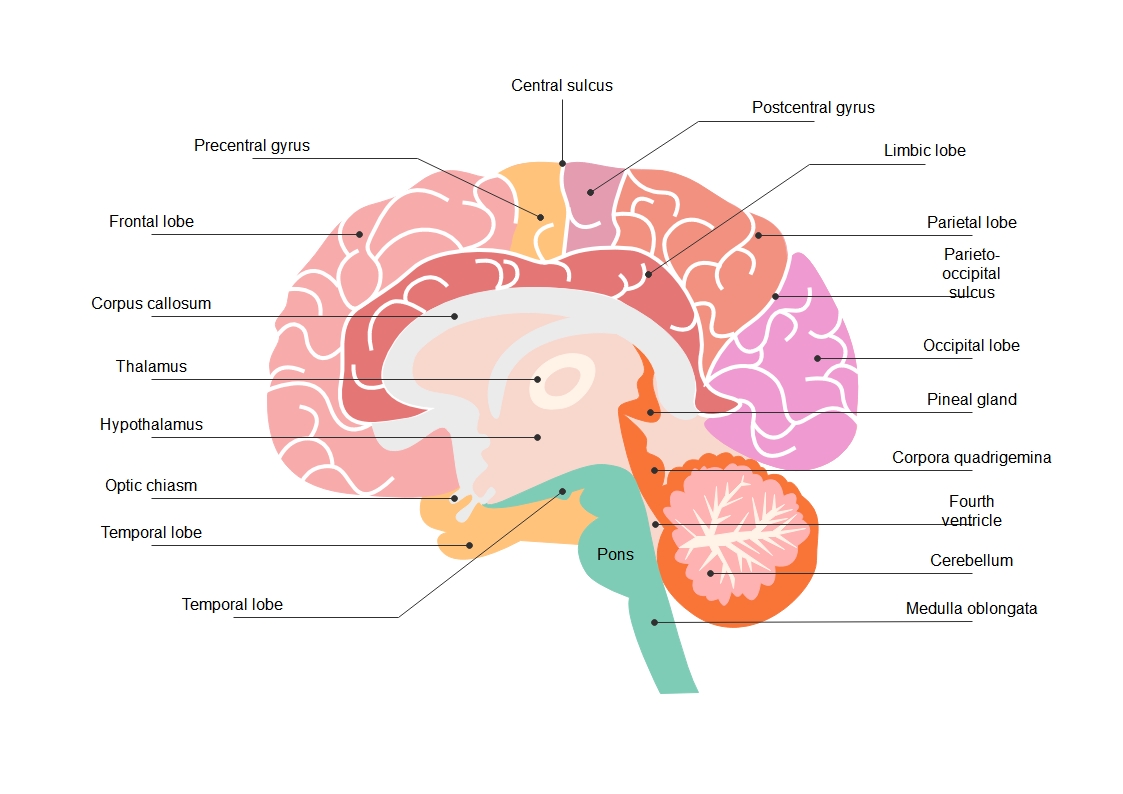
About this heart blood flow diagram template
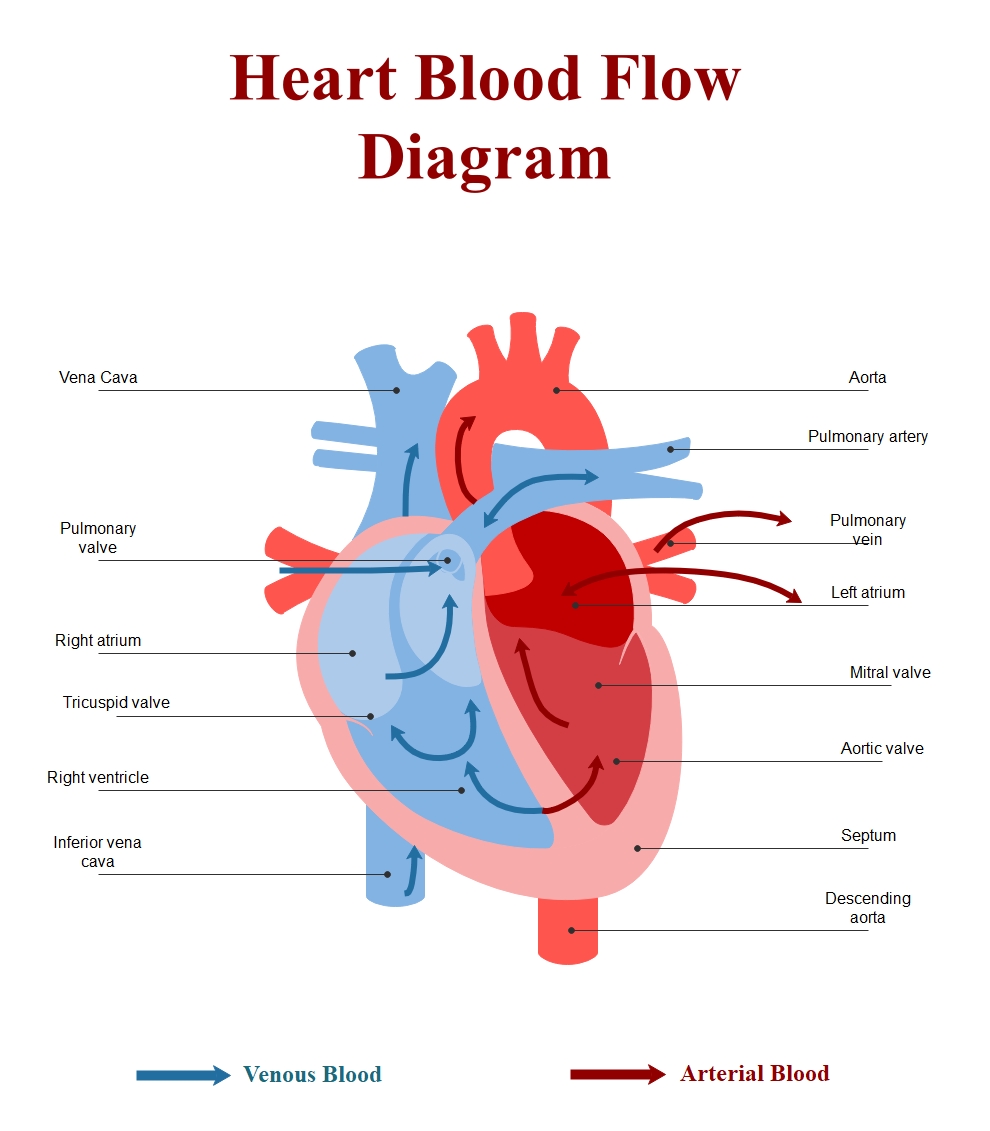
This heart blood flow diagram template provides a clear visual guide to the circulatory system. It uses color-coded arrows and detailed labels to help users understand the complex journey blood takes through the chambers and valves of the heart.
Venous Blood Return
Deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart from the body. This process is crucial for transporting waste carbon dioxide back to the lungs for gas exchange. It involves several key structures for proper circulation.
- Vena Cava
- Right Atrium
- Tricuspid Valve
- Right Ventricle
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Pulmonary Valve
Arterial Blood Distribution
Oxygenated blood enters the left side of the heart from the lungs. This oxygen-rich blood is then pumped with high pressure to the rest of the body, ensuring all tissues receive the nutrients they need to function.
- Pulmonary Vein
- Left Atrium
- Mitral Valve
- Aortic Valve
- Aorta
- Descending Aorta
FAQs about this Template
-
How does blood flow through the heart in order?
Blood follows a specific path to ensure efficiency. First, deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From there, it is pumped through the pulmonary valve to the lungs. Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, moves through the mitral valve to the left ventricle, and exits via the aorta.
-
What is the difference between arterial and venous blood?
Arterial blood is typically rich in oxygen and appears bright red. It travels away from the heart to supply the body's tissues. In contrast, venous blood is deoxygenated and carries carbon dioxide back to the heart. It usually appears darker or bluish in diagrams. The pulmonary system is the only place where these roles are reversed for the vessels.
-
Why are valves important in a heart diagram?
Heart valves are critical because they ensure blood flows in only one direction. This prevents backflow, which would make the heart pump inefficiently and cause health issues. The diagram shows four main valves: the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves. Each opens and closes in a synchronized rhythm to maintain the high-pressure circulation needed for human life and metabolic activity.