Remote work has become the norm in today’s digitally driven world. Accessing work resources and data exchanges is seamless, regardless of geography, all thanks to wide area networks. Today, businesses and international enterprises use WAN telecommunication to connect devices across continents, ensuring fast and secure data transfers.
Want to know how WAN manages the network traffic, prevents lag, and facilitates speedy transfers? Here is a Wide Area Network diagram complete guide with its key components, examples, and a short tutorial.
In this article
What is a Wide Area Network?
A WAN or Wide Area Network is a telecommunication network over a wider geography, used for computer networking. In simple words, it is a network of computers connected for data and resource sharing via a centralized system that is not limited to a single place. The Internet (3G, 4G) is an excellent example of a WAN.
Typically, Wide Area Networks are used to connect remote offices, international businesses, a company's data centers, and provide remote access to an enterprise's resources. All these entities can allow for connectivity through wireless networks, private networks, cellular networks, or internet access.
That said, professional installation and regular maintenance are crucial to sustaining the performance of a WAN network. Hence, they can be a bit more expensive than other network structures.
How Does a Wide Area Network Work?
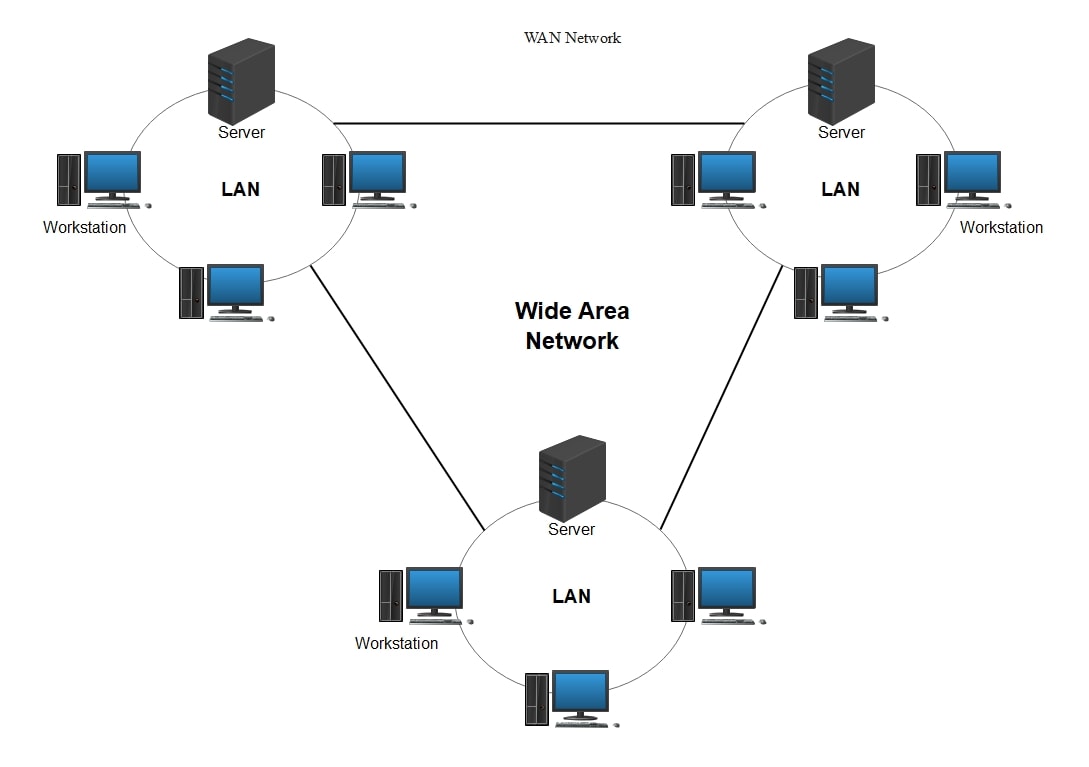
The basic working principle of a WAN is connecting multiple LANs (Local Area Networks) and facilitating a connection between them. The Wide Area Network architecture helps understand the design and structure of the network over a certain geography.
The data in this architecture uses packets for transmission. These packets are small units of information directed through the network (of devices). Next, the routers (after analyzing their addresses) direct these packets to the desired destination by using optimal paths. Factors like the bandwidth, congestion, and quality of the connection determine these paths.
Key Components of WAN
- Network typology: WANs can be point-to-point or hub and spoke. In point-to-point architectures, the connection is a straightforward link between two spaces (data centers, offices etc). In comparison, the hub and spoke architecture creates a centralized space connected to different remote locations for resource access.
- Transmission media: WAN uses different transmission media for information sharing. This includes leased lines (communication from service provider), satellite signals (for remote access), or fiber optic cables.
- Protocols: WAN uses specific protocols for data transfers. One fundamental protocol is IP, or Internet Protocol.
- WAN devices: A WAN setup consists of several combinations of devices, such as routers, switches, modems, etc.
- WAN services: Common WAN services include MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) for efficient data transmission via packets and VPNs (Virtual Private Network) for secure communication on public networks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WAN
Difference Between WAN, LAN, and MAN
Computer networking is further categorized into types, depending on the purpose and size of the connection. Let's discuss the key differences among the three most common networks used worldwide.
LAN - Local Area Network
LAN is a connection setup consisting of a collection of devices in a limited private area. It can be a lab, home, or business property. LAN has shorter delays and better transmission speed. Hence, it is best suited for connecting printers and computers and sharing resources like games, files, etc. Businesses can use this network for about 5000 devices in one building.
MAN - Metropolitan Area Network
MAN is a telecommunication connection spanning a larger area than LAN. It can be small towns, cities, etc. Unlike LAN, the MAN setup is not restricted to a particular building, and connects at least two devices within the city or different cities. Because it is expensive, MAN is owned publicly and not by private companies.
WAN - Wide Area Network
WAN is a connection established using satellites or telephonic lines. WAN, in comparison with LAN and MAN, covers the widest area, which can span countries and even continents. Businesses use WANs to centralize their data sharing and make communication seamless, despite geographical barriers. Broadband services (3G, 4G) are examples of this network.
| WAN | LAN | MAN |
| Wide Area Network | Local Area Network | Metropolitan Area Network |
| Larger areas (countries, continents) | Small areas (buildings, campuses, etc). | Large areas (cities) |
| Private, Public | Private | Private, Public |
| Low | High | Average |
| Difficult than LAN and MAN | Easy maintenance | Difficult than LAN |
| Higher delays | Shorter delays | Moderate delays |
| Very Low | Higher | Higher |
| A huge group of computers | Single pair of devices | Multiple computers |
| Less | Better than other networks | Less |
How to Draw a WAN Network Diagram using EdrawMax?
Making sense of network structures on the canvas can be challenging, as you are dealing with multiple types of connections, devices, and complex sites. Hence, a good way is to start with advanced diagramming tools like EdrawMax. Its extensive symbol library and design assistance help you plot network structures with clarity.
Let's see how you can make a WAN diagram using EdrawMax.
Step1Prepare for Your WAN Diagram
Before you jump into the drawing process, achieve clarity about the purpose and scope of your WAN diagram. Determine what your physical sites (data centers, users, etc) and who the connection caters to (IT team, clients, etc). Also, gather information about the network devices, connection types, etc.
- Once done, download and install the EdrawMax desktop version.
- Log in to your Wondershare account. Or, register your email if it is the first time.
Step2Access the Canvas
- Explore the dashboard and click More > Network under the Home tab.
- Choose your desired network diagram format to enter the editing panel.
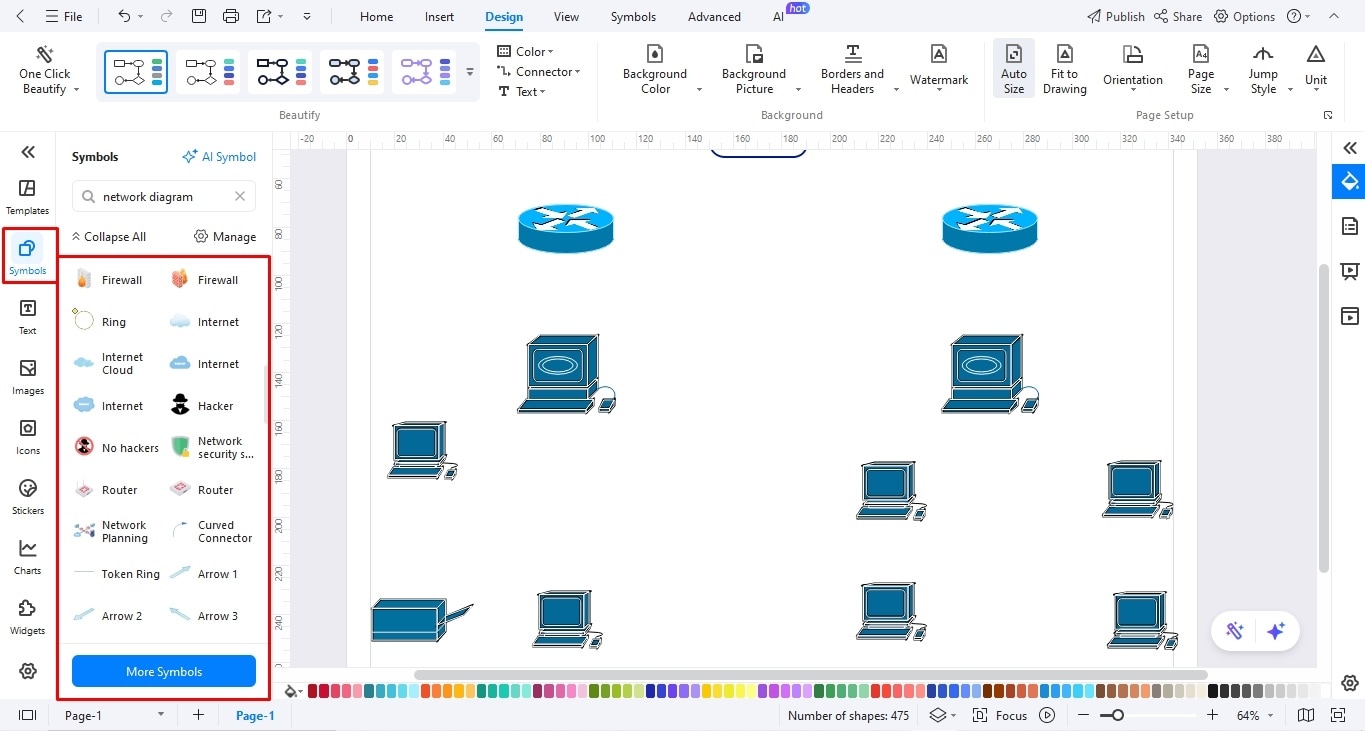
Step3Plot the Physical Structure (Layout and Network Devices)
- Once on the canvas, the first step is drawing a basic layout of your site.
- Locate the symbol library on the left side of the canvas and search for network diagram icons.
- Drag and drop your site's symbols (Headquarters, data centers, remote users, etc).
- Once a basic layout is complete, you may add the network devices.
- Again, visit the symbol library and choose icons to display devices (routers, switches, etc).
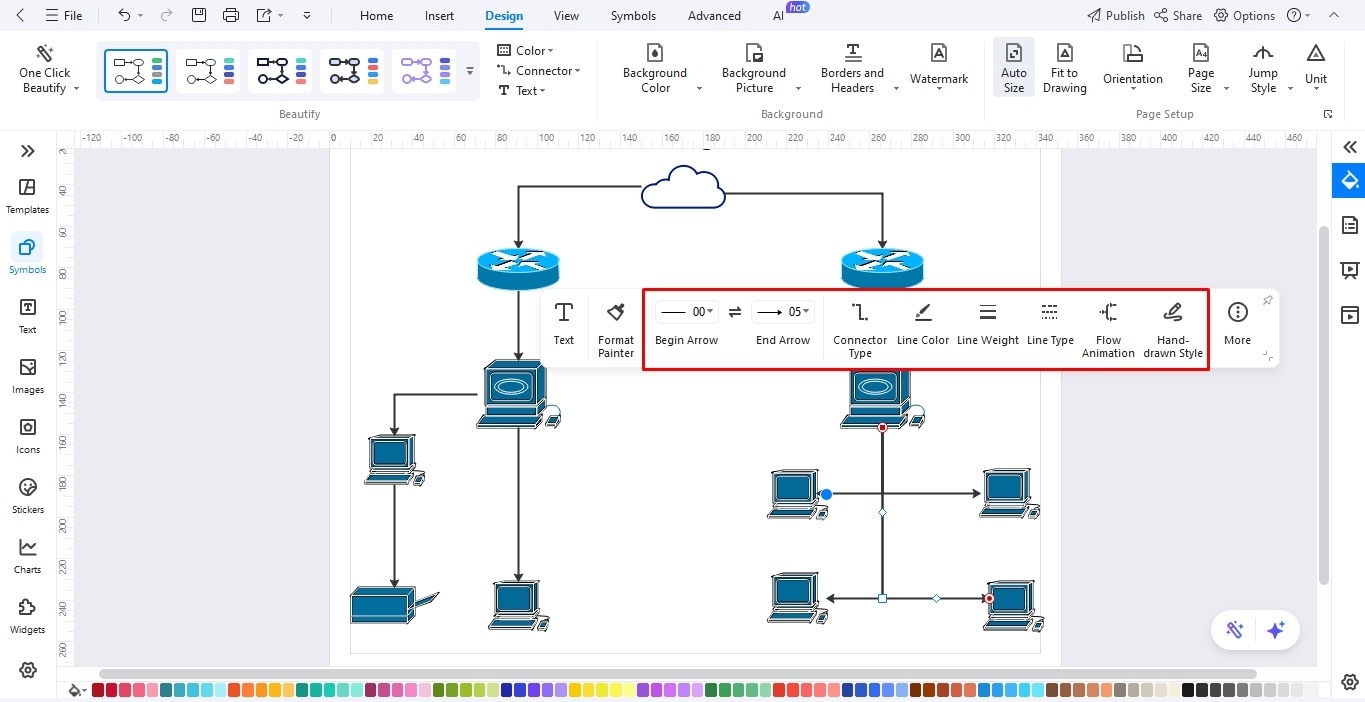
Step4Add WAN Links
- Proceed now to establish the network links.
- Select any shape and use its connection points to link with other icons on the canvas.
- You can customize the style, thickness, and color of the connector from the on-screen prompt.
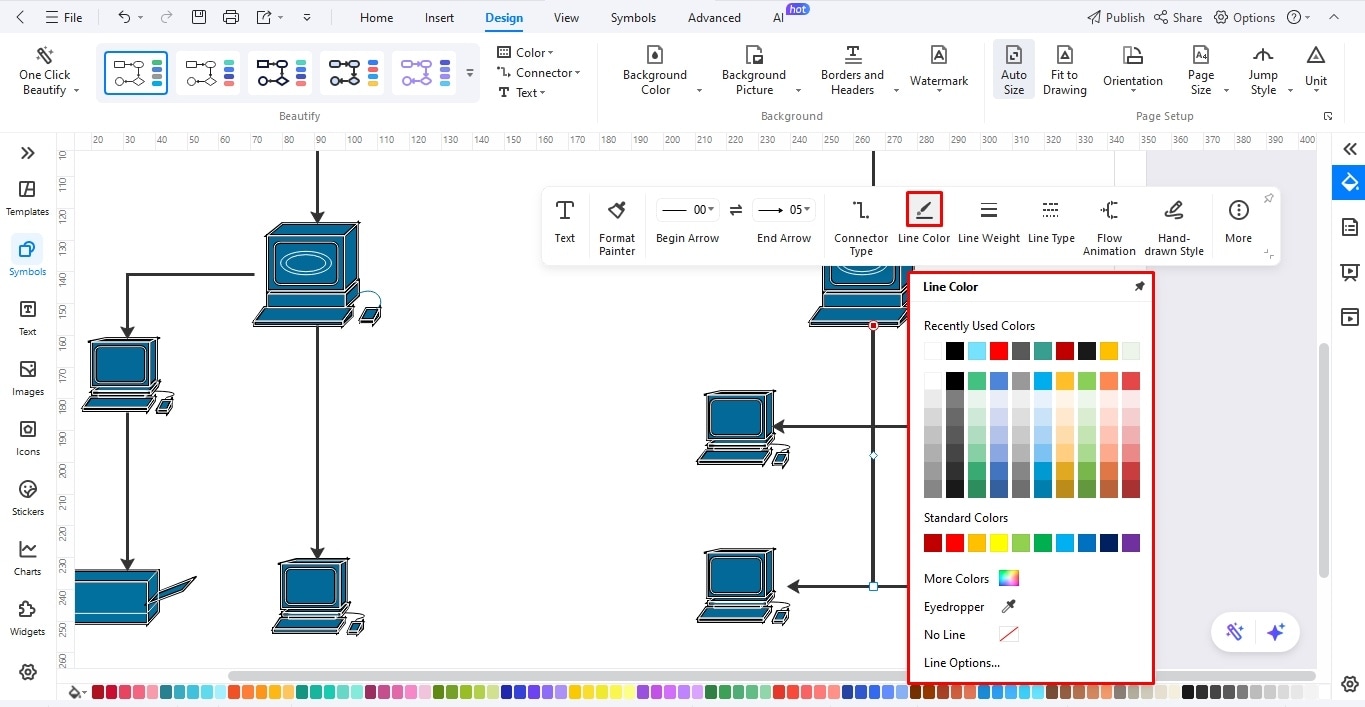
Step5Bonus Step: Color-Code the Connections
- Color-coding is an essential element of a WAN diagram. It helps your viewers better understand what each connection represents.
- For this, select any connector you want to code and change its color from the on-screen prompt.
- You may use the format painter to save time and apply color to same-category connections.
Step6Label Diagram Elements
- Labelling each symbol in the WAN diagram can help audiences with the clarity of the flow and purpose. For this,
- Double-click anywhere in the canvas and start typing.
- Change the font details (style, size, color) from the on-screen prompt.
- You may also add legends to explain what each color and icon represents.
Step7Download Your WAN Diagram!
- Take a moment to review the connection details. Satisfied? Download the diagram to your device.
- Visit the File menu from the top-left corner, click Export, and choose your desired format.
- Graphics (PNG, JPG, JPEG, etc).
- MS Office (Word, PPT, Excel, Visio).
- PDF for documentation.
WAN Wide Area Network Diagram Examples
First time plotting the WAN diagrams? Examples are always an excellent idea to get familiar with the structural nuances. Here are some basic Wide Area Network diagrams you can edit on EdrawMax to understand elements, connections, and functions.
Organization Wide Area Network Diagram
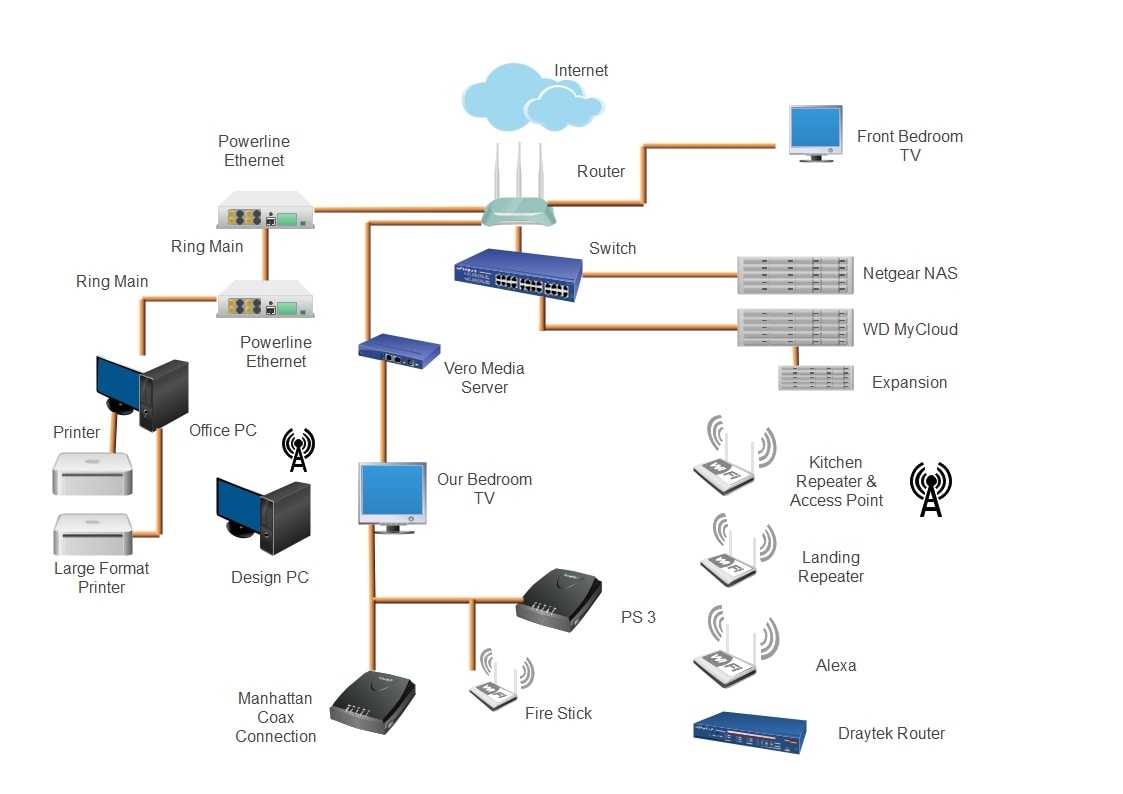
This Wide Area Network diagram example is a typical display of a WAN connection. It showcases how the components interact with each other to achieve a broader network connectivity. Generally, remote businesses, hospitals, and other public institutions employ these systems for data sharing.
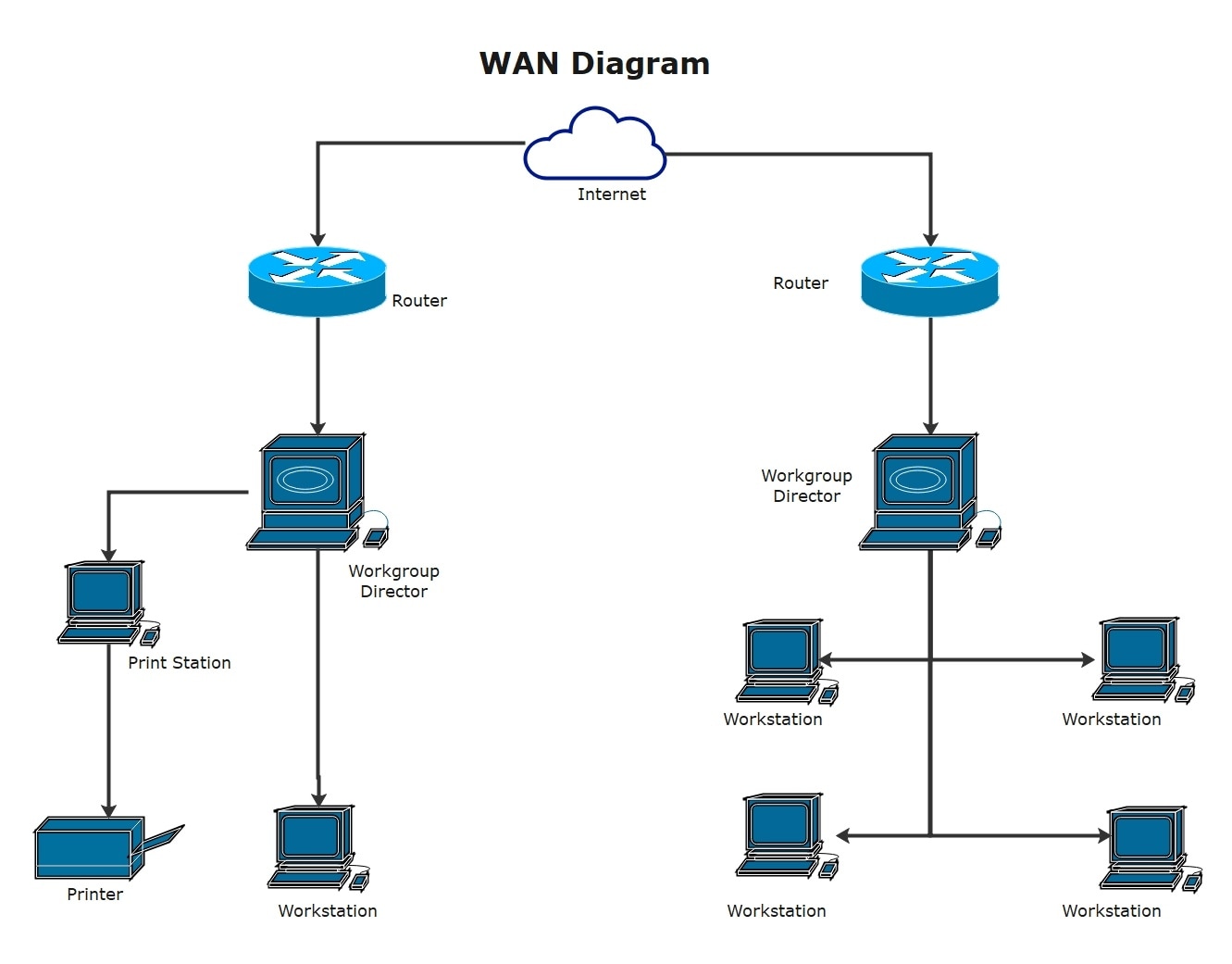
Basic Workspace WAN Diagram
This WAN diagram shows a small-scale computer connection over a wider geography. The routers in the structure connect to the workgroup director, who then distributes the resources among different workstations. This way, a centralized data transfer mechanism is established.
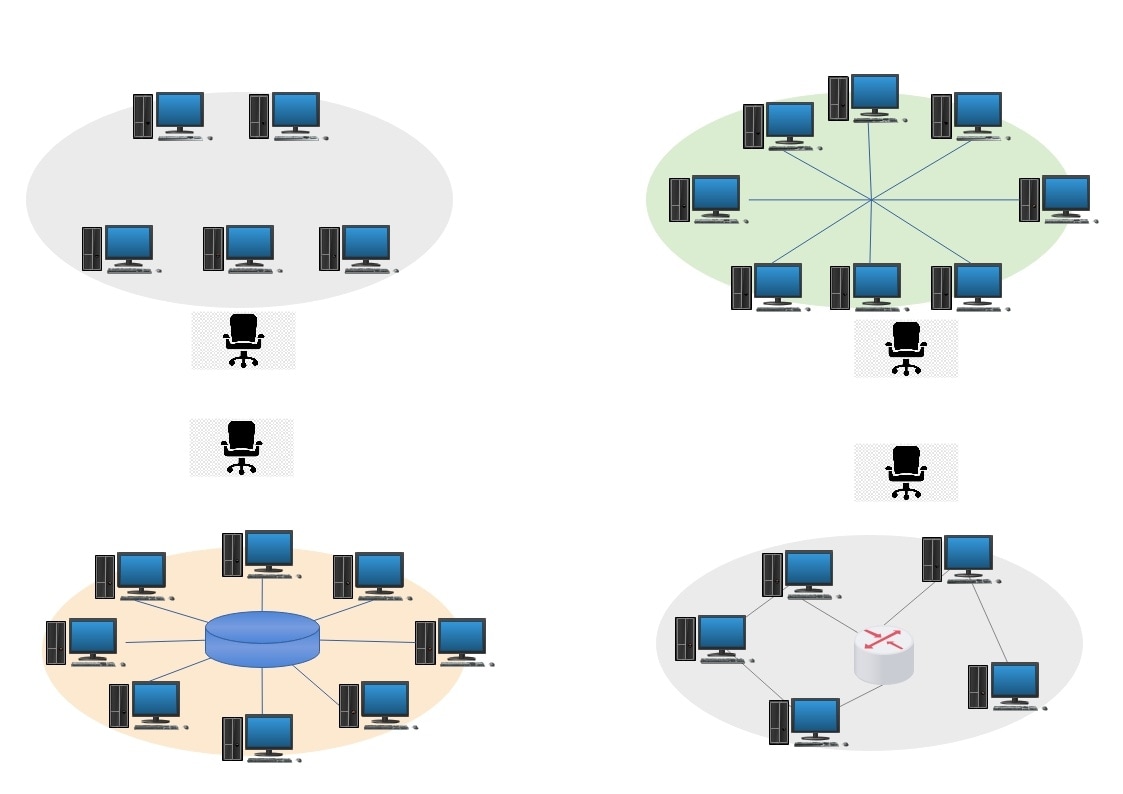
Ring Main Typology WAN Diagram
A typical example of how a WAN works is in a circular loop. See how PCs, switches, and routers are all connected in a ring-like structure. Such a setup works best for preventing delays, as the traffic in the circle is rerouted. With a high reliability, the ring system works best for critical applications.
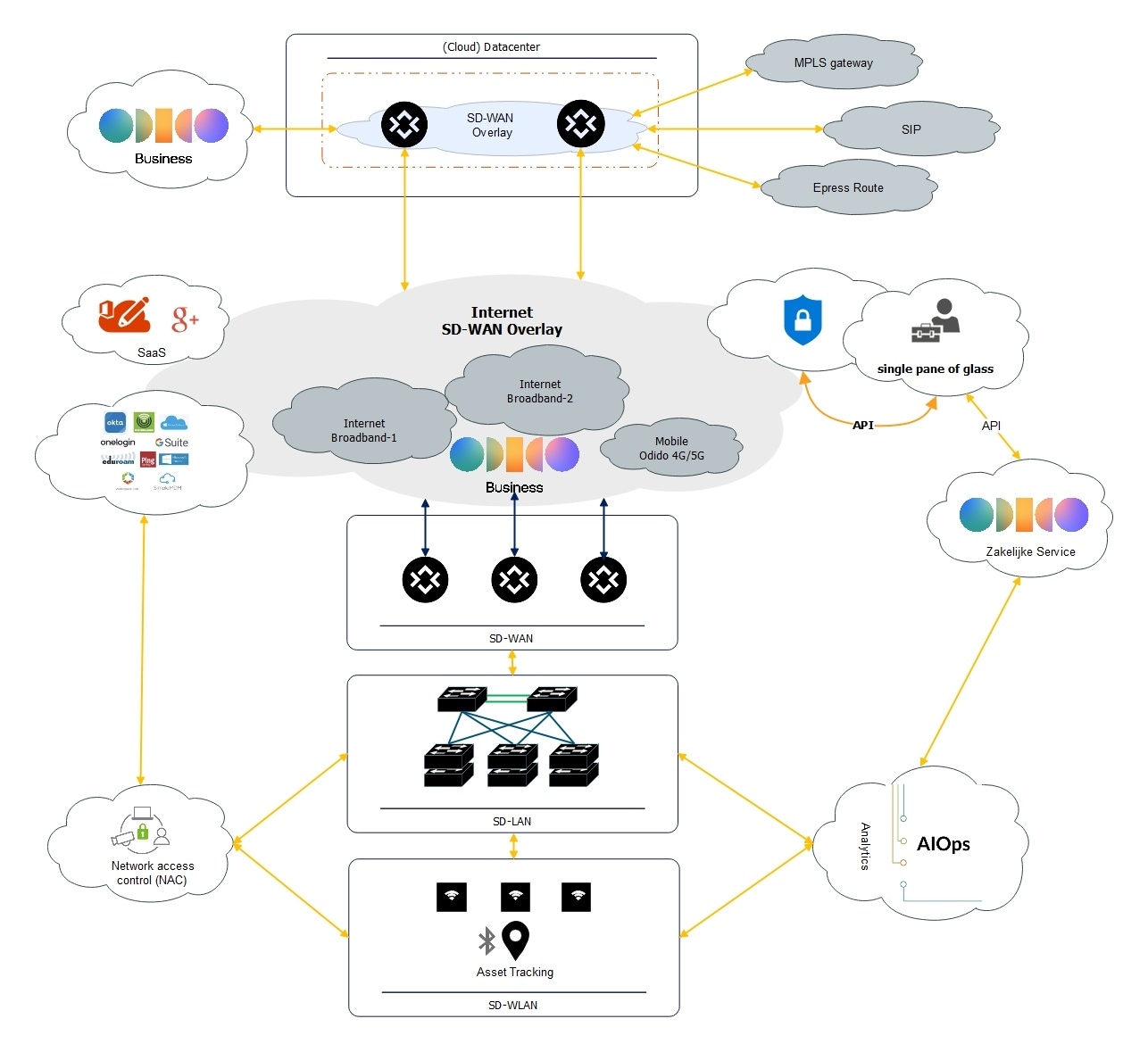
SD-WAN Overlay Network Architecture Diagram
This Wide Area Network diagram example shows a sub-type SD-WAN illustrating a connection between cloud datacenters and IoT devices. This end-to-end structure has various management elements to ensure optimized performance and better connectivity.
WAN and Core Switch Wide Area Network Diagram
Here is yet another example of how a WAN diagram connects with a core switch in a company. The WAN router connects with external networks, like the internet router, to enable data transmission. This way, remote users can access this information. Similarly, the core switch established a data exchange mechanism between the sub-components of the structure.
Use EdrawMax to Start Your WAN Drawing Journey Now!
Setting up a network is inarguably the most important yet the hardest IT task in an enterprise. Plotting clear connection structure, color coding categories, and differentiating encryptions demands advanced diagramming assistance.
Thankfully, EdrawMax is an intelligent canvas that simplifies this process for you. Designers can find affordable yet efficient solutions in its editable templates, ample canvas space, and design assistance.
Key Features
- Massive template community: EdrawMax has a huge community of designers and architects uploading their routine work, including complex network diagrams. You can edit these examples to save time and get inspiration from them.
- Resizable vector symbols: This diagramming software features numerous industry-standard network diagram symbols. Plot everything from sites to equipment, peripheral devices, and more. Moreover, all these symbols are resizable and editable.
- Intuitive UI: EdrawMax toolkit is designed with beginners in mind. Anyone, regardless of their design skills, can benefit from the drag-and-drop interface and easily accessible floating buttons.
- Multi-format export/ import assistance: Download your diagrams in over ten formats with EdrawMax, including graphics, MS Office, PDF, etc. It even allows importing unfinished projects from Visio and CAD. So, you can edit them further in the canvas.
- AI research assistance: Edraw AI is the advanced chat assistance you need to get ideas and make inquiries. It helps you with research, diagram alignment, and content structuring effectively.
Wrapping Up
WAN technology is inevitably a solid foundation of any enterprise with global operations. Understanding the wide area network structures is easy with a clear understanding of its key components and architecture. You can learn this with WAN examples on EdrawMax. Its resourceful toolkit and ample canvas even allow plotting a network diagram from scratch.
So, try out the free version to see if it is worth the time.




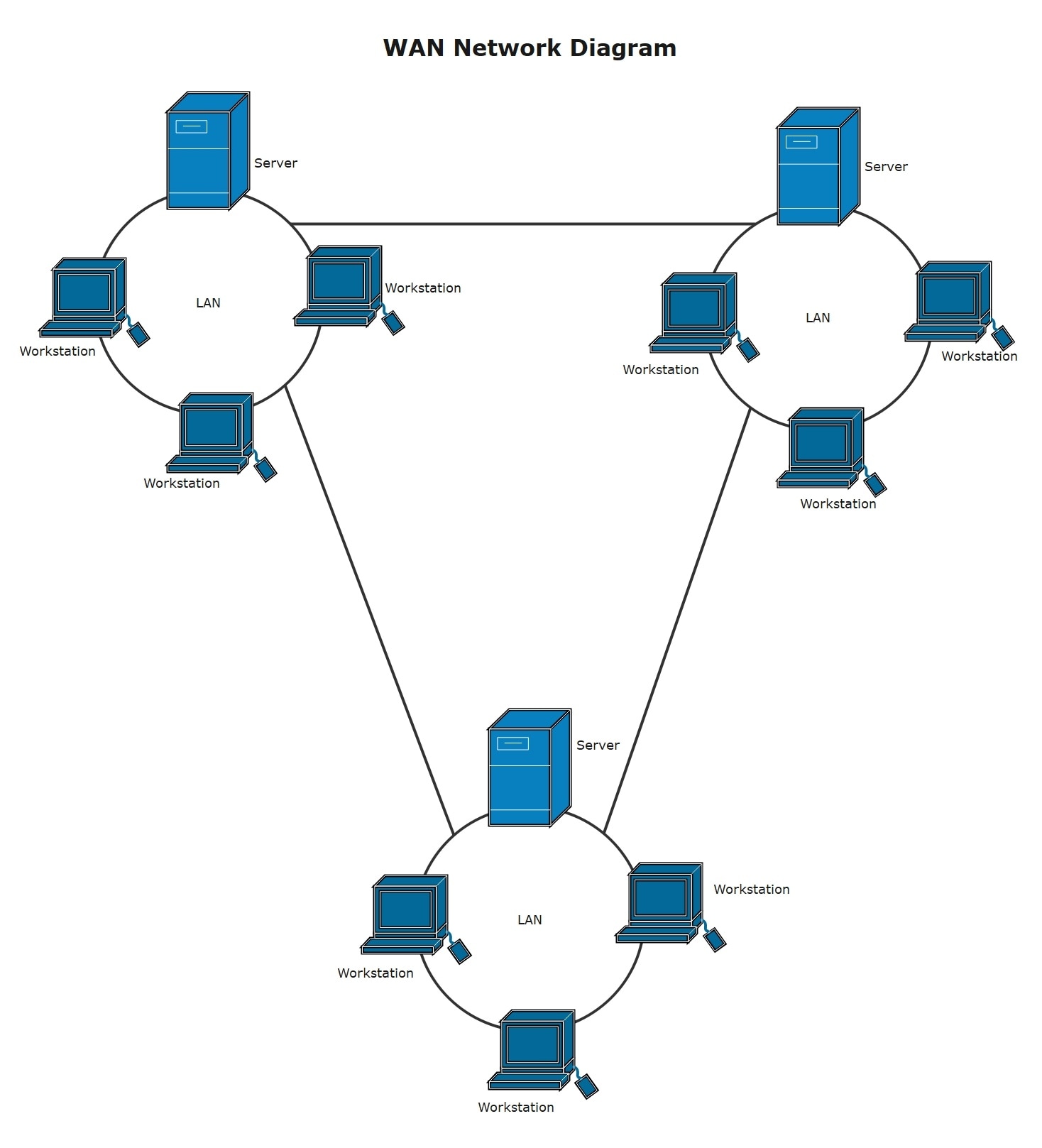
 below.
below.  below.
below.