ATM system modeling provides a clear, high-level view of how ATMs operate and how critical security is maintained. These models help all stakeholders—users, moderators, and support teams—understand processes easily and ensure smooth operations.
UML use case diagrams are an effective tool to capture system interactions. They illustrate how different actors, such as customers, bank networks, and maintenance staff, interact with functions like cash withdrawal, balance inquiries, and PIN changes.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to ATM management using UML use case diagrams. It covers their purpose, key elements, and detailed steps to create diagrams with EdrawMax. Real-world challenges and best practices are also discussed to help you build robust, professional diagrams that improve communication and collaboration among clients, developers, and testers.
In this article
Overview of an ATM Management System
An ATM system supports common banking tasks and ensures they are safe and reliable. Key functions include:
- Deposits and withdrawals
- Balance inquiries
- PIN changes
- Funds transfers
- Admin and maintenance tasks (cash refill, diagnostics)
Additionally, the system controls account validation, user authentication, and real-time communication with bank servers. Alerts, logging, and monitoring all contribute to the service's continued availability.
Security issues (fraud, skimming, cyberattacks), operational complexity (many states, many errors), and scalability and maintenance across numerous machines are frequently the sources of difficulties. A use case diagram pictures the system’s scope and the operations performed by different actors. Before going into a low level, this provides an overview to the analysts, developers, testers, and operations.
Basic Concepts and Applications of Use Case Diagrams
Use case diagrams help depict the system’s end-to-end functionality. In the context of ATM management, they capture who interacts with the ATM and what goals they achieve through it.
Actors
- Customer/User: Withdraws cash, deposits funds, checks balances.
- Bank System: Validates transactions and processes requests.
- Maintenance Personnel: Handles hardware maintenance, cash replenishment, and software updates.
Purpose of UML Use Case Diagrams
- Provide a visual representation or a semi-technical overview of the entire system’s functionality from the user’s angle.
- Help identify the complete functionality of the ATM system effectively. This primarily outlines the scope of the ATM system to facilitate comprehensive modeling of the entire ATM system.
- These can be considered a base or starting point for system engineers and quality assurance engineers, ensuring a consistent understanding of the requirements.
Application in ATM Management Systems
An ATM system typically supports:
- Withdraw Cash – the most common function.
- Deposit Funds – Cash or Cheque Deposits.
- Check Balance – quick account inquiry.
- Change PIN – security updates.
- Transfer Funds – between accounts.
- Admin Functions – cash refills, system diagnostics, and maintenance.
Compared to other Diagrams
Use case diagrams are better than class diagrams as they highlight the user’s behavior. At the same time, other UML models depict the structure and workflows.
When designing an ATM system, it is important to maintain consideration for user interactions and end-user goals (and very importantly so for financial applications).
Value for Teams
- Developers: Aligns coding tasks with user needs.
- Testers: Basis for test-case generation.
- Operations staff: Understands system functionality for training and support.
- Stakeholders: A non-technical view of what the ATM system delivers.
Relationships
- Include: Authentication is included in almost all transactions.
- Extend: “Error Handling” extends cash withdrawal in case of insufficient funds.
- Generalization: A Supervisor actor may generalize a regular Maintenance Technician with added privileges.
Examples of Use Case Diagram for ATM Management System
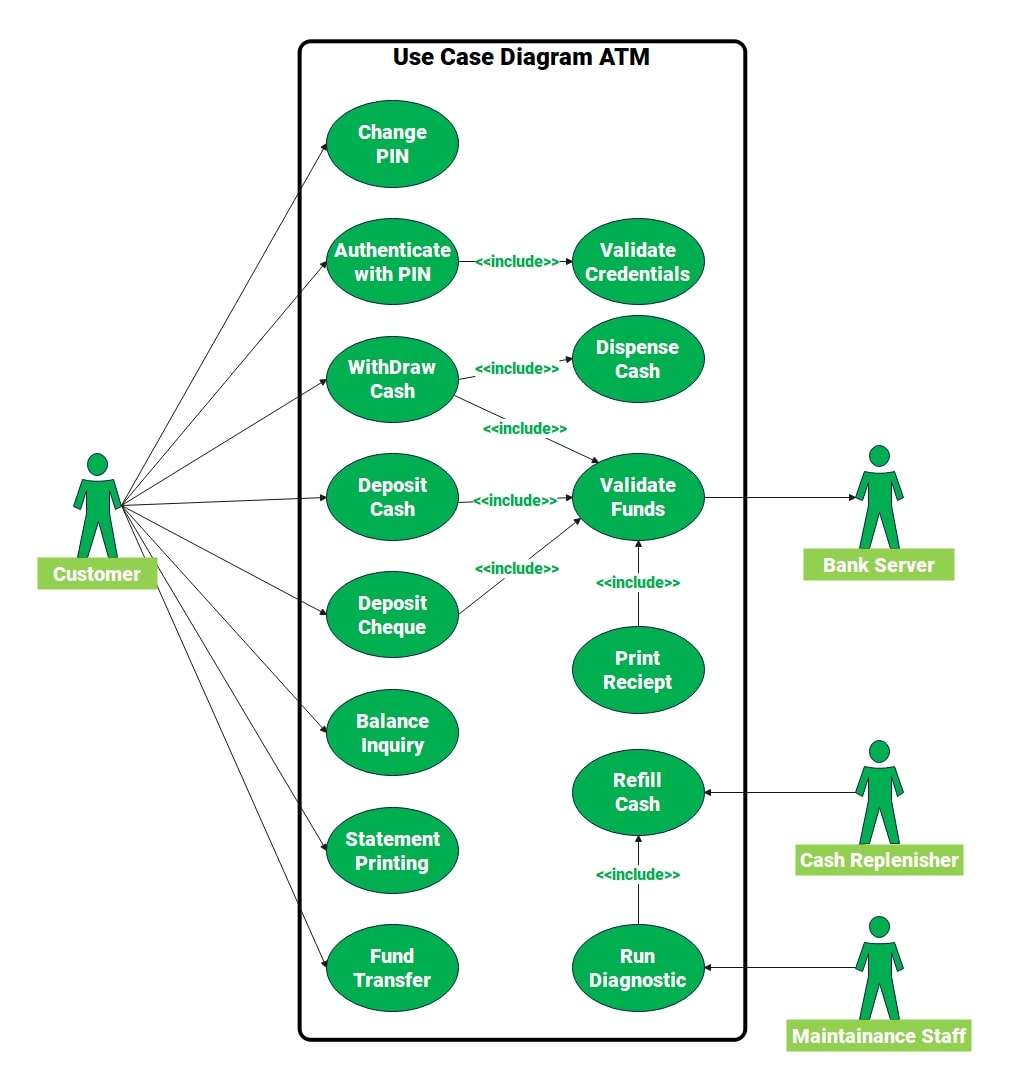
Use Case Diagram for ATM Staff
This ATM use case diagram shows how customers, the bank, and the machine interact. Customers can take actions including cash withdrawals, pay-in, transfer money, and change PIN. Each transaction links to queries. These include checking credentials and verifying funds from the bank server.
Cash out also involves disbursing cash, and deposits and transfers need confirmation of funds. It includes features such as balance inquiries, mini statement prints, and receipt printing. Customer services like cash replenishment and maintenance keep ATMs running smoothly. They provide essential services, including cash supply and diagnostics.
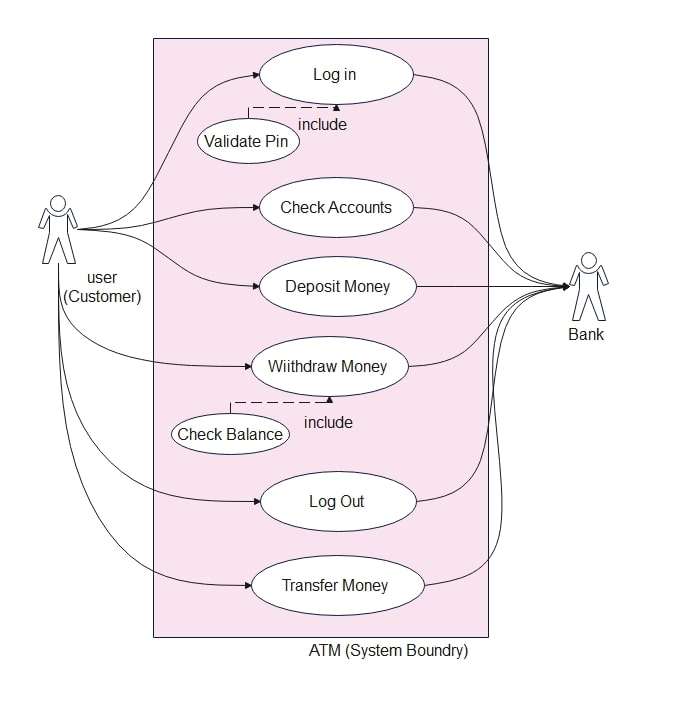
Use Case Diagram for Core User Functions
This ATM UML Use Case Diagram was made to help visualize the structure of the ATM system. The client logs in, including the checking of the PIN to authenticate. Once they log in, users can manage their accounts. They can withdraw money, deposit cash, transfer funds, and check their balances.
Roll back, deposit, and withdraw all requests to the bank system for validation and transactions. The customer can log out after finishing the transactions to terminate the session. The diagram highlights fundamental ATM functionalities with respect to dependencies, like checking the balance during a withdrawal, making managing money safer and easier.
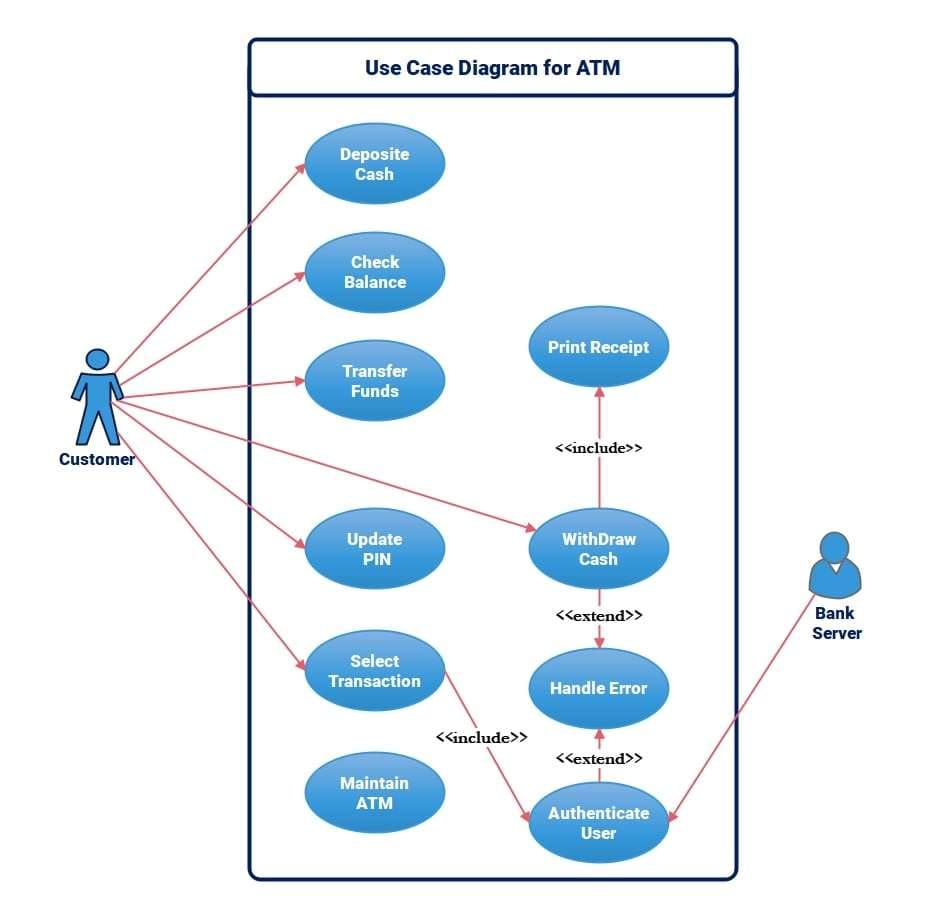
Use Case Diagram for ATM Cash Withdrawal
This is a UML use case diagram for an automated teller machine (ATM). Some actions customers can perform include depositing cash, balance inquiries, funds transfer, PIN change, and cash withdrawal. Cashing out covers receipt printing and can range from handling errors.
Authentication is a key factor for secure access in communication with the bank server. The diagram shows that users can select transactions and perform maintenance on the ATM. Built-in features, like error control and logon, give a clear view of how the ATM handles secure and efficient money exchanges.
How to Make a Use Case Diagram for ATM Management
Once you agree on scope and goals, you can turn the plan into a diagram your whole team can see, comment on, and update. EdrawMax makes this quick.
EdrawMax supports UML use case diagrams, flowcharts, network diagrams, and more. You drag and drop actors and use cases, label them, and export to PNG, PDF, SVG, Visio, and other formats. The template library speeds up your first draft, and team collaboration keeps reviews on track.
Steps to Create ATM Management System Use Case Diagrams
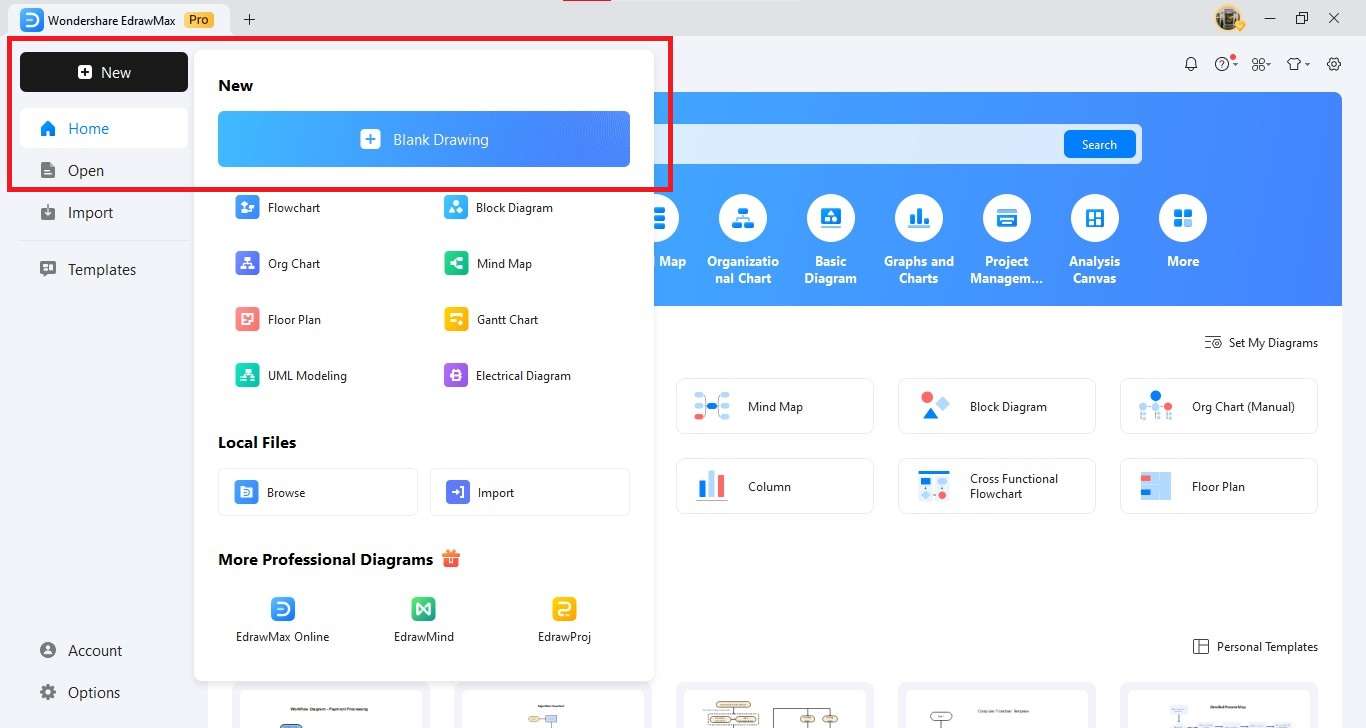
Step1 Create a New Canvas
- Open EdrawMax on your desktop.
- In the left panel, click New and expand the options.
- Choose Blank Drawing to start with a fresh canvas.
Step2 Insert Use Case Symbols
- Open the Symbol Library on the left.
- Enable UML Use Case symbols (actors, use cases, system boundaries).
- Drag and drop them onto your canvas as needed.
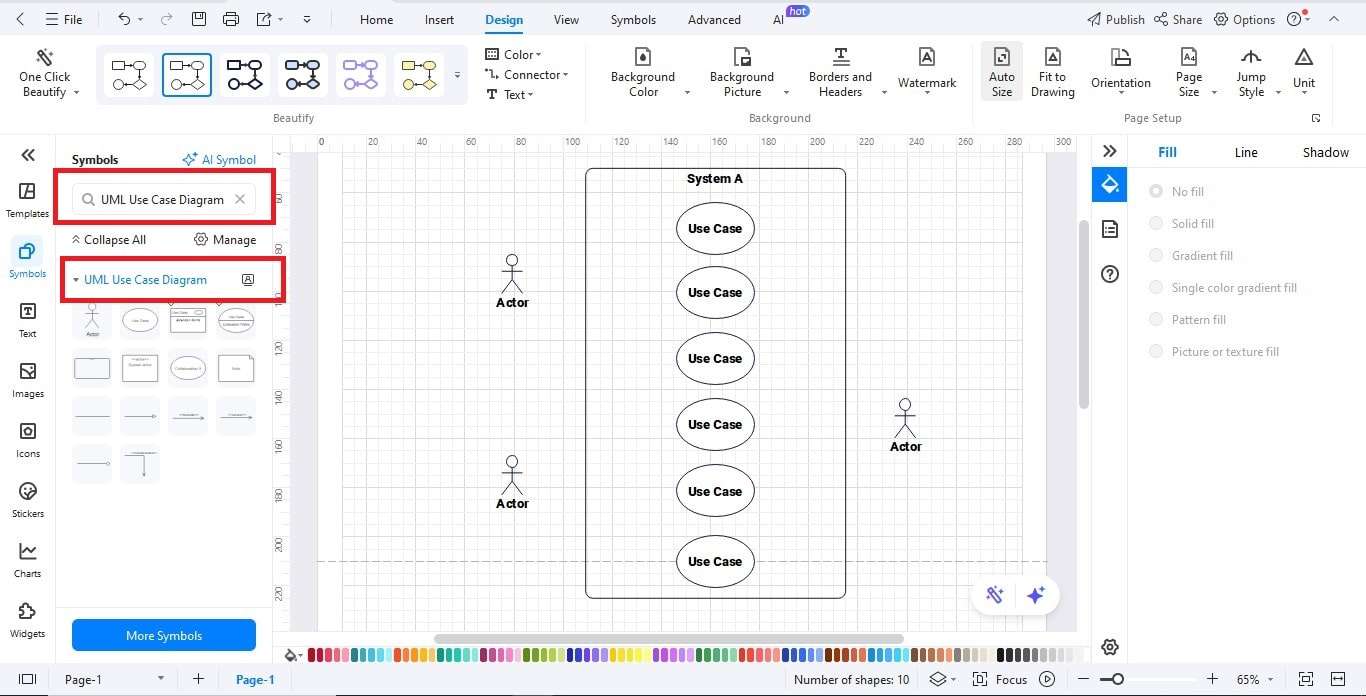
Step3 Add Actors
- Place key actors like the Customer and Bank System.
- Add optional actors like Bank Staff or Network System if needed.
- Keep actors outside the system boundary for clarity.
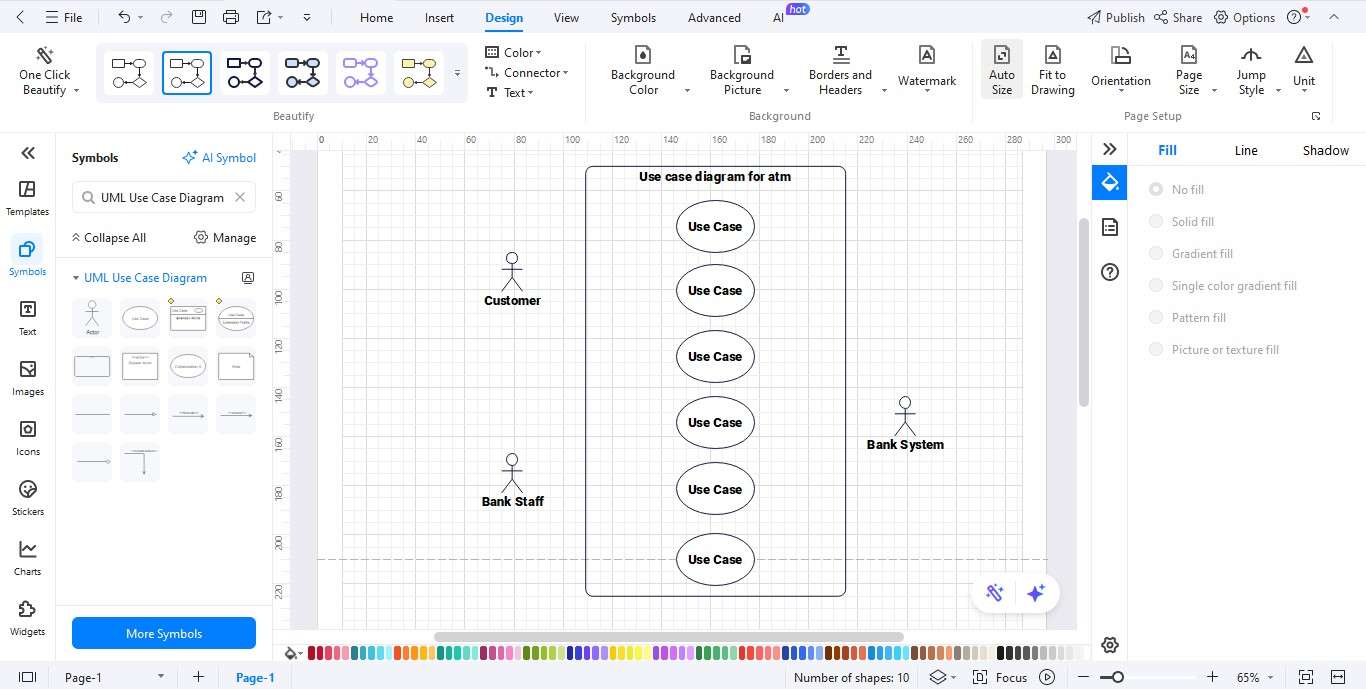
Step4 Define Use Cases
- Insert use cases inside the system boundary, including: Withdraw Cash, Deposit Funds, Check Balance, Transfer Funds, and Change PIN.
- Clearly label each use case.
- Connect each use case to its corresponding actor.
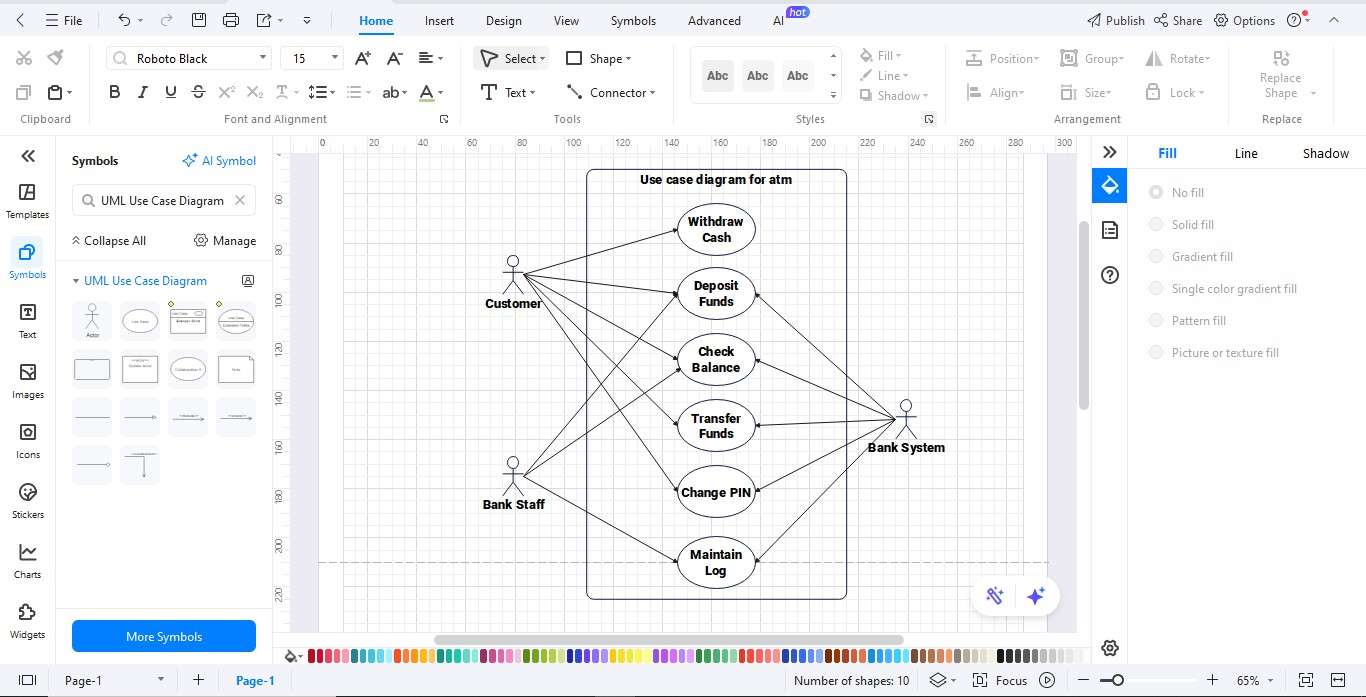
Step5 Customize Your Diagram
- Use the Format toolbar to change colors, fonts, and line styles.
- Apply alignment and spacing tools for a tidy layout.
- Add titles or notes if needed.
Step6 Export Your Diagram
- Click the Export option when your diagram is ready.
- Choose a format: JPG, PNG, PDF, Word, Visio, or SVG.
- Save the diagram to share or present easily.
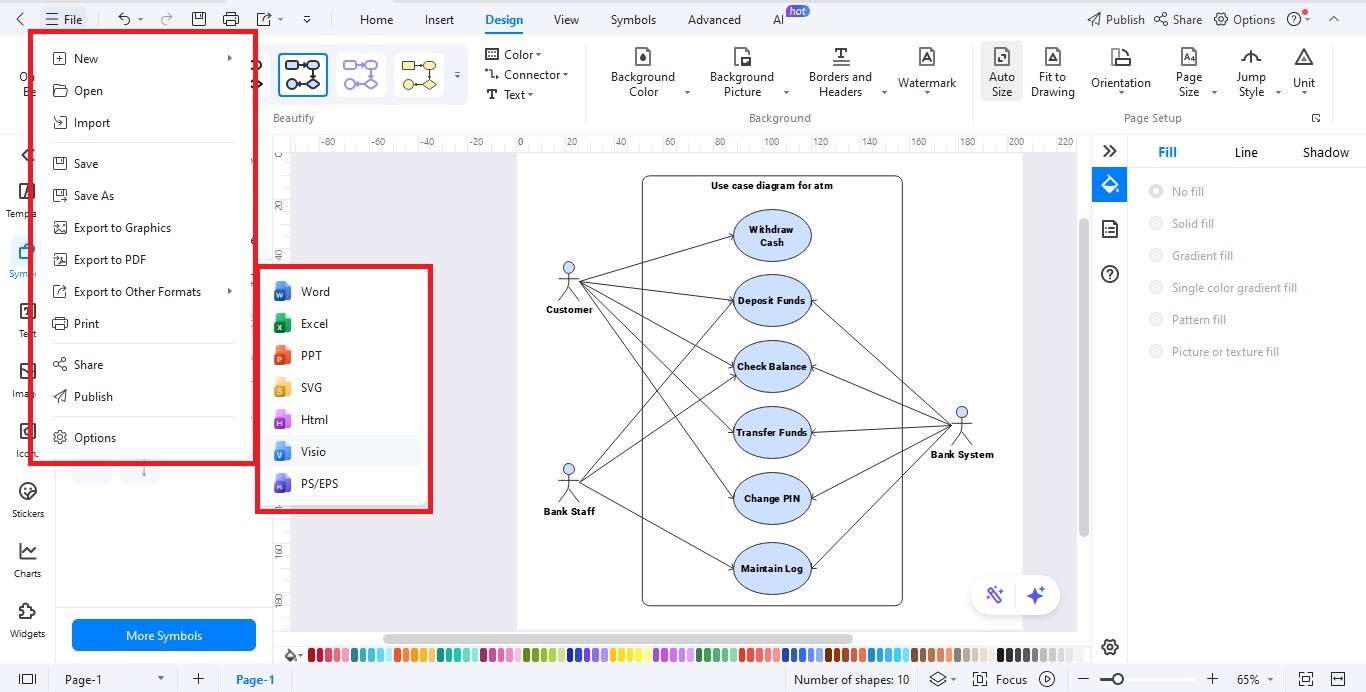
Ending Notes
Use Case diagrams are among the most productive methods for modeling user–system interactions during ATM management. Use case diagrams provide clarity to the stakeholders. These diagrams also guarantee that the functionality is covered when developing and operationalizing an ATM.
Organizations can create, update, and share ATM use case diagrams quickly. This has been made effective with the use of EdrawMax. The collaborative features of EdrawMax make it a significant tool among others. The inclusion of symbols/diagrams and the ability to export diagrams make it powerful in any working environment.
Some other diagramming tools can be useful when we are modeling ATM use cases with associated code or for educational uses. However, EdrawMax provides the best technical accuracy and ease of use. Having Edrawmax is considered to be the best choice for technical and non-technical users.
As ATMs advance to serve customers with different services and compliance issues, use case diagrams